In this guide, we are going to learn how to install Apache Guacamole on Debian 10. Apache Guacamole is a clientless HTML5 web based remote desktop gateway which provides remote access to servers and desktops through a web browser. It supports standard protocols like VNC, RDP, and SSH.
Installing Guacamole on Debian 10
Guacamole is made up of two parts;
guacamole-server, which provides the guacd proxy and all the native, server-side components required by Guacamole to connect to remote desktops.guacamole-clientwhich provides the client to be served by the servlet container which is usuallyTomcat.
You need to install both of these components to setup Apache Guacamole web-based remote desktop client.
Install Guacamole Server on Debian 10
Run system Update
Ensure your system package cache is up-to-date;
apt updateInstall Required Build Tools
To install guacamole-server, you need to build it from the source. This, therefore, requires that you need install the required build tools before you can start to build guacamole-server component;
apt install -y build-essential libcairo2-dev libjpeg62-turbo-dev libpng-dev \
libtool-bin libossp-uuid-dev libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libavutil-dev libswscale-dev \
libpango1.0-dev libssh2-1-dev libvncserver-dev libtelnet-dev \
libssl-dev libvorbis-dev libwebp-dev libpulse-devNext, install FreeRDP libraries enable support for RDP via Guacamole. You need to install FreeRDP libraries from Debian Backport repositories. Otherwise, if you install from the default Debian repositories, you might encounter such an error while compiling Guacamole server;
configure: error:
--------------------------------------------
You are building against a development version of FreeRDP. Non-release
versions of FreeRDP may have differences in behavior that are impossible to
check for at build time. This may result in memory leaks or other strange
behavior.
*** PLEASE USE A RELEASED VERSION OF FREERDP IF POSSIBLE ***
If you are ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN that building against this version of FreeRDP
is OK, rerun configure with the --enable-allow-freerdp-snapshots
--------------------------------------------So to overcome this, install Backport repos and install FreeRDP libraries;
echo "deb http://deb.debian.org/debian buster-backports main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/backports.listapt updateapt install freerdp2-dev/buster-backportsA comprehensive description of these dependency tools is available on required dependencies section.
Building Guacamole Server on Debian 10
To build guacamole-server, download the latest source archive tarball from Guacamole releases page. Apache Guacamole 1.3.0 is the latest release version as of this writing.
You can simply run the command below to download Apache Guacamole 1.3.0.
To make this easy, just set a variable for the current stable release version on the terminal.
VER=1.3.0wget https://downloads.apache.org/guacamole/$VER/source/guacamole-server-$VER.tar.gzOnce the download is done, extract the source tarball.
tar xzf guacamole-server-$VER.tar.gzNavigate to guacamole server source code directory;
cd guacamole-server-$VERRun the configure script to check if any required dependency is missing and to adapt Guacamole server to your system.
./configure --with-init-dir=/etc/init.dFor more configure options, run, ./configure --help.
...
------------------------------------------------
guacamole-server version 1.3.0
------------------------------------------------
Library status:
freerdp2 ............ yes
pango ............... yes
libavcodec .......... yes
libavformat.......... yes
libavutil ........... yes
libssh2 ............. yes
libssl .............. yes
libswscale .......... yes
libtelnet ........... yes
libVNCServer ........ yes
libvorbis ........... yes
libpulse ............ no
libwebsockets ....... no
libwebp ............. yes
wsock32 ............. no
Protocol support:
Kubernetes .... no
RDP ........... yes
SSH ........... yes
Telnet ........ yes
VNC ........... yes
Services / tools:
guacd ...... yes
guacenc .... yes
guaclog .... yes
FreeRDP plugins: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/freerdp2
Init scripts: /etc/init.d
Systemd units: no
Type "make" to compile guacamole-server.Pay attention to out of the configure script.
Compile and install Guacamole Server on Debian 10;
makemake installNext, run the ldconfig command to create the necessary links and cache to the most recent shared libraries found in the guacamole server directory.
ldconfigRunning Guacamole-Server on Debian 10
Reload systemd configuration files and start and enable guacd (Guacamole Daemon) to run on boot after the installation.
systemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl start guacdsystemctl enable guacdTo check the status;
systemctl status guacd● guacd.service - LSB: Guacamole proxy daemon
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/guacd; generated)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2021-03-27 16:18:30 EAT; 6s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 20717 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/guacd start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 2359)
Memory: 10.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/guacd.service
└─20720 /usr/local/sbin/guacd -p /var/run/guacd.pid
Mar 27 16:18:29 debian systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Guacamole proxy daemon...
