In this guide, you will learn how to install and setup GVM 20.08 on Debian 10. Greenbone Vulnerability Management (GVM), previously known as OpenVAS, is a network security scanner which provides a set of network vulnerability tests (NVTs) to detect security loopholes in systems and applications. As of this writing, GVM 20.08 is the current stable release and is the first release that uses a calendar based versioning (August of 2020).
With the release of GVM 20.08, GVM 10 and GVM 11 were set to retire by end of 2020.
Install GVM on Debian 10
Prerequisites
In this demo, we will install and setup GVM from source code. As such, below are the system requirements I would personally recommend.
- At least 4 GB RAM
- At least 4 vCPUs
- More than 8 GB disk space (We used 16 GB in this demo)
These requirements will vary depending on your use cases, however. Just be sure to provide “enough”.
Run System Update
To begin with, update and upgrade your system packages;
apt updateapt upgradeCreate GVM User on Ubuntu
In this demo, we will run GVM 20.08 as a non privileged system user. Thus, create gvm system user account.
useradd -r -d /opt/gvm -c "GVM User" -s /bin/bash gvmCreate the GVM user directory as specified by option -d in the command above and set the user and group ownership to gvm.
mkdir /opt/gvmchown gvm: /opt/gvmInstall Required Build Tools
In order to successfully build GVM 20.08 on Debian 10, you need to install a number of required dependencies and build tools.
apt install gcc g++ make bison flex libksba-dev curl redis libpcap-dev \
cmake git pkg-config libglib2.0-dev libgpgme-dev nmap libgnutls28-dev uuid-dev \
libssh-gcrypt-dev libldap2-dev gnutls-bin libmicrohttpd-dev libhiredis-dev \
zlib1g-dev libxml2-dev libradcli-dev clang-format libldap2-dev doxygen \
gcc-mingw-w64 xml-twig-tools libical-dev perl-base heimdal-dev libpopt-dev libunistring-dev graphviz \
libsnmp-dev python3-setuptools python3-paramiko python3-lxml python3-defusedxml python3-dev gettext python3-polib xmltoman \
python3-pip texlive-fonts-recommended texlive-latex-extra --no-install-recommends xsltproc sudo vim rsyncInstall Yarn on Debian 10
Next, install Yarn JavaScript package manager
curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add -echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.listapt updateapt install yarn -yInstall PostgreSQL on Debian 10
GVM 20.08 uses PostgreSQL as the backend database. Therefore, run the command below to install PostgreSQL on Debian 10;
apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib postgresql-server-dev-allCreate PostgreSQL User and Database
Once the installation is done, create the PostgreSQL user and database for Greenbone Vulnerability Management Daemon (gvmd). Note that the database and user should be created as PostgreSQL user, postgres.
sudo -Hiu postgres
createuser gvm
createdb -O gvm gvmdGrant PostgreSQL User DBA Roles
psql gvmd
create role dba with superuser noinherit;
grant dba to gvm;
create extension "uuid-ossp";
create extension "pgcrypto";
\q
exitOnce that is done, restart PostgreSQL;
systemctl restart postgresqlsystemctl enable postgresqlWant to get started in CyberSecurity? Check the link below;
Cybersecurity: The Beginner’s Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurity
Building GVM 20.08 from Source Code
There are different tools required to install and setup GVM. These include;
- GVM Libraries
- OpenVAS Scanner
- OSPd
- ospd-openvas
- Greenbone Vulnerability Manager
- Greenbone Security Assistant
- Python-GVM
- GVM-Tools
- OpenVAS SMB
Every component has README.md and a INSTALL.md file that explains how to build and install it.
Since we are running GVM as non-privileged user, gvm, then we will install all the GVM configuration files and libraries under, /opt/gvm.
Update the PATH environment variable on /etc/environment, to include the GVM binary path such that it looks like;
echo "PATH=\$PATH:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin" > /etc/profile.d/gvm.shAdd GVM library path to /etc/ld.so.conf.d.
echo "/opt/gvm/lib" > /etc/ld.so.conf.d/gvm.confBuild and Install GVM 20.08 on Debian 10
Switch to GVM user, gvm and create a temporary directory to store GVM source files.
su - gvmmkdir gvm-sourceDownload GVM 20.08 Source Files
Navigate to temporary directory created above and run the subsequent commands to clone the GVM github branch files.
cd gvm-sourcegit clone -b gvm-libs-20.08 https://github.com/greenbone/gvm-libs.gitgit clone -b master https://github.com/greenbone/openvas-smb.gitgit clone -b openvas-20.08 https://github.com/greenbone/openvas.gitgit clone -b ospd-20.08 https://github.com/greenbone/ospd.gitgit clone -b ospd-openvas-20.08 https://github.com/greenbone/ospd-openvas.gitgit clone -b gvmd-20.08 https://github.com/greenbone/gvmd.gitgit clone -b gsa-20.08 https://github.com/greenbone/gsa.gitOnce the source files are in place, proceed to build and install GVM 20.08 on Debian 10.
Note the current working directory;
pwd/opt/gvm/gvm-sourcels -1gsa
gvmd
gvm-libs
openvas
openvas-smb
ospd
ospd-openvasNote that we will install all GVM 20.08 files and libraries to a non-standard location, /opt/gvm. As such, you need to set the PKG_CONFIG_PATH environment variable to the location of your pkg-config files before configuring:
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATHBe sure to replace the path, /opt/gvm, accordingly.
I would suggest you take a snapshot of your machine at this point, just in case things don’t work out, you can revert to this stage without having to start from scratch!
Build and Install GVM 11 Libraries
From within the source directory, /opt/gvm/gvm-source, in this setup, change to GVM libraries directory;
cd gvm-libsCreate a build directory and change into it;
mkdir build
cd buildConfigure the build;
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvmNext, compile and install GVM libraries
makemake installBuild and Install OpenVAS scanner and OpenVAS SMB
Open Vulnerability Assessment Scanner (OpenVAS) is a full-featured scan engine that executes a continuously updated and extended feed of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs).
OpenVAS SMB provides modules for the OpenVAS Scanner to interface with Microsoft Windows Systems through the Windows Management Instrumentation API and a winexe binary to execute processes remotely on that system.
Build and install openvas-smb;
cd ../../openvas-smb/
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make
make installBuild and install OpenVAS scanner;
cd ../../openvasProceed to build and install openvas.
