In this tutorial, you will learn how to easily install PowerDNS Admin on Debian 11/Debian 10. PowerDNS Admin is a web administrative interface for PowerDNS. It enables you to easily create and manage DNS zones from a web browser.
PowerDNS Admin provides advanced features for managing PowerDNS. These include;
- Multiple domain management
- Domain template
- User management
- User access management based on domain
- User activity logging
- Support Local DB / SAML / LDAP / Active Directory user authentication
- Support Google / Github / Azure / OpenID OAuth
- Support Two-factor authentication (TOTP)
- Dashboard and pdns service statistics
- DynDNS 2 protocol support
- Edit IPv6 PTRs using IPv6 addresses directly (no more editing of literal addresses!)
- Limited API for manipulating zones and records
Installing PowerDNS Admin on Debian 11/Debian 10
Install and Setup PowerDNS on Debian 11/Debian 10
Follow the link below to install PowerDNS on Debian 11/Debain 10:
Easily Install and Setup PowerDNS on Debian 11/Debian 10
NOTE: We installed PowerDNS Admin on the same server with PowerDNS already installed.
Install Required Package Dependencies
Install Python 3 library and development tools
apt install python3-devInstall various required build tools and package dependencies.
apt install libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev libssl-dev libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libxmlsec1-dev libffi-dev pkg-config apt-transport-https virtualenv build-essential libmariadb-dev git python3-flask -yInstall NodeJS on Debian 10/Debian 11;
apt install curl sudo git -ycurl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_17.x | sudo -E bash -apt install -y nodejsInstall Yarn on Debian 11/Debian 10
curl -sL https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/yarnkey.gpg >/dev/nullecho "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/yarnkey.gpg] https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.listapt update
apt install yarn -yInstall Nginx HTTP Server Debian 10/Debian 11
apt install nginx -yClone PowerDNS Admin Source Code to Web Root Directory
Clone PowerDNS Admin git source code to your Nginx web root directory.
In this setup, we use, /var/www/html/pdns, as our PowerDNS Admin web root directory. It can be different for your case.
git clone https://github.com/ngoduykhanh/PowerDNS-Admin.git /var/www/html/pdnsCreate PowerDNS Admin Virtualenv
Navigate to the PowerDNS Admin web root directory and create a virtualenv.
cd /var/www/html/pdns/virtualenv -p python3 flaskNext, active your Python 3 Virtual environment and install required Python 3 libraries
source ./flask/bin/activatepip install -r requirements.txtConfigure PowerDNS Admin Database Connection
Exit the virtualenv.
deactivateEdit the default PowerDNS admin configuration file, $WEB_ROOT/powerdnsadmin/default_config.py, to define the database connection details.
Replace the $WEB_ROOT with the path to your web root directory.
vim /var/www/html/pdns/powerdnsadmin/default_config.pyOn the basic App configs, you can replace the SALT and SECRET_KEY keys, set the bind address and port;
### BASIC APP CONFIG
SALT = 'xohDoozee8Zuneekooch9ohrieghei'
SECRET_KEY = 'hohru1aethaeyahpheH7Gaathaikah'
BIND_ADDRESS = '192.168.58.22'
PORT = 9191
HSTS_ENABLED = False
OFFLINE_MODE = False
On the database configs, configure your PowerDNS database connection details. Note that we are using the details already created while setting up PowerDNS as defined in our guide.
### DATABASE CONFIG
SQLA_DB_USER = 'pdnsadmin'
SQLA_DB_PASSWORD = 'PdnSPassW0rd'
SQLA_DB_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SQLA_DB_NAME = 'kifarunixdemopdns'
SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS = True
Save and exit the configuration.
Next, reactivate the virtualenv run the DB migration;
cd /var/www/html/pdns/source ./flask/bin/activateexport FLASK_APP=powerdnsadmin/__init__.pyflask db upgradeOnce the command above completes, generate asset files with yarn;
yarn install --pure-lockfileflask assets buildDeactivate virtual environment.
deactivateRunning PowerDNS Admin
Once it is setup, you can run PowerDNS admin in standalone mode, by executing the run.py in the web root directory.
In this setup, we will be using Nginx web server to access the PowerDNS Admin.
Enable PowerDNS API access
“The PowerDNS Authoritative Server features a built-in webserver that exposes a JSON/REST API. This API allows for controlling several functions, reading statistics and modifying zone content, metadata and DNSSEC key material“.
