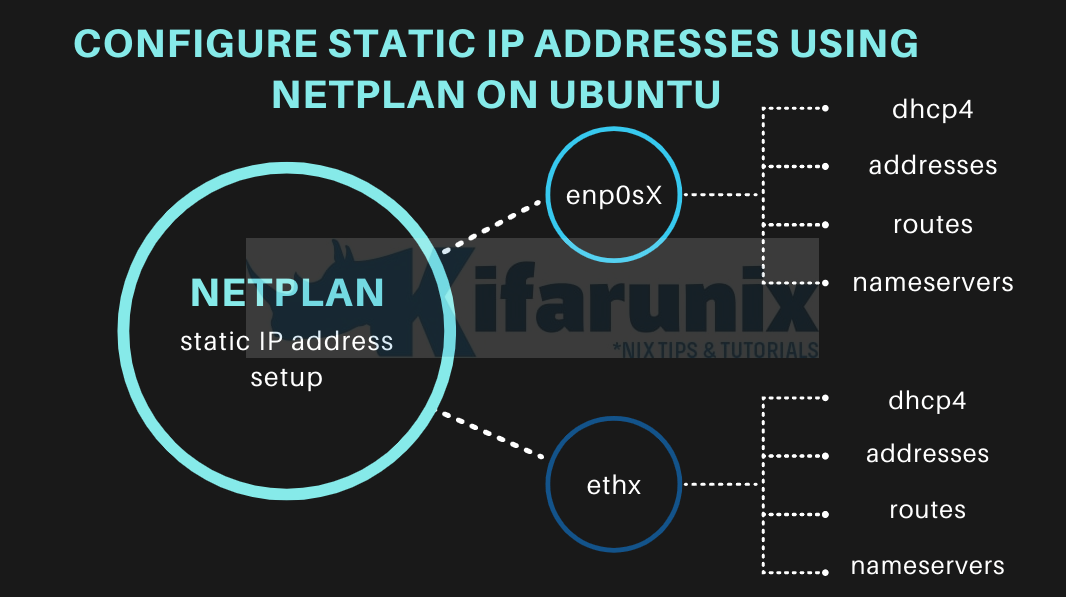
How to set static IP addresses using Netplan on Ubuntu? In this tutorial, you will learn how to configure static IP addresses using Netplan on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04/22.04. To manage network interfaces, recent versions of Ubuntu uses the Netplan utility. Netplan is a YAML network configuration abstraction for various back-ends.
Table of Contents
Configuring Static IP Addresses using Netplan on Ubuntu
The Netplan command has replaced the commonly used static interfaces IP address configuration file, /etc/network/interfaces, with various network configuration files in the /etc/netplan/ directory. The files in this directory are in yaml format.
On Ubuntu 18.04 server and later, networkd renderer is used to control network interfaces.
If you need to connect to WiFi in Linux using NMCLI command, then you can check our guide by following the link below;
Connect to WiFi in Linux Using NMCLI command
Using Netplan to Configure Static IP Addresses on Ubuntu
Before we proceed to configure static IP address on an interface on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04 Server, let us have a look at the format of the default netplan configuration file, /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
less /etc/netplan/01-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: yes
From the above output, DHCP is enabled for interface enp0s3 and is thus relying on DHCP server for IP addresses assignment.
To set static IP address on an interface using Netplan on Ubuntu, we will use the same format as in the output of the configuration file above.
We will have to disable the DHCP server for our interface along with adding other details as shown below. In the example below, we will configure enp0s8 interface as follows;
- static IP address 192.168.59.81
- netmask 255.255.255.0
- gateway 192.168.59.1
- nameserver 1.1.1.1, 4.2.2.2.
To reduce too much work, we will just copy the above configuration file and do some modification.
cp /etc/netplan/{01,02}-netcfg.yamlvim /etc/netplan/02-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.59.81/24]
routes:
- to: 0.0.0.0/0
via: 192.168.59.1
nameservers:
addresses: [1.1.1.1,4.2.2.2]
Save the configuration file and apply the changes using the command below.
Before you can save the changes, first of all check if any error with configuration;
netplan trySample output;
Do you want to keep these settings?
Press ENTER before the timeout to accept the new configuration
Changes will revert in 107 seconds
If there is any error, it will be printed out. Otherwise, you will be asked to Press ENTER to save changes before timeout is reached.