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make
make installConfiguring OpenVAS Scanner
The host scan information is stored temporarily on Redis server. The default configuration of Redis server is /etc/redis/redis.conf.
Switch back to privileged user and proceed.
exitTo begin run the command below to create the cache to the installed shared libraries;
ldconfigNext, copy OpenVAS scanner Redis configuration file, redis-openvas.conf, to the same Redis config directory;
cp /opt/gvm/gvm-source/openvas/config/redis-openvas.conf /etc/redis/Update the ownership of the configuration.
chown redis:redis /etc/redis/redis-openvas.confUpdate the path to Redis unix socket on the /opt/gvm/etc/openvas/openvas.conf using the db_address parameter as follows;
echo "db_address = /run/redis-openvas/redis.sock" > /opt/gvm/etc/openvas/openvas.confNote, the Unix socket path is defined on /etc/redis/redis-openvas.conf file.
chown gvm:gvm /opt/gvm/etc/openvas/openvas.confAdd gvm user to redis group;
usermod -aG redis gvmYou can also optimize Redis server itself improve the performance by making the following adjustments;
Increase the value of somaxconn in order to avoid slow clients connections issues.
echo "net.core.somaxconn = 1024" >> /etc/sysctl.confRedis background save may fail under low memory condition. To avoid this, enable memory overcommit (man 5 proc).
echo 'vm.overcommit_memory = 1' >> /etc/sysctl.confReload sysctl variables created above.
sysctl -pTo avoid creation of latencies and memory usage issues with Redis, disable Linux Kernel’s support for Transparent Huge Pages (THP). To easily work around this, create a systemd service unit for this purpose.
cat > /etc/systemd/system/disable_thp.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Disable Kernel Support for Transparent Huge Pages (THP)
[Service]
Type=simple
ExecStart=/bin/sh -c "echo 'never' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled && echo 'never' > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOLReload systemd configurations;
systemctl daemon-reloadStart and enable this service to run on system boot.
systemctl enable --now disable_thpRestart OpenVAS Redis server
systemctl enable --now redis-server@openvasA number of Network Vulnerability Tests (NVTs) require root privileges to perform certain operations. Since openvas is launched from an ospd-openvas process, via sudo, add the line below to sudoers file to ensure that the gvm user used in this demo can run the openvas with elevated rights using passwordless sudo.
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/openvas" > /etc/sudoers.d/gvmAlso, update the secure_path to include the GVM /sbin paths, /opt/gvm/sbin.
visudoDefaults secure_path="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/snap/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin"Also, enable gvm user to run GSA web application daemon, gsad, with passwordless sudo.
echo "gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad" >> /etc/sudoers.d/gvmUpdate NVTs
Update Network Vulnerability Tests feed from Greenbone Security Feed/Community Feed using the greenbone-nvt-sync command.
The greenbone-nvt-sync command must not be executed as privileged user root, hence switch back to GVM user we created above and update the NVTs.
su - gvmNext, update the NVTs as openvas user;
greenbone-nvt-syncOnce the update is done, you need to update Redis server with the same VT info from VT files;
sudo openvas --update-vt-infoBuild and Install Greenbone Vulnerability Manager
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/gvm/lib/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATHcd gvm-source/gvmd
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make
make installBuild and Install Greenbone Security Assistant
cd ../../gsa
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/opt/gvm
make
make installGenerate GVM Certificates
Next, run the command below to generate certificates gvmd. Server certificates are used for authentication while client certificates are primarily used for authorization. More on man gvm-manage-certs.
gvm-manage-certs -aKeeping the feeds up-to-date
The gvmd Data, SCAP and CERT Feeds should be kept up-to-date by calling the greenbone-feed-sync script regularly (e.g. via a cron entry):
sudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type GVMD_DATAsudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type SCAPsudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type CERTPlease note: The CERT feed sync depends on data provided by the SCAP feed and should be called after syncing the later.
Also, in case the commands fail with such an error;
rsync: read error: Connection reset by peer (104)
rsync error: error in socket IO (code 10) at io.c(794) [receiver=3.1.3]
rsync: connection unexpectedly closed (1047 bytes received so far) [generator]
rsync error: error in rsync protocol data stream (code 12) at io.c(235) [generator=3.1.3]Try adding --rsync option to the command, for example;
sudo -Hiu gvm greenbone-feed-sync --type CERT --rsyncBuild and Install OSPd and OSPd-OpenVAS
Open Scanner Protocol (OSP) creates a unified interface for different security scanners and makes their control flow and scan results consistently available under the central Greenbone Vulnerability Manager service.
As much as you can build them from the source, it has been made such that you can install using Python package manager, pip as shown below;
su - gvmpip3 install wheelpip3 install python-gvm gvm-toolsBuild and install OSPd and OSPd-openvas:
cd /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd
python3 -m pip install .cd /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd-openvas
python3 -m pip install .Running OpenVAS Scanner, GSA and GVM services
In order to make the management of OpenVAS scanner, GSA (WebUI service) and GVM daemon, create systemd service unit files for each of them as follows.
Log out as gvm user and execute the commands below as a privileged user.
exitCreating Systemd Service units for GVM services
Create OpenVAS systemd service
cat > /etc/systemd/system/openvas.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Control the OpenVAS service
After=redis.service
After=postgresql.service
[Service]
ExecStartPre=-rm -rf /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd-openvas.pid /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock /opt/gvm/var/run/gvmd.sock
Type=simple
User=gvm
Group=gvm
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 /opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas \
--pid-file /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd-openvas.pid \
--log-file /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log \
--lock-file-dir /opt/gvm/var/run -u /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Reload systemd service unit configurations.
systemctl daemon-reloadsystemctl start openvasCheck the status of the service;
systemctl status openvas● openvas.service - Control the OpenVAS service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/openvas.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Thu 2021-02-11 04:22:34 EST; 12s ago
Process: 2785 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -rf /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd-openvas.pid /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock /opt/gvm/var/run/gvmd.sock (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 2786 ExecStart=/usr/bin/python3 /opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas --pid-file /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd-openvas.pid --log-file /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log --
Main PID: 2786 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 2359)
Memory: 61.4M
CGroup: /system.slice/openvas.service
├─2788 /usr/bin/python3 /opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas --pid-file /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd-openvas.pid --log-file /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log --lock-fil
├─2790 /usr/bin/python3 /opt/gvm/.local/bin/ospd-openvas --pid-file /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd-openvas.pid --log-file /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm/ospd-openvas.log --lock-fil
├─2798 openvas --update-vt-info
└─2799 openvas --update-vt-info
Feb 11 04:22:34 debian systemd[1]: Starting Control the OpenVAS service...