- Open PowerDNS configuration file
- Enable API
- Generate and set the API Key;
vim /etc/powerdns/pdns.conf
#################################
# api Enable/disable the REST API (including HTTP listener)
#
# api=no
api=yes
#################################
# api-key Static pre-shared authentication key for access to the REST API
#
# api-key=
api-key=ahqu4eiv2vaideep8AQu9nav5Aing0
Save and exit the file and restart PowerDNS;
systemctl restart pdnsCreate PowerDNS Admin Nginx Site
Create PowerDNS Admin Nginx site with the contents below. Replace web root directory accordingly.
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/pdns-admin.conf
server {
listen *:80;
server_name pdnsadmin.kifarunix-demo.com;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /var/www/html/pdns;
access_log /var/log/nginx/pdnsadmin_access.log combined;
error_log /var/log/nginx/pdnsadmin_error.log;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffers 32 4k;
proxy_buffer_size 8k;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 64;
location ~ ^/static/ {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
root /var/www/html/pdns/powerdnsadmin;
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ {
expires 365d;
}
location ~* ^.+.(css|js)$ {
expires 7d;
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket;
proxy_read_timeout 120;
proxy_connect_timeout 120;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
Save and exit the file.
Remove the default Nginx default site.
mv /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default{,.old}Run config syntax check.
nginx -tnginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulSet ownership of Pdns Admin web root directory to web user;
chown -R www-data: /var/www/html/pdnsRestart Nginx;
systemctl restart nginxCreate PowerDNS Admin Systemd Service Unit
To be able to run PowerDNS Admin as a systemd service, create a unit file by running the command below;
cat > /etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=PowerDNS-Admin
Requires=pdnsadmin.socket
After=network.target
[Service]
PIDFile=/run/pdnsadmin/pid
User=pdns
Group=pdns
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/html/pdns
ExecStart=/var/www/html/pdns/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/pdnsadmin/pid --bind unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket 'powerdnsadmin:create_app()'
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
cat > /etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.socket << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=PowerDNS-Admin socket
[Socket]
ListenStream=/run/pdnsadmin/socket
[Install]
WantedBy=sockets.target
EOL
echo "d /run/pdnsadmin 0755 pdns pdns -" >> /etc/tmpfiles.d/pdnsadmin.confmkdir /run/pdnsadmin/chown -R pdns: /run/pdnsadmin/chown -R pdns: /var/www/html/pdns/powerdnsadmin/Reload System Configurations and start and enable PowerDNS Admin service to run on system boot;
systemctl enable --now pdnsadmin.service pdnsadmin.socketCheck the status;
systemctl status pdnsadmin.service pdnsadmin.socket
● pdnsadmin.service - PowerDNS-Admin
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2021-11-28 02:00:51 EST; 10s ago
Main PID: 13859 (gunicorn)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 2359)
Memory: 65.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/pdnsadmin.service
├─13859 /var/www/html/pdns/flask/bin/python3 /var/www/html/pdns/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/pdnsadmin/pid --bind unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket powerdnsadmin:creat
└─13862 /var/www/html/pdns/flask/bin/python3 /var/www/html/pdns/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/pdnsadmin/pid --bind unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket powerdnsadmin:creat
Nov 28 02:00:51 debian systemd[1]: Started PowerDNS-Admin.
Nov 28 02:00:51 debian gunicorn[13859]: [2021-11-28 02:00:51 -0500] [13859] [INFO] Starting gunicorn 20.0.4
Nov 28 02:00:51 debian gunicorn[13859]: [2021-11-28 02:00:51 -0500] [13859] [INFO] Listening at: unix:/run/pdnsadmin/socket (13859)
Nov 28 02:00:51 debian gunicorn[13859]: [2021-11-28 02:00:51 -0500] [13859] [INFO] Using worker: sync
Nov 28 02:00:51 debian gunicorn[13859]: [2021-11-28 02:00:51 -0500] [13862] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 13862
● pdnsadmin.socket - PowerDNS-Admin socket
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/pdnsadmin.socket; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2021-11-28 02:00:51 EST; 10s ago
Listen: /run/pdnsadmin/socket (Stream)
CGroup: /system.slice/pdnsadmin.socket
Nov 28 02:00:51 debian systemd[1]: Listening on PowerDNS-Admin socket.
