I want to run a single node Kubernetes cluster on my local machine. But how? Well, this step-by-step guide will take you through all the steps required to install Minikube on Debian 12 so that you can start to learn and experiment Kubernetes on your local development system.
Table of Contents
Installing Minikube on Debian 12
So, what are the steps to install Minikube?
Prerequisites
Before you can use Minikube, there are a number of requirements that you need to consider;
Kubernetes Concepts;
What are the core concepts in Kubernetes?
System Resources
Ensure your system has;
- At least 2 CPUs
- At least 2GB of free RAM
- At least 20GB of free Disk space
Minikube Drivers
Drivers are components that Minikube uses to interact with various virtualization technologies used to run Kubernetes cluster. They can be a container or virtual machine manager, such as: Docker, QEMU, Hyperkit, Hyper-V, KVM, Parallels, Podman, VirtualBox, or VMware Fusion/Workstation.
You can check how to install Docker, VirtualBox or KVM on Debian 12 by following the links below;
How to Install Docker CE on Debian 12
Install VirtualBox 7 on Debian 12
We will be using Docker in this guide to run Minikube.
Internet Access
Ensure the system has Internet connection. This is required to download various Minikube components.
Install Kubectl
Install Kuberenetes command line tool, kubectl;
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlVerify the kubectl version;
kubectl version --client --output=yaml
clientVersion:
buildDate: "2023-06-14T09:53:42Z"
compiler: gc
gitCommit: 25b4e43193bcda6c7328a6d147b1fb73a33f1598
gitTreeState: clean
gitVersion: v1.27.3
goVersion: go1.20.5
major: "1"
minor: "27"
platform: linux/amd64
kustomizeVersion: v5.0.1
Installing Minikube on Debian 12
Installing Minikube on Debian is as easy as executing the commands below;
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube_latest_amd64.debsudo apt install ./minikube_latest_amd64.debOnce the installation is done, you should be able to proceed with using Minikube.
Let’s check the version;
minikube versionSample output;
minikube version: v1.30.1
commit: 08896fd1dc362c097c925146c4a0d0dac715ace0Starting Minikube
We are running the next commands with a non root user;
su - kifarunixAdd your user to Docker group;
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERLog out and login as user again
Ensure you are part of the Docker group;
iduid=1000(kifarunix) gid=1000(kifarunix) groups=1000(kifarunix),100(users),992(docker),995(vboxsf)Minikube Help Page
Run the command below to check Minikube help information;
minikube --help
minikube provisions and manages local Kubernetes clusters optimized for development workflows.
Basic Commands:
start Starts a local Kubernetes cluster
status Gets the status of a local Kubernetes cluster
stop Stops a running local Kubernetes cluster
delete Deletes a local Kubernetes cluster
dashboard Access the Kubernetes dashboard running within the minikube cluster
pause pause Kubernetes
unpause unpause Kubernetes
Images Commands:
docker-env Provides instructions to point your terminal's docker-cli to the Docker Engine inside minikube.
(Useful for building docker images directly inside minikube)
podman-env Configure environment to use minikube's Podman service
cache Manage cache for images
image Manage images
Configuration and Management Commands:
addons Enable or disable a minikube addon
config Modify persistent configuration values
profile Get or list the current profiles (clusters)
update-context Update kubeconfig in case of an IP or port change
Networking and Connectivity Commands:
service Returns a URL to connect to a service
tunnel Connect to LoadBalancer services
Advanced Commands:
mount Mounts the specified directory into minikube
ssh Log into the minikube environment (for debugging)
kubectl Run a kubectl binary matching the cluster version
node Add, remove, or list additional nodes
cp Copy the specified file into minikube
Troubleshooting Commands:
ssh-key Retrieve the ssh identity key path of the specified node
ssh-host Retrieve the ssh host key of the specified node
ip Retrieves the IP address of the specified node
logs Returns logs to debug a local Kubernetes cluster
update-check Print current and latest version number
version Print the version of minikube
options Show a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
Other Commands:
completion Generate command completion for a shell
license Outputs the licenses of dependencies to a directory
Use "minikube --help" for more information about a given command.
Start Local Kubernetes cluster
You can show start Minikube local kubernetes cluster by running;
minikube start --driver=dockerSo what does this command do?
- It starts control plane node minikube in cluster.
- Pulls the base image required to create Kubernetes cluster
- Next, it downloads preconfigured set of Kubernetes binaries to bootstrap the cluster.