Feb 11 04:22:34 debian systemd[1]: Started Control the OpenVAS service.
Enable OpenVAS scanner to run on system boot;
systemctl enable openvasCreate GSA systemd service Unit file
cat > /etc/systemd/system/gsa.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Control the OpenVAS GSA service
After=openvas.service
[Service]
Type=simple
User=gvm
Group=gvm
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
cat > /etc/systemd/system/gsa.path << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Start the OpenVAS GSA service when gvmd.sock is available
[Path]
PathChanged=/opt/gvm/var/run/gvmd.sock
Unit=gsa.service
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Create GVM Systemd Service unit file
cat > /etc/systemd/system/gvm.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Control the OpenVAS GVM service
After=openvas.service
[Service]
Type=simple
User=gvm
Group=gvm
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/opt/gvm/sbin/gvmd --osp-vt-update=/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
cat > /etc/systemd/system/gvm.path << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Start the OpenVAS GVM service when opsd.sock is available
[Path]
PathChanged=/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock
Unit=gvm.service
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Reload system unit configs and start the services;
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable --now gvm.{path,service}
systemctl enable --now gsa.{path,service}Checking the status;
systemctl status gvm.{path,service}● gvm.path - Start the OpenVAS GVM service when opsd.sock is available
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gvm.path; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (waiting) since Thu 2021-02-11 04:24:50 EST; 31s ago
Feb 11 04:24:50 debian systemd[1]: Started Start the OpenVAS GVM service when opsd.sock is available.
● gvm.service - Control the OpenVAS GVM service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gvm.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Thu 2021-02-11 04:24:50 EST; 31s ago
Main PID: 2885 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 8 (limit: 2359)
Memory: 336.5M
CGroup: /system.slice/gvm.service
├─2886 gvmd: Waiting for incoming connections
├─2938 gpg-agent --homedir /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg --use-standard-socket --daemon
├─2947 gvmd: Reloading NVTs
├─2948 gvmd: Syncing SCAP: Updating CPEs
├─2949 gvmd: OSP: Updating NVT cache
├─2950 gvmd: Syncing CERT
├─2957 sh -c xml_split -s40Mb split.xml && head -n 2 split-00.xml > head.xml && echo '</cpe-list>' > tail.xml && for F in split-*.xml; do awk 'NR>3 {print las
└─2958 /usr/bin/perl -w /usr/bin/xml_split -s40Mb split.xml
Feb 11 04:24:50 debian systemd[1]: Started Control the OpenVAS GVM service
systemctl status gsa.{path,service}● gsa.path - Start the OpenVAS GSA service when gvmd.sock is available
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gsa.path; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2021-02-11 04:24:51 EST; 55s ago
Feb 11 04:24:51 debian systemd[1]: Started Start the OpenVAS GSA service when gvmd.sock is available.
● gsa.service - Control the OpenVAS GSA service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/gsa.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (exited) since Thu 2021-02-11 04:24:51 EST; 55s ago
Process: 2907 ExecStart=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 2907 (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 2359)
Memory: 3.9M
CGroup: /system.slice/gsa.service
├─2909 /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad
└─2910 /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad
Feb 11 04:24:51 debian systemd[1]: Started Control the OpenVAS GSA service.
Feb 11 04:24:52 debian sudo[2907]: gvm : TTY=unknown ; PWD=/ ; USER=root ; COMMAND=/opt/gvm/sbin/gsad
Feb 11 04:24:52 debian sudo[2907]: pam_unix(sudo:session): session opened for user root by (uid=0)
Feb 11 04:24:52 debian sudo[2907]: Oops, secure memory pool already initialized
Feb 11 04:24:52 debian sudo[2907]: pam_unix(sudo:session): session closed for user root
Various Log files are located under the /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm directory.
ls /opt/gvm/var/log/gvmgsad.log gvmd.log openvas.log ospd-openvas.logCreate GVM Scanner
Since we launched the scanner and set it to use our non-standard scanner host path (/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock), we need to create and register our scanner;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --create-scanner="Kifarunix-demo OpenVAS Scanner" --scanner-type="OpenVAS" --scanner-host=/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sockNext, you need to verify your scanner. For this, you first need to get the scanner identifier;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --get-scanners08b69003-5fc2-4037-a479-93b440211c73 OpenVAS /var/run/ospd/ospd.sock 0 OpenVAS Default
6acd0832-df90-11e4-b9d5-28d24461215b CVE 0 CVE
50afbf2b-d854-4b6d-879f-c62aa62254d2 OpenVAS /opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock 9390 Kifarunix-demo OpenVAS ScannerBased on the output above, our scanner UUID is, 50afbf2b-d854-4b6d-879f-c62aa62254d2.
Verify the scanner;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --verify-scanner=50afbf2b-d854-4b6d-879f-c62aa62254d2Command output;
Scanner version: OpenVAS 20.8.2.Create OpenVAS (GVM) Admin User
Create OpenVAS administrative user by running the command below;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --create-user adminThis command generates a random password for the user. See sample output below;
User created with password 'fee42e66-117c-42f8-9b48-429e51194a13'.If you want to create a user and at the same time create your own password;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --create-user gvmadmin --password=StronGP@SSOtherwise, you can reset the password of an already existing user;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --user=<USERNAME> --new-password=<PASSWORD>An administrator user can later create further users or administrators via clients like the Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA).
If you want to reset the GVM admin password, simply run the command below;
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --user=admin --new-password=<new-password>Replace the <new-password> with your password.
Set the Feed Import Owner
According to gvmd/INSTALL.md, certain resources that were previously part of the gvmd source code are now shipped via the feed. An example is the config “Full and Fast”.
gvmd will only create these resources if a “Feed Import Owner” is configured:
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --modify-setting 78eceaec-3385-11ea-b237-28d24461215b --value <uuid_of_user>The UUIDs of all created users can be found using
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --get-users --verboseSample output;
admin 9a9e5070-d2f0-4802-971e-c9d61e682c21Then modify the gvmd settings with the user UUID.
sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd --modify-setting 78eceaec-3385-11ea-b237-28d24461215b --value 9a9e5070-d2f0-4802-971e-c9d61e682c21Accessing GVM 20.08 (OpenVAS)
Greenbone Security Assistant (GSA) WebUI daemon opens port 443 and listens on all interfaces. If firewall is running, open this port to allow external access.
ufw allow 443/tcpYou can now access GSA via the url https:<serverIP-OR-hostname>. Accept the self-signed SSL warning and proceed.
