In this guide, we are going to learn how to install phpMyAdmin on Debian 12. phpMyAdmin is a free and opensource application written in PHP that facilitates the administration and management of MySQL and MariaDB over the Web.
Table of Contents
Installing phpMyAdmin on Debian 12
What are the common Uses of phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin allows administrators to;
- browse through databases and tables;
- create, copy, rename, alter and drop databases;
- create, copy, rename, alter and drop tables;
- perform table maintenance;
- add, edit and drop fields;
- execute any SQL-statement, even multiple queries;
- create, alter and drop indexes;
- load text files into tables;
- create and read dumps of tables or databases;
- export data to SQL, CSV, XML, Word, Excel, PDF and LaTeX formats;
- administer multiple servers;
- manage MySQL users and privileges;
- check server settings and runtime information with configuration hints;
- check referential integrity in MyISAM tables;
- create complex queries using Query-by-example (QBE), automatically
connecting required tables; - create PDF graphics of database layout;
- search globally in a database or a subset of it;
- transform stored data into any format using a set of predefined
functions, such as displaying BLOB-data as image or download-link; - manage InnoDB tables and foreign keys;
Prerequisites for Installing phpMyAdmin
Since phpMyAdmin is a web based tool for administering MySQL or MariaDB, and is written on PHP, the most basic requirement that you need is either a LAMP or LEMP Stack. This demo uses the former.
Install LAMP Stack on Debian 12
We have describe extensively how to install LAMP stack on Debian 12 in our previous guide whose link is provided below;
- L: Install Debian 12 on VirtualBox
- A: Install Apache Web Server on Debian 12 . You can use Nginx instead (Quickly Install Nginx web Server on Debian 12).
- M: Install MariaDB 10 on Debian 12
- P: How to Install PHP 8 on Debian 12
Install Required PHP Modules
Install other required PHP modules for phpMyAdmin;
apt install php8.2-{bz2,mbstring,zip,gd,curl,xml,common,opcache,imagick}
See list of requirements on phpMyAdmin requirements page.
Similarly, ensure Apache PHP modules are installed;
apt install libapache2-mod-phpInstalling phpMyAdmin on Debian 12
Install phpMyAdmin
phpMyAdmin 5.2.1, which is the current latest stable release version as of this writing, is available on the default Debian 12 repos. You can install it as follows;
apt updateapt install phpmyadminSelect Web Server for phpMyAdmin
When prompted to choose a web server to use, you can select Apache or whichever you want.
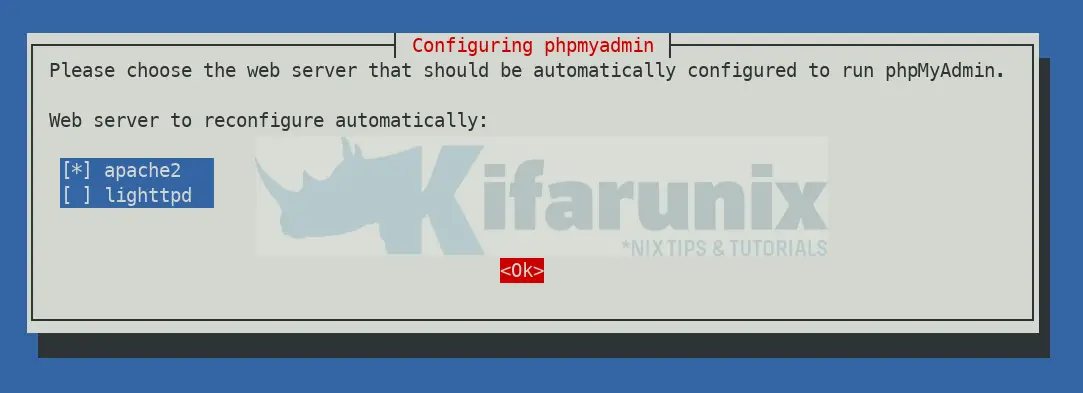
Configuring Database for phpMyAdmin
So, there are two options here;
- If you have created the phpMyAdmin database and database credentials manually, choose
Noon the prompt. - To configure phpMyAdmin database credentials with
dbconfig-commontool, selectYeson the prompt and proceed.