Mar 27 16:18:30 debian guacd[20718]: Guacamole proxy daemon (guacd) version 1.3.0 started
Mar 27 16:18:30 debian guacd[20717]: Starting guacd: guacd[20718]: INFO: Guacamole proxy daemon (guacd) version 1.3.0 started
Mar 27 16:18:30 debian guacd[20717]: SUCCESS
Mar 27 16:18:30 debian systemd[1]: Started LSB: Guacamole proxy daemon.
Mar 27 16:18:30 debian guacd[20720]: Listening on host 127.0.0.1, port 4822
Install Tomcat Servlet
Apache Tomcat is used to serve guacamole client content to users that connects to guacamole server via the web browser. To install Tomcat, run the command below;
apt install tomcat9 tomcat9-admin tomcat9-common tomcat9-user -yTomcat9 is started and enabled to run on system boot upon installation. Check the status by running the command below;
systemctl status tomcat9.service● tomcat9.service - Apache Tomcat 9 Web Application Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/tomcat9.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2021-03-27 16:24:56 EAT; 16s ago
Docs: https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-9.0-doc/index.html
Main PID: 22522 (java)
Tasks: 37 (limit: 2359)
Memory: 100.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/tomcat9.service
└─22522 /usr/lib/jvm/default-java/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/var/lib/tomcat9/conf/logging.properties -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache.juli.C
Mar 27 16:25:03 debian tomcat9[22522]: Deployment of deployment descriptor [/etc/tomcat9/Catalina/localhost/host-manager.xml] has finished in [5,851] ms
Mar 27 16:25:03 debian tomcat9[22522]: Deploying deployment descriptor [/etc/tomcat9/Catalina/localhost/manager.xml]Apache Tomcat listens on port 8080/tcp by default;
ss -altnp | grep 80LISTEN 0 100 *:8080 *:* users:(("java",pid=24615,fd=37))To allow external access to the serverlet, open the serverlet port 8080/tcp on UFW, if at all UFW is installed and enabled.
ufw allow 8080/tcpInstalling Guacamole Client on Debian 10
guacamole-client contains provides web application that will serve the HTML5 Guacamole client to users that connect to your server. The web application will then connect to guacd on behalf of connected users in order to serve them any remote desktop they are authorized to access.
Create Guacamole configuration directory;
mkdir /etc/guacamoleDownload Guacamole-client Binary
Guacamole client can be installed from source code or from ready binary. Binary installation is used in this demo.
Download Guacamole-client from Guacamole releases page for the respective latest version (v1.3.0 as of this writing) and store it in the configuration directory created above.
To download the current release version, v1.3.0 as of this writing, simply run the command below;
Similarly, we use the same client version variable;
VER=1.3.0wget https://downloads.apache.org/guacamole/$VER/binary/guacamole-$VER.war -O /etc/guacamole/guacamole.warCreate a symbolic link of the guacamole client to Tomcat webapps directory as shown below;
ln -s /etc/guacamole/guacamole.war /var/lib/tomcat9/webapps/Restart Tomcat to deploy the new web application;
systemctl restart tomcat9Restart guacd daemon as well;
systemctl restart guacdConfigure Apache Guacamole on Debian 10
Guacamole has two major configuration files;
/etc/guacamolewhich is referenced by theGUACAMOLE_HOMEenvironment variable/etc/guacamole/guacamole.propertieswhich is the main configuration file used by Guacamole and its extensions.
There are also guacamole extensions and libraries configurations. You need to create the directories for these configs;
mkdir /etc/guacamole/{extensions,lib}Set the guacamole home directory environment variable and add it to /etc/default/tomcat9 configuration file.
echo "GUACAMOLE_HOME=/etc/guacamole" >> /etc/default/tomcat9Configure Guacamole Server Connections
To define how Guacamole connects to guacd, create the guacamole.properties file under /etc/guacamole directory with the following content.
vim /etc/guacamole/guacamole.propertiesguacd-hostname: localhost
guacd-port: 4822
user-mapping: /etc/guacamole/user-mapping.xml
auth-provider: net.sourceforge.guacamole.net.basic.BasicFileAuthenticationProviderAfter that, save and exit the configuration file.
Next, link the Guacamole configurations directory to Tomcat servlet directory as shown below.
ln -s /etc/guacamole /usr/share/tomcat9/.guacamoleConfigure Guacamole Authentication Method
Guacamole’s default authentication method reads all users and connections from a single file called user-mapping.xml.
In this file,you need to define the users allowed to access Guacamole web UI, the servers to connect to and the method of connection.
Other authentication methods are supported, but beyond the scope of this tutorial.
To begin with, generate the MD5 hash of passwords for the user to be used for logging into Guacamole web user interface. Replace you password accordingly;
echo -n password | openssl md5Output;
(stdin)= 5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99or
printf '%s' password | md5sumOutput;
5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99 -Be sure to replace password with your strong password.