Accessing PowerDNS Admin Web Interface
Open Nginx on firewall to allow external access;
ufw allow "Nginx Full"As per our configuration above, you can access PowerDNS Admin web interface via the address http://server-hostname. You should be able to see the PowerDNS Admin login screen. (if not, check status of the PowerDNS admin service or Nginx error logs for hints).
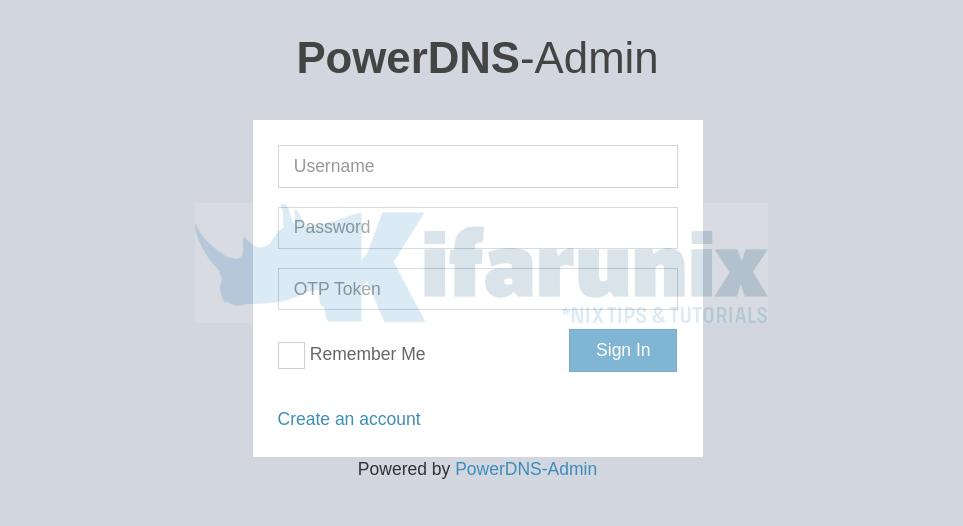
Create PowerDNS Admin administrative user account
Click Create an account to create the very first PowerDNS Admin admin user. Enter the user details.
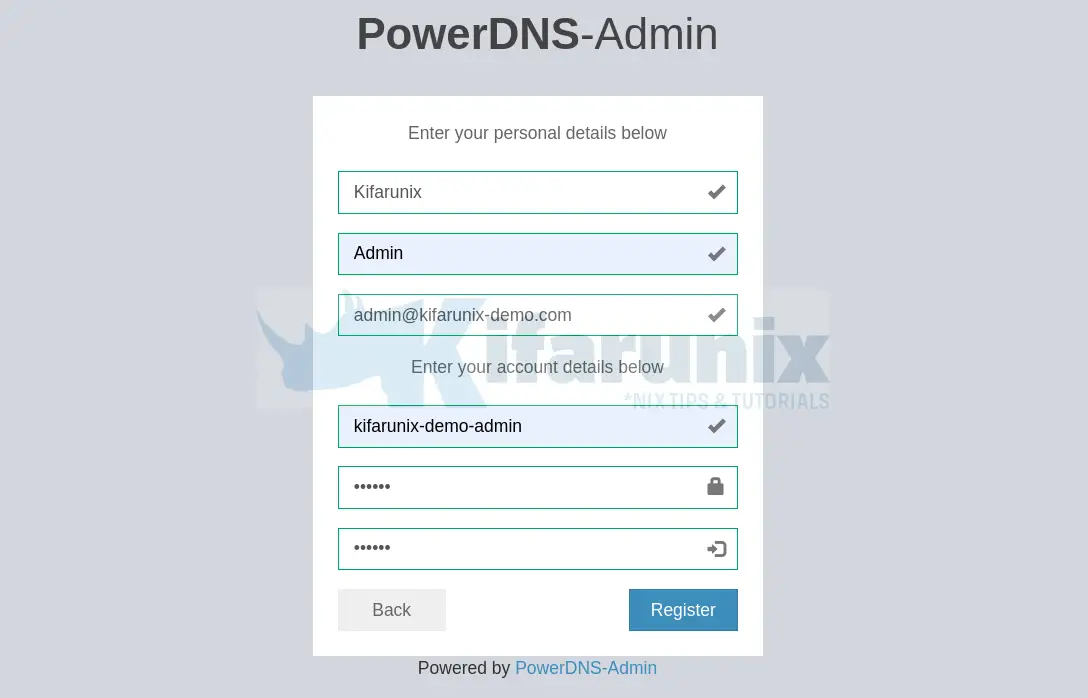
Click Register to create an account.