Login with the administrative credentials generated above.
Port lists
And there you go. That is all it take to install and Setup GVM. You can now start running your scans.
In case you see The SCAP database is required, upon accessing the NVTs, CVEs, then the SCAP database might still being rebuild. Check the gvmd.log file;
tail -f /opt/gvm/var/log/gvm/gvmd.logmd manage:MESSAGE:2021-02-12 06h17.42 utc:11210: No SCAP database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-02-12 06h17.46 utc:11210: Setting GnuPG dir to '/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg'
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-02-12 06h17.46 utc:11210: Using OpenPGP engine version '2.2.12'
md manage:WARNING:2021-02-12 06h17.47 utc:11237: update_scap: No SCAP db present, rebuilding SCAP db from scratch
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h17.53 utc:11237: update_scap: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h17.53 utc:11237: Updating CPEs
...The error will disappear once the SCAP database rebuild completes and such logs appear on gvmd.log file;
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h48.36 utc:13337: Updating CVSS scores for OVAL definitions
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h48.45 utc:13337: Updating placeholder CPEs
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h54.31 utc:13337: Updating Max CVSS for DFN-CERT
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h54.57 utc:13337: Updating DFN-CERT CVSS max succeeded.
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 06h54.57 utc:13337: Updating Max CVSS for CERT-Bund
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 07h05.02 utc:13337: Updating CERT-Bund CVSS max succeeded.
md manage: INFO:2021-02-12 07h05.14 utc:13337: update_scap_end: Updating SCAP info succeededNOTE: When creating a scan task, be sure to select the Scanner we created above.
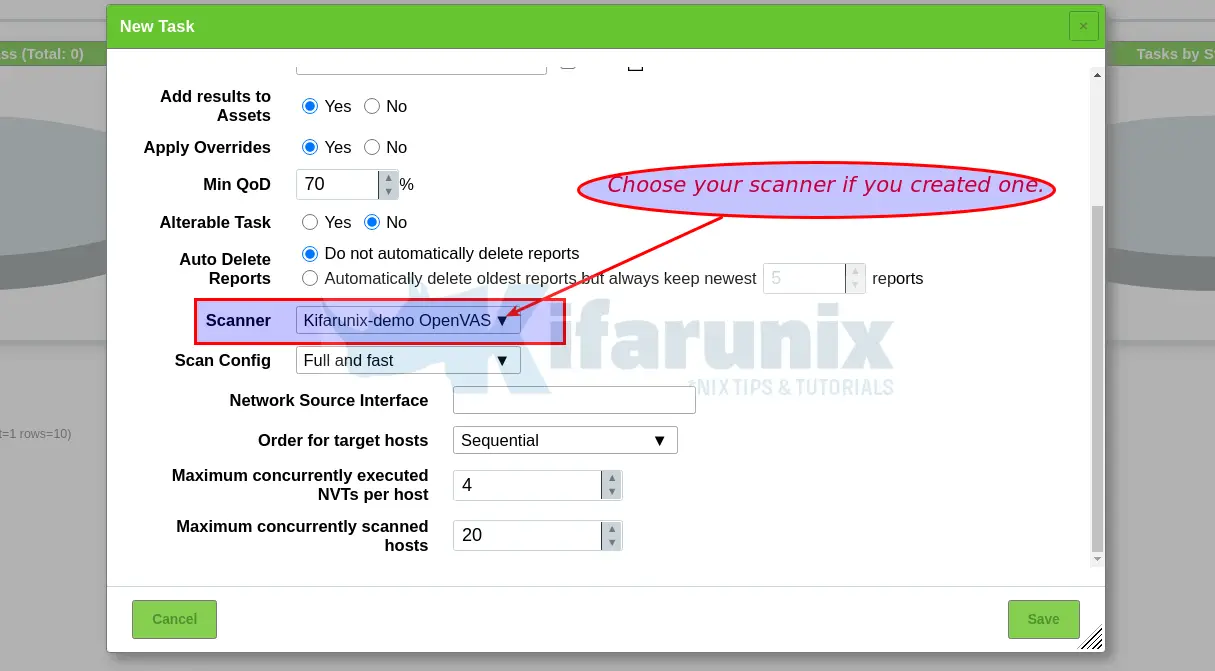
You can now create your target hosts to scan and schedule the scans to run at your own preferred time.
Did I miss anything, drop it in the comments section!! Enjoy
Reference
Source files README.md and INSTALL.md files
Related Tutorials
Install OpenVAS 10 (GVM) on Debian 10 Buster
Install OpenVAS 9 with PostgreSQL in Ubuntu 18.04
How to Add and Scan a Target for Vulnerabilities on OpenVAS Scanner
How to Install and Setup OpenVAS 9 Vulnerability Scanner on Ubuntu 18.04
How to Install and Use WPScan WordPress Vulnerability Scanner Ubuntu 18.04


Followed your guide however when i attempt to login i get “An error occurred during making the request. Most likely the web server does not respond.”
Any help would be appreciated
Hi Philip, is GSA service running?
This manual doesn’t work. Many problems with the permissions under Linux for root and normal user and problems with the compile of the packages
Hi,
What kind of errors you get?
Compilierung-Problems at SMB and the Scanner
make[2]: *** [winexe/CMakeFiles/winexe.dir/build.make:140: winexe/winexe] Fehler 1
make[1]: *** [CMakeFiles/Makefile2:151: winexe/CMakeFiles/winexe.dir/all] Fehler 2
make: *** [Makefile:152: all] Fehler 2
Were you able to solve this problem?
Got a problem with custom scanner. Scan still at 0% for long.
Any solution ?
Worked great on a Raspberry Pi 4 with 8GB of RAM, running stock Raspberry Pi OS (32 bit)!
I needed to go to stock OS as AnyDesk is needed in this particular use case, which works neither on Kali 64bit nor 32bit.