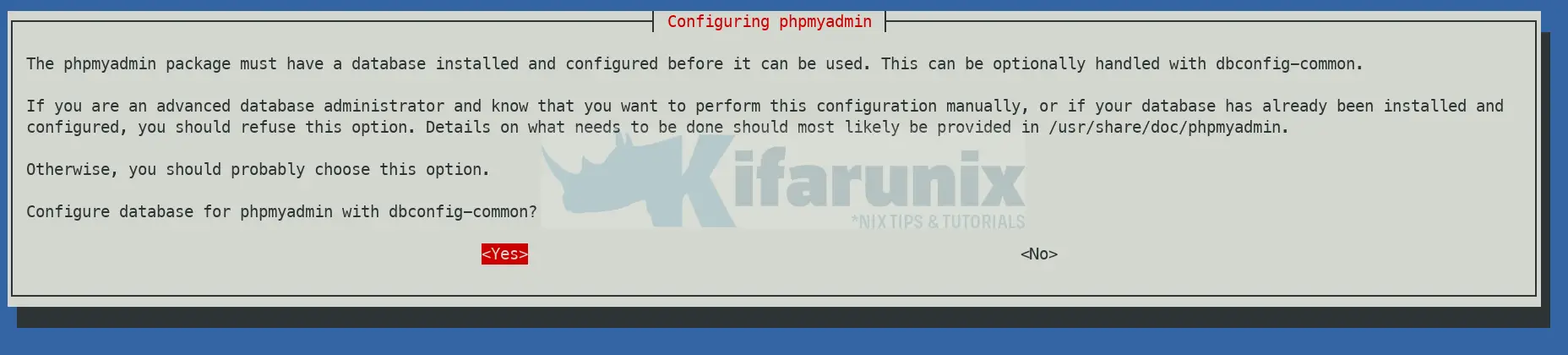
Next, create the phpMyAdmin database account password and proceed with installation.
Apache VirtualHost for phpMyAdmin
The installer automatically creates and enable Apache virtual host configuration file for phpMyAdmin as shown below;
cat /etc/apache2/conf-available/phpmyadmin.conf
# phpMyAdmin default Apache configuration
Alias /phpmyadmin /usr/share/phpmyadmin
<Directory /usr/share/phpmyadmin>
Options SymLinksIfOwnerMatch
DirectoryIndex index.php
# limit libapache2-mod-php to files and directories necessary by pma
<IfModule mod_php7.c>
php_admin_value upload_tmp_dir /var/lib/phpmyadmin/tmp
php_admin_value open_basedir /usr/share/phpmyadmin/:/usr/share/doc/phpmyadmin/:/etc/phpmyadmin/:/var/lib/phpmyadmin/:/usr/share/php/:/usr/share/javascript/
</IfModule>
# PHP 8+
<IfModule mod_php.c>
php_admin_value upload_tmp_dir /var/lib/phpmyadmin/tmp
php_admin_value open_basedir /usr/share/phpmyadmin/:/usr/share/doc/phpmyadmin/:/etc/phpmyadmin/:/var/lib/phpmyadmin/:/usr/share/php/:/usr/share/javascript/
</IfModule>
</Directory>
# Disallow web access to directories that don't need it
<Directory /usr/share/phpmyadmin/templates>
Require all denied
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share/phpmyadmin/libraries>
Require all denied
</Directory>
phpMyAdmin Database Details
If you used phpMyAdmin dbconfig-common tool to create the database, you should be able to get these details on the MariaDB database server.
Thus, login and check;
mysql -u root -pshow databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| phpmyadmin |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Check tables;
use phpmyadmin;show tables;
+------------------------+
| Tables_in_phpmyadmin |
+------------------------+
| pma__bookmark |
| pma__central_columns |
| pma__column_info |
| pma__designer_settings |
| pma__export_templates |
| pma__favorite |
| pma__history |
| pma__navigationhiding |
| pma__pdf_pages |
| pma__recent |
| pma__relation |
| pma__savedsearches |
| pma__table_coords |
| pma__table_info |
| pma__table_uiprefs |
| pma__tracking |
| pma__userconfig |
| pma__usergroups |
| pma__users |
+------------------------+
19 rows in set (0.001 sec)
You can get the credentials in the file /etc/phpmyadmin/config-db.php;
cat /etc/phpmyadmin/config-db.php
<?php
##
## database access settings in php format
## automatically generated from /etc/dbconfig-common/phpmyadmin.conf
## by /usr/sbin/dbconfig-generate-include
##
## by default this file is managed via ucf, so you shouldn't have to
## worry about manual changes being silently discarded. *however*,
## you'll probably also want to edit the configuration file mentioned
## above too.
##
$dbuser='phpmyadmin';
$dbpass='ChangeME';
$basepath='';
$dbname='phpmyadmin';
$dbserver='localhost';
$dbport='3306';
$dbtype='mysql';
Configure phpMyAdmin on Debian 12
The installer creates a phpMyAdmin configuration with the content below;
cat /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php
<?php
/**
* Debian local configuration file
*
* This file overrides the settings made by phpMyAdmin interactive setup
* utility.