- Setup Kubernetes on Docker
- Configures container networking interface
- Enable some Minikube add-ons such as for storage.
See sample output;
😄 minikube v1.30.1 on Debian 12.0
✨ Using the docker driver based on user configuration
📌 Using Docker driver with root privileges
👍 Starting control plane node minikube in cluster minikube
🚜 Pulling base image ...
💾 Downloading Kubernetes v1.26.3 preload ...
> preloaded-images-k8s-v18-v1...: 397.02 MiB / 397.02 MiB 100.00% 1.25 Mi
> gcr.io/k8s-minikube/kicbase...: 373.53 MiB / 373.53 MiB 100.00% 1.04 Mi
🔥 Creating docker container (CPUs=2, Memory=2200MB) ...
🐳 Preparing Kubernetes v1.26.3 on Docker 23.0.2 ...
▪ Generating certificates and keys ...
▪ Booting up control plane ...
▪ Configuring RBAC rules ...
🔗 Configuring bridge CNI (Container Networking Interface) ...
▪ Using image gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner:v5
🔎 Verifying Kubernetes components...
🌟 Enabled addons: storage-provisioner, default-storageclass
🏄 Done! kubectl is now configured to use "minikube" cluster and "default" namespace by default
Check Minikube Status
You can check Minikube status using the command below;
minikube status
minikube
type: Control Plane
host: Running
kubelet: Running
apiserver: Running
kubeconfig: Configured
Administering Kubernetes on Minikube
You should now be able to administer Kubernetes on Minikube.
Minikube SSH Login
You can SSH into minikube using the command below;
minikube sshYou land into the the minikube docker shell.
Run docker commands inside;
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
0d92ee88b84f 6e38f40d628d "/storage-provisioner" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes k8s_storage-provisioner_storage-provisioner_kube-system_6afa8ea3-36d7-41ad-938f-843f25aa6d4a_1
be75fdc607c6 5185b96f0bec "/coredns -conf /etc…" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes k8s_coredns_coredns-787d4945fb-49k2m_kube-system_e37b1967-be5d-4554-a46f-05a2997de74e_0
fe9b2a99b6ec registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes k8s_POD_coredns-787d4945fb-49k2m_kube-system_e37b1967-be5d-4554-a46f-05a2997de74e_0
9a9a928c9cf7 92ed2bec97a6 "/usr/local/bin/kube…" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes k8s_kube-proxy_kube-proxy-q8thm_kube-system_9f6fae56-0458-49d6-8ba5-82ec9c2189b1_0
7dc47e863ff0 registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes k8s_POD_kube-proxy-q8thm_kube-system_9f6fae56-0458-49d6-8ba5-82ec9c2189b1_0
c1fcaf7f7d56 registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 4 minutes ago Up 4 minutes k8s_POD_storage-provisioner_kube-system_6afa8ea3-36d7-41ad-938f-843f25aa6d4a_0
04d74488c2bf 1d9b3cbae03c "kube-apiserver --ad…" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_kube-apiserver_kube-apiserver-minikube_kube-system_cdcbce216c62c4407ac9a51ac013e7d7_0
c6561bab22ad ce8c2293ef09 "kube-controller-man…" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_kube-controller-manager_kube-controller-manager-minikube_kube-system_466b9e73e627277a8c24637c2fa6442d_0
37040d7add6b 5a7904736932 "kube-scheduler --au…" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_kube-scheduler_kube-scheduler-minikube_kube-system_0818f4b1a57de9c3f9c82667e7fcc870_0
698ab8856b5e fce326961ae2 "etcd --advertise-cl…" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_etcd_etcd-minikube_kube-system_a121e106627e5c6efa9ba48006cc43bf_0
38cb851be00c registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_POD_kube-scheduler-minikube_kube-system_0818f4b1a57de9c3f9c82667e7fcc870_0
80d9696d3a3f registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_POD_kube-controller-manager-minikube_kube-system_466b9e73e627277a8c24637c2fa6442d_0
9fb63368a575 registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_POD_kube-apiserver-minikube_kube-system_cdcbce216c62c4407ac9a51ac013e7d7_0
cea349f8a641 registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9 "/pause" 5 minutes ago Up 5 minutes k8s_POD_etcd-minikube_kube-system_a121e106627e5c6efa9ba48006cc43bf_0
Check docker images;
docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
registry.k8s.io/kube-apiserver v1.26.3 1d9b3cbae03c 3 months ago 134MB
registry.k8s.io/kube-controller-manager v1.26.3 ce8c2293ef09 3 months ago 123MB
registry.k8s.io/kube-scheduler v1.26.3 5a7904736932 3 months ago 56.4MB
registry.k8s.io/kube-proxy v1.26.3 92ed2bec97a6 3 months ago 65.6MB
registry.k8s.io/etcd 3.5.6-0 fce326961ae2 6 months ago 299MB
registry.k8s.io/pause 3.9 e6f181688397 8 months ago 744kB
registry.k8s.io/coredns/coredns v1.9.3 5185b96f0bec 12 months ago 48.8MB
gcr.io/k8s-minikube/storage-provisioner v5 6e38f40d628d 2 years ago 31.5MB
docker system df
TYPE TOTAL ACTIVE SIZE RECLAIMABLE
Images 8 8 751.9MB 3.967MB (0%)
Containers 15 14 162B 0B (0%)
Local Volumes 0 0 0B 0B
Build Cache 0 0 0B 0B
Get Kubernetes Cluster Resource Information
Let’s run a few Kubernetes commands;
- Get Kubernetes cluster information;
kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://192.168.49.2:8443
CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.49.2:8443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
- Lists all the nodes in the current namespace.