I needed two more prerequites in addition to what you wrote:
apt install graphviz # fix warnings about dot missing
apt install libunistring-dev # fix linker error
Thanks for the great write-up!
thanks for the feedback. dependencies updated
If openvas-smb fails in “make” phase, you will need to:
apt install libunistring-dev
Hello,
thanks for the tuto but GSA doesn’t work when i run systemctl enable –now gsa.{path,service}
it tell me there are a problem with pam_unix(sudo:auth): auth could not identify password for [gvm …
Thank’s for any help.
Hi,
Sounds like you didnt allow gvm user to run openvas and gsad with passwordless sudo.
This two command had been done:
echo “gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/openvas” > /etc/sudoers.d/gvm
echo “gvm ALL = NOPASSWD: /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad” >> /etc/sudoers.d/gvm
Then it is an issue with your pam auth module
Do you have any “bad” characters in your password?
Like space, exclamation mark et cetera…
Hey koromicha. Thanks a lot for your work and writeup! top
unfortunately I got a problem starting at the NVT part:
sudo openvas –update-vt-info
The error message is
“openvas: error while loading shared libraries: libopenvas_nasl.so.20: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory”
the library is in the lib folder. I don’t get it.
As a side effect gvm and gsa daemon don’t start either.
scanadm@vulscan:~$ ls -lh lib/
insgesamt 9,5M
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 17 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_base.so -> libgvm_base.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 49 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_base.so.20 -> libgvm_base.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 223K Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_base.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 19 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_boreas.so -> libgvm_boreas.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 51 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_boreas.so.20 -> libgvm_boreas.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 137K Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_boreas.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 16 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_gmp.so -> libgvm_gmp.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 48 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_gmp.so.20 -> libgvm_gmp.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 65K Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_gmp.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 16 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_osp.so -> libgvm_osp.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 48 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_osp.so.20 -> libgvm_osp.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 60K Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_osp.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 22 Apr 7 18:09 libgvm-pg-server.so -> libgvm-pg-server.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 52 Apr 7 18:09 libgvm-pg-server.so.20 -> libgvm-pg-server.so.20.08.1~git-7a247dbeb-gvmd-20.08
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 97K Apr 7 18:09 libgvm-pg-server.so.20.08.1~git-7a247dbeb-gvmd-20.08
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 17 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_util.so -> libgvm_util.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 49 Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_util.so.20 -> libgvm_util.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 308K Apr 7 17:14 libgvm_util.so.20.8.2~git-aa3bba16-gvm-libs-20.08
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 21 Apr 7 17:20 libopenvas_misc.so -> libopenvas_misc.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 25 Apr 7 17:20 libopenvas_misc.so.20 -> libopenvas_misc.so.20.8.2
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 196K Apr 7 17:19 libopenvas_misc.so.20.8.2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 21 Apr 7 17:20 libopenvas_nasl.so -> libopenvas_nasl.so.20
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 25 Apr 7 17:20 libopenvas_nasl.so.20 -> libopenvas_nasl.so.20.8.2
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 1,1M Apr 7 17:19 libopenvas_nasl.so.20.8.2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 23 Apr 7 17:17 libopenvas_wincmd.so -> libopenvas_wincmd.so.21
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 46 Apr 7 17:17 libopenvas_wincmd.so.21 -> libopenvas_wincmd.so.21.4.0~git-1756788-master
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 2,8M Apr 7 17:17 libopenvas_wincmd.so.21.4.0~git-1756788-master
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 26 Apr 7 17:17 libopenvas_wmiclient.so -> libopenvas_wmiclient.so.21
lrwxrwxrwx 1 scanadm scanadm 49 Apr 7 17:17 libopenvas_wmiclient.so.21 -> libopenvas_wmiclient.so.21.4.0~git-1756788-master
-rw-r–r– 1 scanadm scanadm 4,6M Apr 7 17:17 libopenvas_wmiclient.so.21.4.0~git-1756788-master
drwxr-xr-x 2 scanadm scanadm 4,0K Apr 7 17:17 pkgconfig
drwxr-xr-x 3 scanadm scanadm 4,0K Apr 7 18:09 systemd
Hi, thanks for the feedback.
Any chance you didnt run the
ldconfigcommand?Thanks for your reply. Appreciate it.
ldconfig sounds logic, that’s right.
I’m sure I’ve done this but I think my session crashed a bit afterwards.
Don’t know if that may be a problem or what else could have caused this.
Is there any chance to “repair” that without starting all over again?
Hi. Not sure if you have found a solution. But I would suggest you start rebuild (sounds like a waste of time, -:)), one step at a time paying attention to the output of each build command.
Hello, thanks a lot for the tutorial.
Install seems to be good but when I try to run à scan I get de error “Interrupted at 0%”
Any idea ?
I’m going to try to understand the problem cheking the log.
Hello again, my log file tells that:
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.26 UTC:26461: Status of task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has changed to Requested
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.26 UTC:26461: Task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has been requested to start by admin
md manage:WARNING:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: Could not connect to Scanner at /var/run/ospd/ospd.sock
md manage:WARNING:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: OSP start_scan 66557342-fb81-4243-82e6-eeb459c062db: Could not connect to Scanner
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: Status of task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has changed to Done
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: Status of task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has changed to Interrupted
Hello thanks a lot for the tutorial.
The install went fine. But when I try to run a scan I get de error “Interrupted at 0 %”
This is what I have in my log file:
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.26 UTC:26461: Status of task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has changed to Requested
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.26 UTC:26461: Task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has been requested to start by admin
md manage:WARNING:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: Could not connect to Scanner at /var/run/ospd/ospd.sock
md manage:WARNING:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: OSP start_scan 66557342-fb81-4243-82e6-eeb459c062db: Could not connect to Scanner
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: Status of task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has changed to Done
event task:MESSAGE:2021-04-15 22h24.32 UTC:26464: Status of task SCAN (1fbebb31-0072-4395-833c-c561d451cca2) has changed to Interrupted
Hi Poncho. I had the same problem. Is something related with python and the instalation of the ospd and ospd-scanner. More info about what is happening to us is recopilated here:
https://community.greenbone.net/t/openvas-scanner-interrupted-at-0/9386
@koromicha I want to express my gratitud to your work by documenting this strugle procedure. Would you be so kind to help us here?
I have tested with GVM 21.04 and 20.08. I am thinking on going for the easy way and install Kali Linux and run just ‘apt install gvm’ v20.8.0
Cheers and hope some solution.