*
* For example configuration see
* /usr/share/doc/phpmyadmin/examples/config.sample.inc.php
* or
* /usr/share/doc/phpmyadmin/examples/config.manyhosts.inc.php
*
* NOTE: do not add security sensitive data to this file (like passwords)
* unless you really know what you're doing. If you do, any user that can
* run PHP or CGI on your webserver will be able to read them. If you still
* want to do this, make sure to properly secure the access to this file
* (also on the filesystem level).
*/
if (!function_exists('check_file_access')) {
function check_file_access(string $path): bool
{
if (is_readable($path)) {
return true;
}
if (! file_exists($path)) {
return false;
}
error_log(
'phpmyadmin: Failed to load ' . $path
. ' Check group www-data has read access and open_basedir restrictions.'
);
return false;
}
}
// Load secret generated on postinst
if (check_file_access('/var/lib/phpmyadmin/blowfish_secret.inc.php')) {
require('/var/lib/phpmyadmin/blowfish_secret.inc.php');
}
/**
* Server(s) configuration
*/
$i = 0;
// The $cfg['Servers'] array starts with $cfg['Servers'][1]. Do not use $cfg['Servers'][0].
// You can disable a server config entry by setting host to ''.
$i++;
/**
* Read configuration from dbconfig-common
* You can regenerate it using: dpkg-reconfigure -plow phpmyadmin
*/
if (check_file_access('/etc/phpmyadmin/config-db.php')) {
require('/etc/phpmyadmin/config-db.php');
}
/* Configure according to dbconfig-common if enabled */
if (!empty($dbname)) {
/* Authentication type */
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'cookie';
/* Server parameters */
if (empty($dbserver)) $dbserver = 'localhost';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['host'] = $dbserver;
if (!empty($dbport) || $dbserver != 'localhost') {
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['connect_type'] = 'tcp';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['port'] = $dbport;
}
//$cfg['Servers'][$i]['compress'] = false;
/* Optional: User for advanced features */
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['controluser'] = $dbuser;
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlpass'] = $dbpass;
/* Optional: Advanced phpMyAdmin features */
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['pmadb'] = $dbname;
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['bookmarktable'] = 'pma__bookmark';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['relation'] = 'pma__relation';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_info'] = 'pma__table_info';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_coords'] = 'pma__table_coords';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['pdf_pages'] = 'pma__pdf_pages';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['column_info'] = 'pma__column_info';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['history'] = 'pma__history';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_uiprefs'] = 'pma__table_uiprefs';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['tracking'] = 'pma__tracking';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['userconfig'] = 'pma__userconfig';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['recent'] = 'pma__recent';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['favorite'] = 'pma__favorite';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['users'] = 'pma__users';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['usergroups'] = 'pma__usergroups';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['navigationhiding'] = 'pma__navigationhiding';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['savedsearches'] = 'pma__savedsearches';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['central_columns'] = 'pma__central_columns';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['designer_settings'] = 'pma__designer_settings';
$cfg['Servers'][$i]['export_templates'] = 'pma__export_templates';
/* Uncomment the following to enable logging in to passwordless accounts,
* after taking note of the associated security risks. */
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['AllowNoPassword'] = TRUE;
/* Advance to next server for rest of config */
$i++;
}
/* Authentication type */
//$cfg['Servers'][$i]['auth_type'] = 'cookie';
/* Server parameters */
//$cfg['Servers'][$i]['host'] = 'localhost';
//$cfg['Servers'][$i]['connect_type'] = 'tcp';
//$cfg['Servers'][$i]['compress'] = false;
/* Uncomment the following to enable logging in to passwordless accounts,
* after taking note of the associated security risks. */
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['AllowNoPassword'] = TRUE;
/**
* phpMyAdmin configuration storage settings.