You can as well cancel the above and apply changes using;
netplan applyCheck the IP add on the enp0s8 interface to confirm the assignment.
ip add show enp0s8
4: enp0s8: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:87:d4:14 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.59.81/24 brd 192.168.59.255 scope global enp0s8
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe87:d414/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
As you can see, the IP address is assigned.
If you want to assign different IPs to different interfaces in the same configuration file, you can do so as follows.
vim /etc/netplan/02-netcfg.yaml
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# For more information, see netplan(5).
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.59.81/24]
routes:
- to: 192.168.59.0/24
via: 192.168.59.1
nameservers:
search: example.com
addresses: [1.1.1.1,4.2.2.2]
enp0s9:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.58.92/24]
routes:
- to: 192.168.58.0/24
via: 192.168.58.1
nameservers:
addresses: [1.1.1.1,4.2.2.2]
Once done with configuration, remember to run the netplan apply command to apply the changes and bring the interfaces up.
That is all about how to configure Static IP Addresses using Netplan on Ubuntu.
See also;
Set Static Routes via an Interface/IP on CentOS/Ubuntu
Other Tutorials
Install and Setup Kolide Fleet on Ubuntu 18.04
Install Microsoft Teams Client on Ubuntu 20.04/18.04


root@Hviet-LC10:~# ifconfig
lo: flags=73 mtu 1500
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0xfe
loop (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
wifi0: flags=4163 mtu 1500
inet 192.168.1.12 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.1.255
inet6 2402:800:6139:de1f:992b:561a:27fd:bfc2 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0
inet6 2402:800:6139:de1f:69c6:1a06:fe8c:fca prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x0
inet6 fe80::992b:561a:27fd:bfc2 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0xfd
ether 00:24:d7:c4:3f:d8 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
>>my ubuntu, so how to set static IP for it “wifi0” =192.168.1.89
Thanks
Can you please explain in details how to setup routes. If you have 4 VMs and it is on NAT Network (192.168.100.0/24) on VirtualBox . how will routes be when setting up static ip on enp0s8 adapter on each of VM. how will -to and via ip will change from one vm to other
routes:
– to: 192.168.59.0/24
via: 192.168.59.1
nameservers:
search: example.com
addresses: [1.1.1.1,4.2.2.2]
Hi, how is your network setup? are you using single host only (192.168.100.0/24) network on 4 vms?
Each VM setup with 2 network adapter in VirtualBox
1: NAT :Host is on 192.168.1.100/24
2: “NAT Network” 192.168.10.0/24
Here is what i came up but it throws error when VMs boot up
—————————————————————————
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.200/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
routes:
– to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.10.101/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.10.1,8.8.8.8]
routes:
– to: 192.168.10.0/24
via: 192.168.10.1
version: 2
VM2
—-
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.201/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
routes:
– to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.10.102/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.10.1,8.8.8.8]
routes:
– to: 192.168.10.0/24
via: 192.168.10.1
version: 2
VM3
—-
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.202/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
routes:
– to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.10.103/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.10.1,8.8.8.8]
routes:
– to: 192.168.10.0/24
via: 192.168.10.1
Hello,
I am trying to create a network of 3 ubuntu-22.04 server VM on virtual box 7. each vm has two network adapters (1 NAT and 1 Nat network) defined.
NatNetwork defined at virtual box level has DHCP enabled and has IPV4Prefix set to 192.168.10.0/24
I have tried to use netplan following couple of articles and guidance from internet. Dont have prior knowledge on netplan
netplan apply command is successful.
Issue I have is that my first VM always come successful but other two get stuck during boot time whcn configuring network. I suspect i have messed up in setting routes or name servers for enp0s8.
Looking for some guidance here. Thanks a lot.
below are content of 00-installer-config.yaml
VM1
—-
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.200/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
routes:
– to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.10.101/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.10.1,8.8.8.8]
routes:
– to: 192.168.10.0/24
via: 192.168.10.1
version: 2
VM2
—-
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.201/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
routes:
– to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.10.102/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.10.1,8.8.8.8]
routes:
– to: 192.168.10.0/24
via: 192.168.10.1
version: 2
VM3
—-
network:
ethernets:
enp0s3:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.1.202/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,8.8.4.4]
routes:
– to: default
via: 192.168.1.1
enp0s8:
dhcp4: no
addresses: [192.168.10.103/24]
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.10.1,8.8.8.8]
routes:
– to: 192.168.10.0/24
via: 192.168.10.1
version: 2