After that, login using the user details you provided. Upon successful login, you should land on PowerDNS Admin interface.
You will see an error asking you to complete the API setup.
For PowerDNS Admin to be able to connect to PowerDNS and manage it, you need to provide:
- the API Key URL, usually,
http://127.0.0.1:8081by default - the API Key you defined in the PowerDNS configuration file.
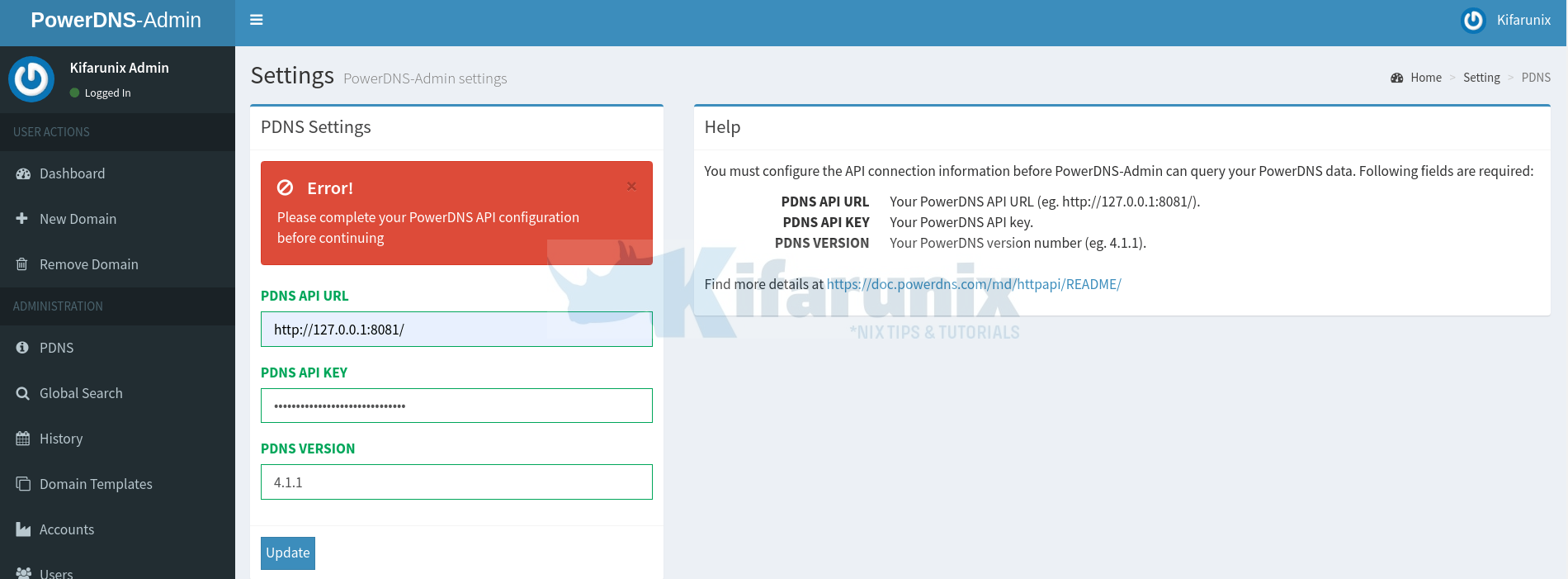
Click Update and the error should just disappear.
Click on the Dashboard to go to PowerDNS Admin dashboard.