*/
/* User used to manipulate with storage */
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlhost'] = '';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlport'] = '';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controluser'] = 'pma';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['controlpass'] = 'pmapass';
/* Storage database and tables */
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['pmadb'] = 'phpmyadmin';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['bookmarktable'] = 'pma__bookmark';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['relation'] = 'pma__relation';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_info'] = 'pma__table_info';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_coords'] = 'pma__table_coords';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['pdf_pages'] = 'pma__pdf_pages';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['column_info'] = 'pma__column_info';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['history'] = 'pma__history';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['table_uiprefs'] = 'pma__table_uiprefs';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['tracking'] = 'pma__tracking';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['userconfig'] = 'pma__userconfig';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['recent'] = 'pma__recent';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['favorite'] = 'pma__favorite';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['users'] = 'pma__users';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['usergroups'] = 'pma__usergroups';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['navigationhiding'] = 'pma__navigationhiding';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['savedsearches'] = 'pma__savedsearches';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['central_columns'] = 'pma__central_columns';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['designer_settings'] = 'pma__designer_settings';
// $cfg['Servers'][$i]['export_templates'] = 'pma__export_templates';
/*
* End of servers configuration
*/
/*
* Directories for saving/loading files from server
*/
$cfg['UploadDir'] = '';
$cfg['SaveDir'] = '';
/* Support additional configurations */
foreach (glob('/etc/phpmyadmin/conf.d/*.php') as $filename)
{
include($filename);
}
Open HTTP/HTTPS port on Firewall
Allow Apache on UFW for external access.
ufw allow "WWW Full"
Accessing phpMyAdmin on Debian 12
You can now access phpMyAdmin from the browser using the address, http://server-host-name_or_IP/phpmyadmin.
Login using your database root user credentials or the user with access to only specific databases.
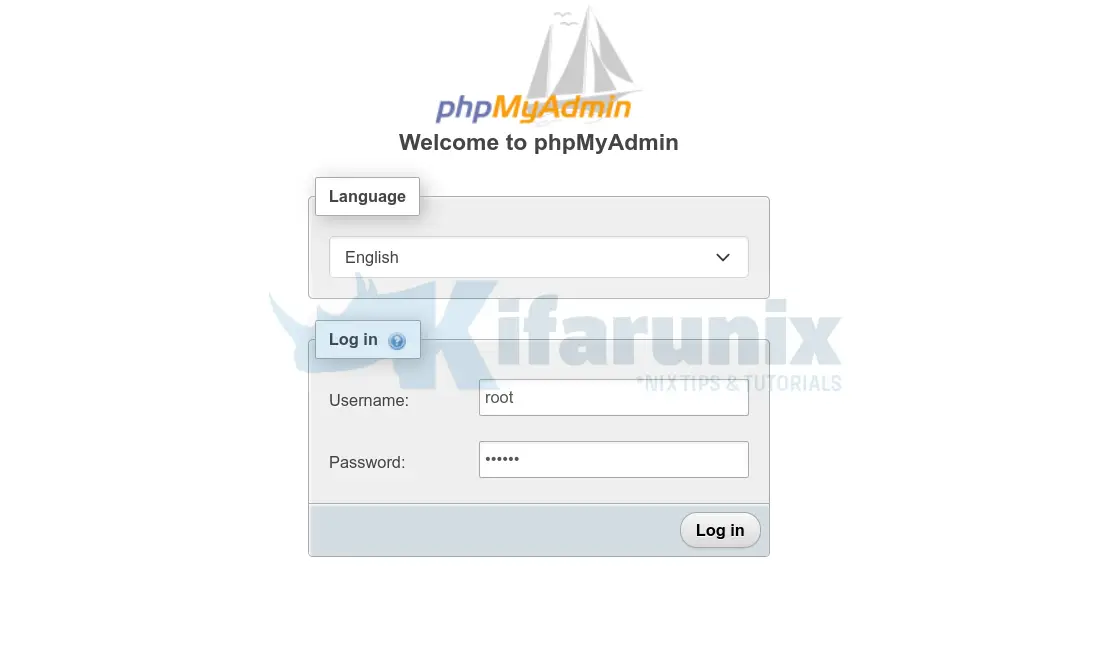
Upon successful login, you get to phpMyAdmin dashboard.