Next, create the default user authentication file, user-mapping.xml with the following contents.
vim /etc/guacamole/user-mapping.xml<user-mapping>
<!-- Per-user authentication and config information -->
<!-- A user using md5 to hash the password
guacadmin user and its md5 hashed password below is used to
login to Guacamole Web UI-->
<authorize
username="guacadmin"
password="5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99"
encoding="md5">
<!-- First authorized Remote connection -->
<connection name="Ubuntu 20.04 Server SSH">
<protocol>ssh</protocol>
<param name="hostname">192.168.57.3</param>
<param name="port">22</param>
</connection>
<!-- Second authorized remote connection -->
<connection name="Windows 7 RDP">
<protocol>rdp</protocol>
<param name="hostname">192.168.56.103</param>
<param name="port">3389</param>
<param name="username">koromicha</param>
<param name="ignore-cert">true</param>
</connection>
</authorize>
</user-mapping>If you dont specify the username and password in the file, you will be prompted to provide them while attempting to login, which i consider it abit secure.
If you need to explicitly define usernames and passwords in the configuration file, add the parameters;
<param name="username">USERNAME</param>
<param name="password">PASSWORD</param>Save and exit the configuration file.
Restart both Tomcat and guacd to effect the changes.
systemctl restart tomcat9 guacdBe sure to check the syslog, /var/log/syslog or /var/log/tomcat9/CATALINA-* for any issues.
Accessing Apache Guacamole from Browse
Apache Guacamole server is now setup. You can access it from web browser using the address http://server-IP:8080/guacamole.

Use the credentials for the user whom you generated an MD5 hash for its password above.
Upon successful login, you get to Apache Guacamole web dashboard and you should be able to see the added connections.

Click on a connection to name to initiate remote login.
For example, to ssh into my Ubuntu server, just click on the connection name. This will get you a login prompt;
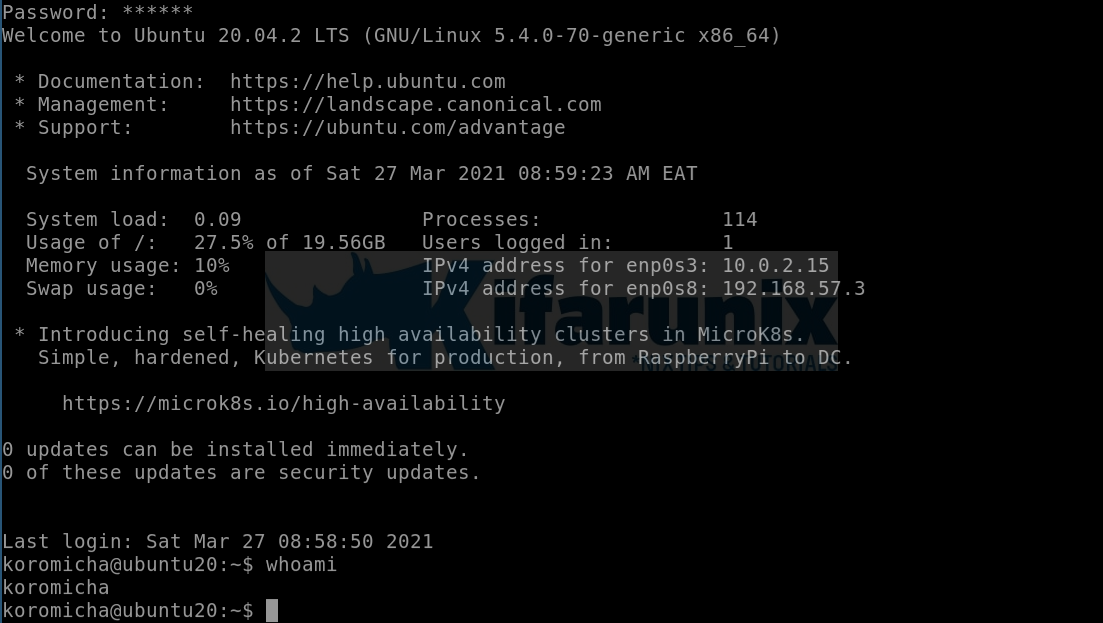
To login to Windows 7 via RDP, just click on Windows 7;

And there you go. Enter your password and proceed to your desktop.
You can now add more connections to your Guacamole.
Related guides;
Configure Guacamole SSL/TLS with Nginx Reverse Proxy
How to Enable RDP/SSH File Transfer Over Guacamole
Other Tutorials
Install Apache Guacamole on Ubuntu 21.04
Install NoMachine Remote Desktop Tool on Kali Linux 2020