Hi Franco92,
Thanks for the feedback.
We are relooking into this and will update soon
Hello!
Thanks for such a detailed tutorial, all worked well following your instructions, the only issue is that when I try to setup a scan it fails with the following error:
Failed to find config ‘daba56c8-73ec-11df-a475-002264764cea’
I’ve tried all the options listed in the GVM community site, but no lock, any pointers on how to solve this?
Hi Alex, sounds like NVTs sync issue
Thanks for this guide I’ve been running this successfully for nearly a year.
In the last couple of weeks GVM has been reporting a critical vulnerability as the GVM libraries are now end-of-life “Report outdated / end-of-life Scan Engine / Environment (local)” stating “Latest available GVM Libraries (gvm-libs) version: 20.8.1”.
How do I update the libraries?
Hi,
Thank you for detailed instruction! It is very helpful.
THere is one correction (perhaps it showed up recently) – you have to build ospd ospd-openvas from source of branch 20.08 It conflicts with ospd ospd-openvas in master.
go to /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd and run under gvm user
python3 -m pip install .
Same for /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd-openvas
Otherwise ospd-openvas process crashes after few seconds of running with an error. There was actually a discussion here:
https://community.greenbone.net/t/ospd-error/7861
Thanks for feedback Alex. We will make the updates
Hey koromicha first of all thanks for the awesome writeup, im having an issue with the sql database, here i attach my logs, the problem is the scap database stays allways in updating and i start seeing sql error messeges in the logs as you can see below and then gvmd crashes, i would appreciate your help 🙂
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h07.40 utc:1569: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h07.41 utc:1571: sql_exec_internal: PQexec failed: ERROR: relation “public.meta” does not exist
LINE 1: SELECT value FROM public.meta WHERE name = ‘database_version…
^
(7)
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h07.41 utc:1571: sql_exec_internal: SQL: SELECT value FROM public.meta WHERE name = ‘database_version’;
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h07.41 utc:1571: sql_x: sql_exec_internal failed
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h07.41 utc:1571: No SCAP database found
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h07.41 utc:1571: No CERT database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h07.52 utc:1571: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h07.52 utc:1571: Created GnuPG dir ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h07.53 utc:1571: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
util gpgme: INFO:2021-06-12 06h07.53 utc:1571: starting key generation …
util gpgme: INFO:2021-06-12 06h07.53 utc:1571: OpenPGP key ‘GVM Credential Encryption’ has been generated
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h08.33 utc:1640: update_scap: No SCAP db present, rebuilding SCAP db from scratch
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.33 utc:1642: Initializing CERT database
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.35 utc:1642: sync_cert: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.35 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.35 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.36 utc:1640: update_scap: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.36 utc:1640: Updating CPEs
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.38 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2017.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.38 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2017.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.41 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.41 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.43 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.43 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.45 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.45 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.48 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.48 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.48 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2011.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.48 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2011.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.50 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.50 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.53 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2010.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.53 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2010.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.54 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.54 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.56 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h08.56 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.00 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.00 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.02 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.02 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.02 utc:1642: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.02 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.04 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K14.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.05 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K19.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.07 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K17.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.10 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K13.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.11 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K18.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.12 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K21.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.13 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K16.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.16 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K15.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.18 utc:1642: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K20.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h09.20 utc:1642: sync_cert: Updating CERT info succeeded.
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h13.52 utc:802: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h13.54 utc:811: No SCAP database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h13.55 utc:811: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h13.55 utc:811: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h15.04 utc:861: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h15.04 utc:861: Creating scanner.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h15.05 utc:861: No SCAP database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h15.05 utc:861: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h15.05 utc:861: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h15.15 utc:884: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h15.15 utc:884: Getting scanners.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h15.16 utc:884: No SCAP database found
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h16.04 utc:901: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h16.04 utc:901: Verifying scanner.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h16.05 utc:901: No SCAP database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h16.05 utc:901: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h16.05 utc:901: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h16.26 utc:926: update_scap: No SCAP db present, rebuilding SCAP db from scratch
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h16.28 utc:926: update_scap: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h16.28 utc:926: Updating CPEs
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h16.36 utc:939: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h16.36 utc:939: Creating user.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h16.37 utc:939: No SCAP database found
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.00 utc:949: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h17.00 utc:949: Getting users.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.01 utc:949: No SCAP database found
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.35 utc:983: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h17.35 utc:983: Modifying setting.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.36 utc:983: No SCAP database found
event port_list:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Port list All TCP and Nmap top 100 UDP (730ef368-57e2-11e1-a90f-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event port_list:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Port list All IANA assigned TCP (33d0cd82-57c6-11e1-8ed1-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event port_list:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Port list All IANA assigned TCP and UDP (4a4717fe-57d2-11e1-9a26-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Report format PDF (c402cc3e-b531-11e1-9163-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Report format CSV Results (c1645568-627a-11e3-a660-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Report format Anonymous XML (5057e5cc-b825-11e4-9d0e-28d24461215b) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.37 utc:987: Report format TXT (a3810a62-1f62-11e1-9219-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.38 utc:987: Report format XML (a994b278-1f62-11e1-96ac-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h17.38 utc:987: Report format ITG (77bd6c4a-1f62-11e1-abf0-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h18.50 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h19.08 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2017.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h19.36 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h19.51 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2002.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h20.01 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h20.47 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2006.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h20.59 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2005.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h21.08 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h21.31 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h21.51 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h22.47 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h23.03 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-06-12 06h23.20 utc:926: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2007.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-06-12 06h36.59 utc:950: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.1~git-e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision e35a75a25-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h37.00 utc:957: sql_open: PQconnectPoll failed
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h37.00 utc:957: sql_open: PQerrorMessage (conn): FATAL: the database system is starting up
md manage:WARNING:2021-06-12 06h37.00 utc:957: init_manage_process: sql_open failed
I already finished this step by step (https://kifarunix.com/install-and-setup-gvm-20-08-on-debian/) and it has multiple errors related with ospd.sock and permissions with the reading of some files. Beside…the redis configuration service has the wrong path. The ospd and ospd-scanner are not compiled in this case. Multiple errors with python, possible that the tuto mix differents branchs of gvm sources.
I want to express my gratitud for the athors of this tutorial. In my case, it wasnt helpfull. I open a topic in the official forum explainin waht happened to me. I am installing GVM 21.04.
https://community.greenbone.net/t/openvas-scanner-interrupted-at-0/9386/12
I also put there the link to my procedure.