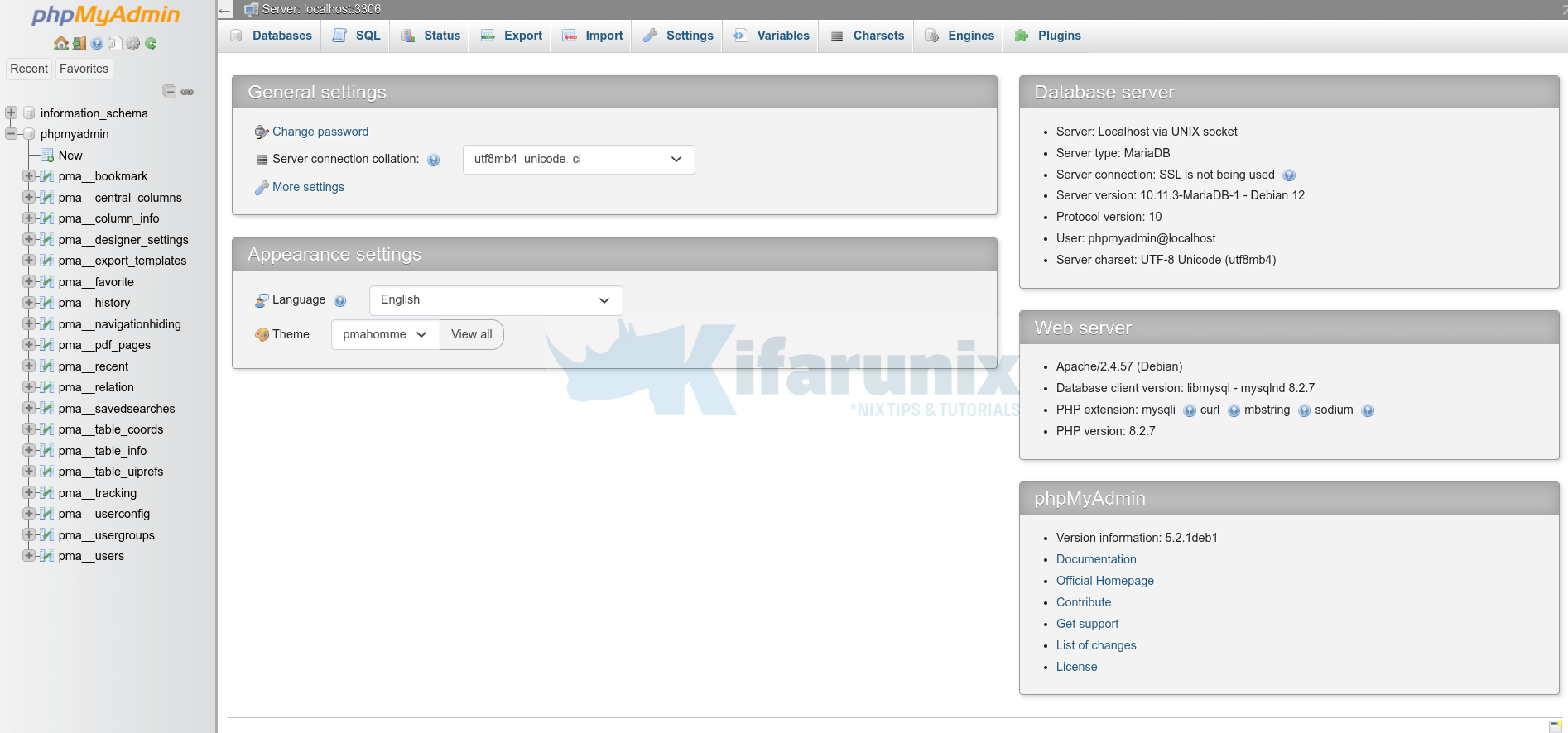
You have successfully installed and setup phpMyAdmin on Debian 12. You can now be able to administer your MySQL or MariaDB from web.
Related Tutorials
Install phpMyAdmin with Nginx on Debian 10 Buster
Install phpMyAdmin on Debian 10 Buster


Precisa configurar o arquivo: /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php
Descomentar essa linha: $cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘AllowNoPassword’] = FALSE;
Em autentication type essa: $cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘AllowNoPassword’] = FALSE;
salvar e sair do editor.
Faça login no MYSQL como root
mysql -u root
Conceda privilégios. Para um novo usuário, execute:
CREATE USER ‘newuser’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ‘newuser’@’localhost’;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Depois so logar e acessar. Nao pode mais como root.
Need to configure the file: /etc/phpmyadmin/config.inc.php
Uncomment this line: $cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘AllowNoPassword’] = FALSE;
In authentication type this: $cfg[‘Servers’][$i][‘AllowNoPassword’] = FALSE;
save and exit the editor.
Log in to MYSQL as root
mysql -u root
Grant privileges. For a new user, run:
CREATE USER ‘newuser’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ‘newuser’@’localhost’;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Then just log in and access. You can no longer use root.