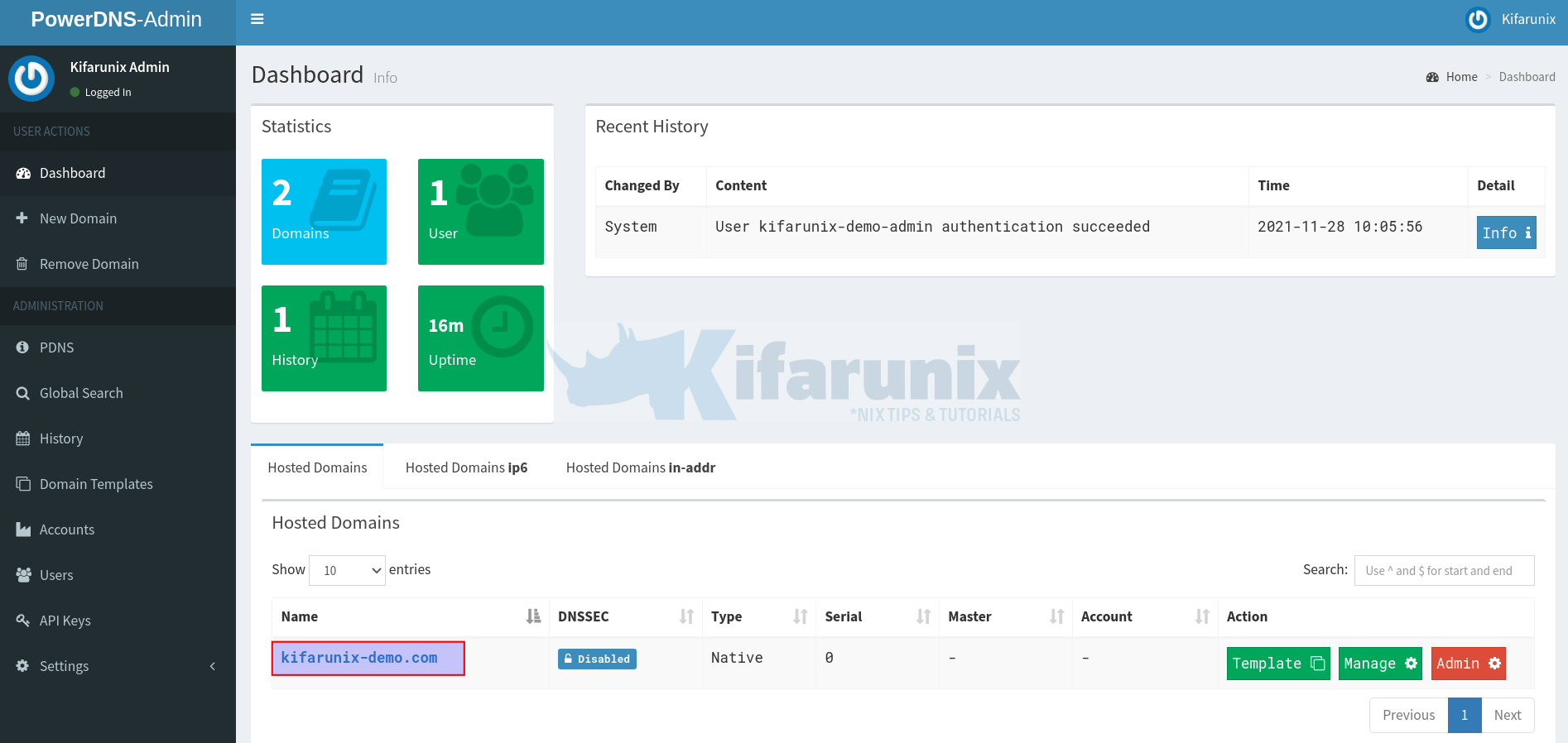
As you can see, we already added the DNS records in our previous guide.
If you click on the domain name under Hosted Domains (highlighted on the screenshot above), you should the records we already added;
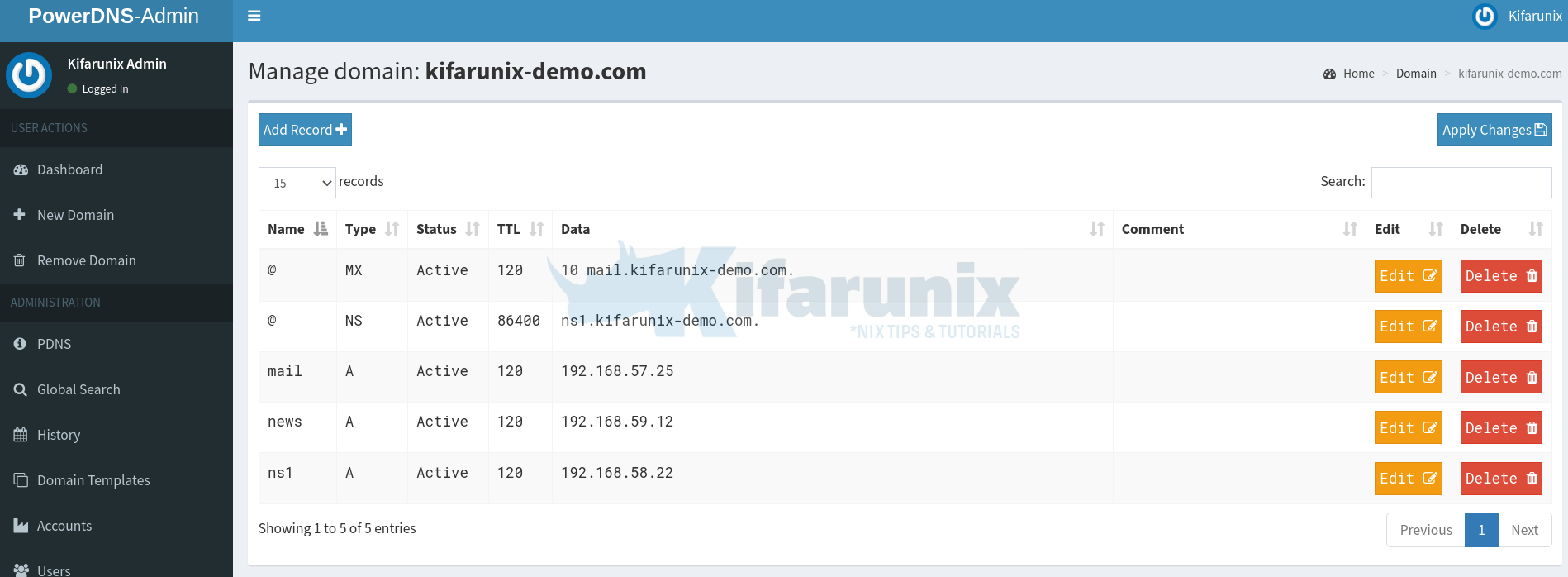
That is the forward zone records.