OS base: Debian Buster 10.9
Cheers
Hi, seems the issue is installation with pip3 fetched a more recent version of ospd/ospd-openvas. Hence, the scanner couldnt be started:
Try to install ospd/ospd-openvas as:
cd /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospdpython3 -m pip install .
cd /opt/gvm/gvm-source/ospd-openvas
python3 -m pip install .
Please, to the authors of this topic, would you check this link?
https://community.greenbone.net/t/openvas-scanner-interrupted-at-0/9386/12
Thanks for such greate tuto…I hope to fix my installation
Koromicha:
Thank you so much for the detailed guide – this is a truly sophisticated and complicated setup. Even though I have built multiple OpenVAS scanners from earlier versions, I would never have been able to figure out all the details with running as gvm user, ospd startup, etc…
Regards;
jeff
We are glad the tutorial was helpful Jeff!
Thanks for the feedback! Enjoy
done nicely on a debian 10.9 with the 21.04 version : GREAT JOB !!!
Just 2 points : had to install libnet1-dev and to install yarn from their repos (curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add ;
echo “deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main” | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list ; apt update ;apt install yarn ;).
One question for the moment how do i set the default scanner to the one we created (via sudo -Hiu gvm gvmd –create-scanner=”Kifarunix-demo OpenVAS Scanner” –scanner-type=”OpenVAS” –scanner-host=/opt/gvm/var/run/ospd.sock ) ?
Hi
I have now built this 3 times, taking extreme care to build it correctly following the instructions,
but it always fails with
md main:WARNING:2021-07-01 08h33.39 utc:28344: update_nvt_cache_retry: rebuild failed
this happens everytime, the scans run but no results
how can i solve this problem “The Greenbone Vulnerability Manager service is not responding. This could be due to system maintenance. Please try again later, check the system status, or contact your system administrator.”
Hello Malol, is gmvd running? What do the logs say?
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h41.30 utc:26988: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h41.30 utc:26989: sql_exec_internal: PQexec failed: ERROR: relation “public.meta” does not exist
LINHA 1: SELECT value FROM public.meta WHERE name = ‘database_version…
^
(7)
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h41.30 utc:26989: sql_exec_internal: SQL: SELECT value FROM public.meta WHERE name = ‘database_version’;
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h41.30 utc:26989: sql_x: sql_exec_internal failed
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h41.30 utc:26989: No SCAP database found
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h41.30 utc:26989: No CERT database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:26989: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:26989: Created GnuPG dir ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:26989: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
util gpgme: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:26989: starting key generation …
util gpgme: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:26989: OpenPGP key ‘GVM Credential Encryption’ has been generated
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:27020: Initializing CERT database
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:27019: update_scap: No SCAP db present, rebuilding SCAP db from scratch
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 utc:27023: OSP service has different VT status (version 202107151255) from database (version (null), 0 VTs). Starting update …
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 UTC:27020: sync_cert: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.31 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.32 utc:27019: update_scap: Updating data from feed
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.32 utc:27019: Updating CPEs
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.35 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.35 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.48 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h41.48 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.03 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.03 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.19 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.19 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.29 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.29 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.29 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2010.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.29 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2010.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h42.35 utc:27075: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.35 utc:27075: Creating scanner.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h42.35 utc:27075: No SCAP database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h42.35 utc:27075: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h42.35 utc:27075: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.36 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2017.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.36 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2017.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h42.45 utc:27098: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.45 utc:27098: Getting scanners.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h42.45 utc:27098: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.51 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h42.51 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.00 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.00 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2013.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.11 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.11 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.21 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.21 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.33 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2011.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.33 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2011.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.44 UTC:27020: update_dfn_xml: dfn-cert-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h43.44 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/dfn-cert-2020.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.05 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K20.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.16 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K19.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h44.17 utc:27125: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.17 utc:27125: Verifying scanner.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h44.17 utc:27125: No SCAP database found
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h44.17 utc:27125: Setting GnuPG dir to ‘/opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/gvmd/gnupg’
util gpgme:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h44.17 utc:27125: Using OpenPGP engine version ‘2.2.12’
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.25 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K14.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.34 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K13.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.37 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K16.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.50 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K18.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h44.58 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K21.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h45.02 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K17.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h45.18 UTC:27020: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/cert-data/CB-K15.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h45.27 UTC:27020: sync_cert: Updating CERT info succeeded.
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h49.49 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2009.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h50.34 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2014.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h51.02 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2008.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h51.37 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2005.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h51.57 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2018.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h53.58 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2017.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h54.29 utc:27313: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h54.29 utc:27313: Creating user.
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.29 utc:27313: sql_open: PQconnectPoll failed
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.29 utc:27313: sql_open: PQerrorMessage (conn): FATAL: role “root” does not exist
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.29 utc:27313: init_manage_process: sql_open failed
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h54.37 utc:27318: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h54.37 utc:27318: Creating user.
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.37 utc:27318: sql_open: PQconnectPoll failed
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.37 utc:27318: sql_open: PQerrorMessage (conn): FATAL: role “root” does not exist
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.37 utc:27318: init_manage_process: sql_open failed
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h54.45 utc:27322: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h54.45 utc:27322: Modifying user password.
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.45 utc:27322: sql_open: PQconnectPoll failed
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.45 utc:27322: sql_open: PQerrorMessage (conn): FATAL: role “root” does not exist
md manage:WARNING:2021-07-15 18h54.45 utc:27322: init_manage_process: sql_open failed
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h55.04 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2002.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h55.35 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2021.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h56.15 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2013.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h56.24 utc:27353: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h56.24 utc:27353: Getting users.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h56.25 utc:27353: No SCAP database found
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h56.38 utc:27361: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h56.38 utc:27361: Getting users.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h56.38 utc:27361: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h56.50 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2010.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h57.19 utc:27375: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h57.19 utc:27375: Getting users.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h57.19 utc:27375: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h57.24 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2003.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h57.30 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2020.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h58.31 utc:27412: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h58.31 utc:27412: Creating user.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h58.32 utc:27412: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h59.18 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2007.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 18h59.33 utc:27432: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h59.33 utc:27432: Creating user.