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
minikube Ready control-plane 7h52m v1.26.3
List all services in the current namespace;
kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 7h53m
You can basically manage your Kubernetes cluster just as would on any prod environment.
Deploy Simple Kubernets Application
Let’s create a simple Nginx manifest file to define the desired state;
vim nginx-deployment.yamlPaste the following content;
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Deploy Nginx;
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yamlList deployments;
kubectl get deployments
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
nginx-deployment 0/2 2 0 13s
Check the pods. You should see two of them due to replica of 2;
kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-6b7f675859-ljsh8 1/1 Running 0 7s
nginx-deployment-6b7f675859-qvnpn 1/1 Running 0 7s
Next, you need to expose this service for external access;
vim nginx-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 30000 # Choose an available port number
Ensure no other service is being exposed via port 31500/tcp defined above.
Apply the service;
kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yamlCheck the services to find out an external port to access it;
kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 60m
nginx-service NodePort 10.107.130.31 80:30000/TCP 3s
get more details;
kubectl describe service nginx-service
Name: nginx-service
Namespace: default
Labels:
Annotations:
Selector: app=nginx
Type: NodePort
IP Family Policy: SingleStack
IP Families: IPv4
IP: 10.107.130.31
IPs: 10.107.130.31
Port: http 80/TCP
TargetPort: 80/TCP
NodePort: http 30000/TCP
Endpoints: 10.244.0.8:80,10.244.0.9:80
Session Affinity: None
External Traffic Policy: Cluster
Events:
Accessing the Service. You can print the url or open service on the default browser;
minikube service nginx-serviceSample browser;
and command line output;
|-----------|---------------|-------------|---------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|---------------|-------------|---------------------------|
| default | nginx-service | http/80 | http://192.168.49.2:30000 |
|-----------|---------------|-------------|---------------------------|
🎉 Opening service default/nginx-service in default browser...
Unfortunately, our service is exposed via docker bridge interface IP and hence, makes it hard to access externally.
You can do port forwarding of Nginx target port to some other unused ports as follows;
kubectl port-forward service/nginx-service --address=0.0.0.0 8080:80Sample output;
Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:8080 -> 80
Handling connection for 8080
Handling connection for 8080Press CTRL+C to cancel.
You should now be able to access your App outside Minikube cluster, http://<server-IP>:8080.