If you click on the reverse zone under the Dashboard > Hosted Domains in-addr, you should see the reverse zone records.
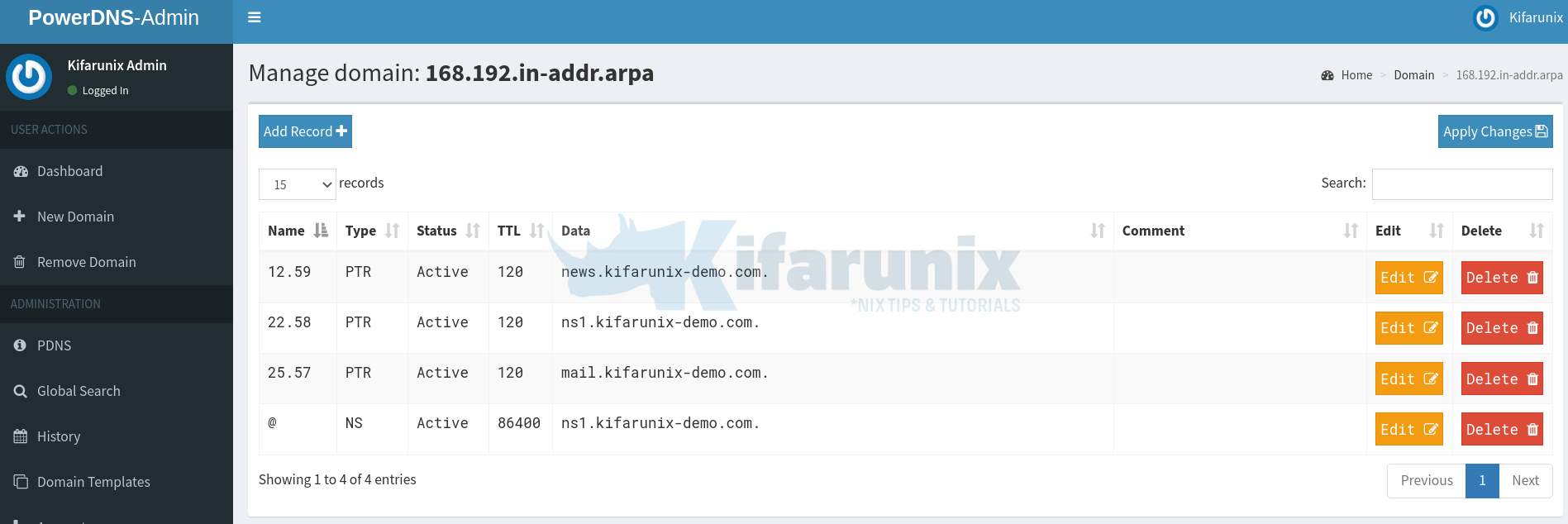
You can now manage your DNS records easily.
That concludes our tutorial.
Other tutorials
Easily Install and Setup PowerDNS Admin on Ubuntu 20.04