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 18h59.47 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2019.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h01.59 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2004.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h02.12 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2012.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h02.39 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2006.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h03.02 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2016.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h03.31 utc:27023: Updating VTs in database … 74973 new VTs, 0 changed VTs
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h03.32 utc:27432: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h03.39 utc:27023: Updating VTs in database … done (74973 VTs).
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h03.51 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2015.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.05 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/nvdcve-2.0-2011.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.20 UTC:27019: Updating OVAL data
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.25 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/c/oval.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.25 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/m/oval.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.25 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/v/family/ios.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.25 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/v/family/pixos.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.25 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/p/oval.xml
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h04.36 utc:27473: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h04.36 utc:27473: Getting users.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h04.36 utc:27473: No SCAP database found
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h05.52 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/i/oval.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h05.55 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/v/family/macos.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h05.55 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/v/family/unix.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h06.01 UTC:27019: Updating /opt/gvm/var/lib/gvm/scap-data/oval/5.10/org.mitre.oval/v/family/windows.xml
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h06.12 UTC:27019: Updating user OVAL definitions.
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h06.12 UTC:27019: Updating CVSS scores and CVE counts for CPEs
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h07.15 utc:27516: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h07.15 utc:27516: Modifying setting.
md main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.23 utc:27536: Greenbone Vulnerability Manager version 20.08.3~git-5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08 (GIT revision 5b83b66a7-gvmd-20.08) (DB revision 233)
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h08.23 utc:27536: Modifying setting.
md manage:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.23 utc:27536: No SCAP database found
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.28 UTC:27540: Scan config Discovery (8715c877-47a0-438d-98a3-27c7a6ab2196) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.31 UTC:27540: Scan config GaussDB Kernel V500R001C00 Security Hardening Guide (2eec8313-fee4-442a-b3c4-fa0d5dc83d61) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.31 UTC:27540: Scan config Huawei Datacom Product Security Configuration Audit Guide (aab5c4a1-eab1-4f4e-acac-8c36d08de6bc) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.31 UTC:27540: Scan config empty (085569ce-73ed-11df-83c3-002264764cea) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.31 UTC:27540: Scan config System Discovery (bbca7412-a950-11e3-9109-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.34 UTC:27540: Scan config IT-Grundschutz Kompendium (c4b7c0cb-6502-4809-b034-8e635311b3e6) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.37 UTC:27540: Scan config EulerOS Linux Security Configuration (9f822ad3-9208-4e02-ac03-78dce3ca9a23) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.37 UTC:27540: Scan config Base (d21f6c81-2b88-4ac1-b7b4-a2a9f2ad4663) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.39 UTC:27540: Scan config openGauss Security Hardening Guide (c2b049f9-6d3d-45be-871f-2252895ed9e8) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.42 UTC:27540: Scan config GaussDB 100 V300R001C00 Security Hardening Guide (Standalone) (61327f09-8a54-4854-9e1c-16798285fb28) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.42 UTC:27540: Scan config Host Discovery (2d3f051c-55ba-11e3-bf43-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event config:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.43 UTC:27540: Scan config Full and fast (daba56c8-73ec-11df-a475-002264764cea) has been created by admin
event port_list:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.44 UTC:27540: Port list All IANA assigned TCP (33d0cd82-57c6-11e1-8ed1-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event port_list:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.44 UTC:27540: Port list All TCP and Nmap top 100 UDP (730ef368-57e2-11e1-a90f-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event port_list:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Port list All IANA assigned TCP and UDP (4a4717fe-57d2-11e1-9a26-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Report format Anonymous XML (5057e5cc-b825-11e4-9d0e-28d24461215b) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Report format ITG (77bd6c4a-1f62-11e1-abf0-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Report format TXT (a3810a62-1f62-11e1-9219-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Report format CSV Results (c1645568-627a-11e3-a660-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Report format PDF (c402cc3e-b531-11e1-9163-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
event report_format:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 19h08.45 UTC:27540: Report format XML (a994b278-1f62-11e1-96ac-406186ea4fc5) has been created by admin
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h09.28 UTC:27019: Updating CVSS scores for OVAL definitions
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h09.31 UTC:27019: Updating placeholder CPEs
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h10.16 UTC:27019: Updating Max CVSS for DFN-CERT
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h10.21 UTC:27019: Updating DFN-CERT CVSS max succeeded.
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h10.21 UTC:27019: Updating Max CVSS for CERT-Bund
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h10.23 UTC:27019: Updating CERT-Bund CVSS max succeeded.
md manage: INFO:2021-07-15 19h10.33 UTC:27019: update_scap_end: Updating SCAP info succeeded
gsad main:MESSAGE:2021-07-15 22h55.32 utc:985: Starting GSAD version 20.8.1
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.07 utc:986: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.07 utc:986: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.07 utc:986: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.07 utc:986: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.08 utc:986: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.08 utc:986: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad gmp:WARNING:2021-07-15 22h56.32 utc:986: Failed to connect to server at /run/gvm/gvmd.sock: No such file or directory
Hi everyone, especial thanks to Koromicha, i cannot log in the web interface:
“The Greenbone Vulnerability Manager service is not responding. This could be due to system maintenance. Please try again later, check the system status, or contact your system administrator.”
Watching gsad.log:
gsad main:MESSAGE:2021-07-20 11h26.44 utc:22190: Starting GSAD version 20.8.1
gsad main:WARNING:2021-07-20 11h33.20 utc:22191: MHD: Error: received handshake message out of context
gsad gmp:WARNING:2021-07-20 11h33.26 utc:22191: Failed to connect to server at /run/gvm/gvmd.sock: No such file or directory
gsad gmp:WARNING:2021-07-20 11h33.26 utc:22191: Authentication failure for ‘administrador’ from 192.168.15.38. Status was 1.
and gsa status is active anda waiting, not running, any ideas?
Thanks in advance
Note the “munix-socket”:
sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/gsa.service
—
[Unit]
Description=Control the OpenVAS GSA service
After=openvas.service
[Service]
Type=simple
User=gvm
Group=gvm
Environment=PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/opt/gvm/bin:/opt/gvm/sbin:/opt/gvm/.local/bin
ExecStart=/usr/bin/sudo /opt/gvm/sbin/gsad –munix-socket=/opt/gvm/var/run/gvmd.sock
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
In version 20.8.4 they changed location of r/run/gvm /etc/openvas /var/lib/openvas and some other directories.
Should one use specifically 20.8.2 version in this manual?