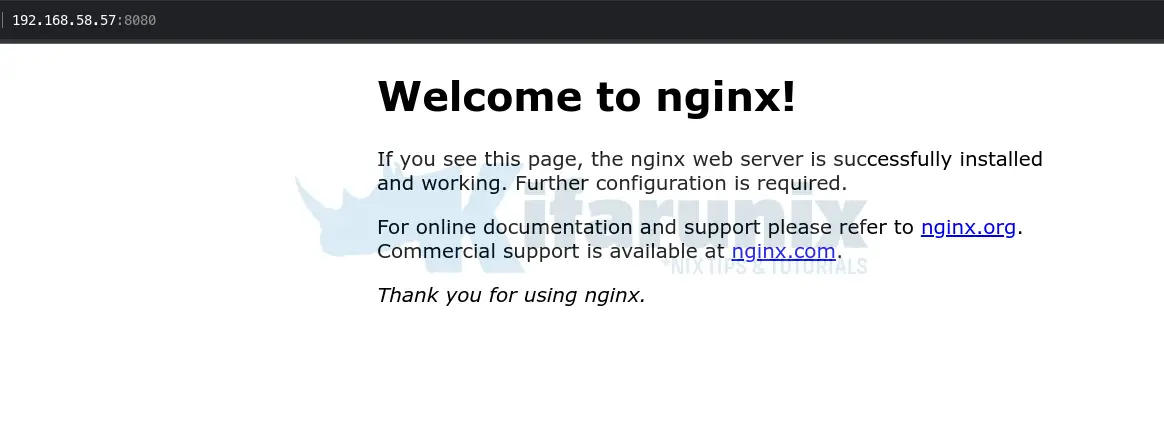
You can now proceed to explore Kubernetes!
Enable Minikube Addons
Addons are components that can be used to extend the functionality of Minikube;
There is quite a number of addons;
minikube addons list
|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|
| ADDON NAME | PROFILE | STATUS | MAINTAINER |
|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|
| ambassador | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Ambassador) |
| auto-pause | minikube | disabled | Google |
| cloud-spanner | minikube | disabled | Google |
| csi-hostpath-driver | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes |
| dashboard | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes |
| default-storageclass | minikube | enabled ✅ | Kubernetes |
| efk | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Elastic) |
| freshpod | minikube | disabled | Google |
| gcp-auth | minikube | disabled | Google |
| gvisor | minikube | disabled | Google |
| headlamp | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (kinvolk.io) |
| helm-tiller | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Helm) |
| inaccel | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (InAccel |
| | | | [[email protected]]) |
| ingress | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes |
| ingress-dns | minikube | disabled | Google |
| istio | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Istio) |
| istio-provisioner | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Istio) |
| kong | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Kong HQ) |
| kubevirt | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (KubeVirt) |
| logviewer | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (unknown) |
| metallb | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (MetalLB) |
| metrics-server | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes |
| nvidia-driver-installer | minikube | disabled | Google |
| nvidia-gpu-device-plugin | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Nvidia) |
| olm | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Operator Framework) |
| pod-security-policy | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (unknown) |
| portainer | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Portainer.io) |
| registry | minikube | disabled | Google |
| registry-aliases | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (unknown) |
| registry-creds | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (UPMC Enterprises) |
| storage-provisioner | minikube | enabled ✅ | Google |
| storage-provisioner-gluster | minikube | disabled | 3rd party (Gluster) |
| volumesnapshots | minikube | disabled | Kubernetes |
|-----------------------------|----------|--------------|--------------------------------|
You can enable an addon using the command;
minikube addons enable <name>For example, enable Minikube dashboard;
minikube addons enable dashboard
💡 dashboard is an addon maintained by Kubernetes. For any concerns contact minikube on GitHub.
You can view the list of minikube maintainers at: https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/blob/master/OWNERS
▪ Using image docker.io/kubernetesui/dashboard:v2.7.0
▪ Using image docker.io/kubernetesui/metrics-scraper:v1.0.8
💡 Some dashboard features require the metrics-server addon. To enable all features please run:
minikube addons enable metrics-server
🌟 The 'dashboard' addon is enabled
Also enable Metrics server;
minikube addons enable metrics-serverYou can check the services for these addons on the kube-system namespace;
kubectl get services --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 18m
default nginx-service NodePort 10.104.193.40 80:30000/TCP 6m15s
kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.96.0.10 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 18m
kube-system metrics-server ClusterIP 10.106.159.6 443/TCP 6m46s
kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.96.233.122 8000/TCP 7m21s
kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.106.205.225 80/TCP 7m21s
To access the dashboard externally;
kubectl port-forward service/kubernetes-dashboard -n kubernetes-dashboard --address=0.0.0.0 8888:80You dashboard is now availanle on http://minikube-server-IP:8888;
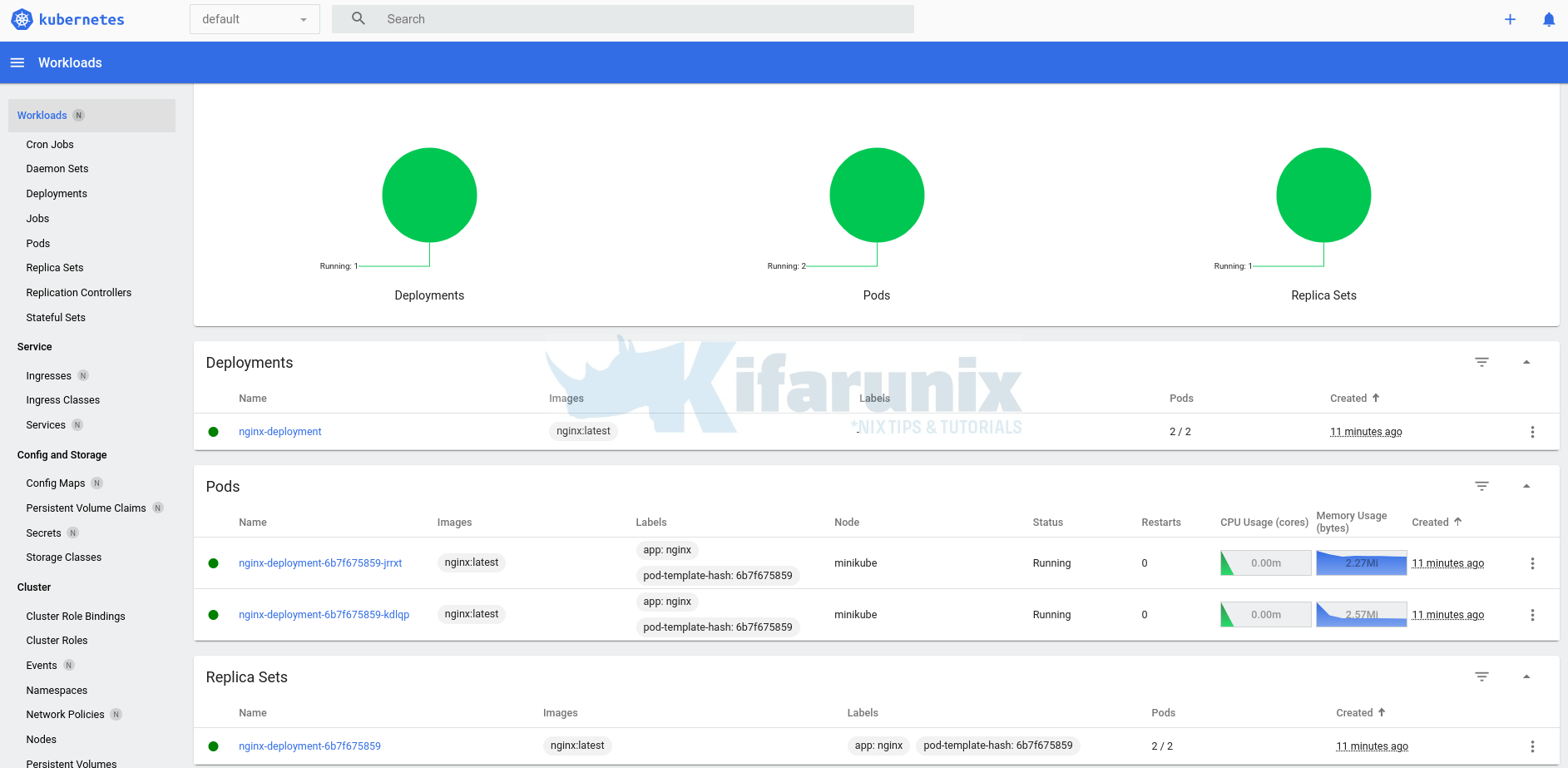
Explore the dashboard further.
Stop and Delete Minikube Profile
You can always stop and delete Minikube profile;
minikube profile listSample output;
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| Profile | VM Driver | Runtime | IP | Port | Version | Status | Nodes | Active |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
| minikube | docker | docker | 192.168.49.2 | 8443 | v1.26.3 | Running | 1 | * |
|----------|-----------|---------|--------------|------|---------|---------|-------|--------|
Or get current profile;
minikube profileStop Minikube;
minikube stopDelete current profile;
minikube deleteor specific profile;
minikube delete --profile <profile name>See example;
minikube delete --profile minikube
🔥 Deleting "minikube" in docker ...
🔥 Deleting container "minikube" ...
🔥 Removing /home/kifarunix/.minikube/machines/minikube ...
💀 Removed all traces of the "minikube" cluster.
And that concludes our guide on how to install Minikube on Debian 12.
Other Tutorials;

