
In this guide, we’ll explore what Red Hat Satellite is, its key features and how its architecture enables centralized control, automation, and scalability. Managing a large-scale Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) infrastructure can be a daunting task without the right tools. That’s where Red Hat Satellite comes in—a powerful system management solution designed to simplify IT operations for organizations running RHEL environments. Red Hat Satellite provides tools for provisioning, patching, configuration management, and subscription tracking, all while focusing on delivering centralized control and automation for large-scale RHEL deployments. It helps IT teams reduce complexity, improve efficiency, and maintain compliance with organizational policies.
Table of Contents
Understanding Red Hat Satellite Architecture and Key Features
What is Red Hat Satellite?
Red Hat Satellite is a comprehensive system management solution tailored specifically for organizations using Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL). It provides a centralized platform for managing provisioning, patching, configuration, and subscription management across large-scale RHEL deployments. By focusing on automation and centralized control, Satellite helps IT teams reduce complexity, improve efficiency, and maintain compliance with organizational policies.
Key functionalities of Red Hat Satellite include:
- Provisioning: Streamline the deployment of new systems with standardized configurations.
- Patching: Automate the deployment of security updates and patches to keep systems secure.
- Configuration Management: Ensure consistency across all managed hosts.
- Subscription Tracking: Monitor and manage Red Hat subscriptions to ensure compliance.
Why is Red Hat Satellite Important?
In today’s fast-paced IT landscape, efficient management of RHEL systems is critical for maintaining security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Here’s why Red Hat Satellite stands out:
- Centralized Management: With Red Hat Satellite, IT teams can manage thousands of RHEL systems from a single interface. This simplifies oversight and reduces the burden of juggling multiple tools or interfaces.
- Compliance and Security: Satellite ensures that systems are always up-to-date with the latest patches and security fixes. This not only enhances security but also helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and internal policies.
- Efficiency Through Automation: By automating repetitive tasks such as patching, provisioning, and configuration management, Satellite minimizes manual effort and reduces the risk of human error. Integration with automation tools like Ansible further enhances productivity.
- Scalability: Red Hat Satellite supports large and complex IT environments, making it an ideal choice for enterprises that need to manage extensive RHEL deployments efficiently.
Key Benefits of Red Hat Satellite for IT Teams
Some of the standout benefits of using Red Hat Satellite in your organization include:
- Patch Management: Automatically deploy security patches and updates across your entire fleet of RHEL systems, ensuring they remain secure and compliant.
- Provisioning: Streamline the process of deploying new systems with predefined configurations, saving time and reducing errors.
- Configuration Management: Enforce consistent configurations across all managed hosts, ensuring uniformity and reducing the risk of misconfigurations.
- Subscription Management: Track and manage Red Hat subscriptions to ensure compliance and avoid licensing issues.
- Reporting and Monitoring: Gain detailed insights into the health and compliance status of your systems through robust reporting and monitoring capabilities.
Red Hat Satellite Architecture Components
To understand how Red Hat Satellite works, let’s break down its architecture and key components.
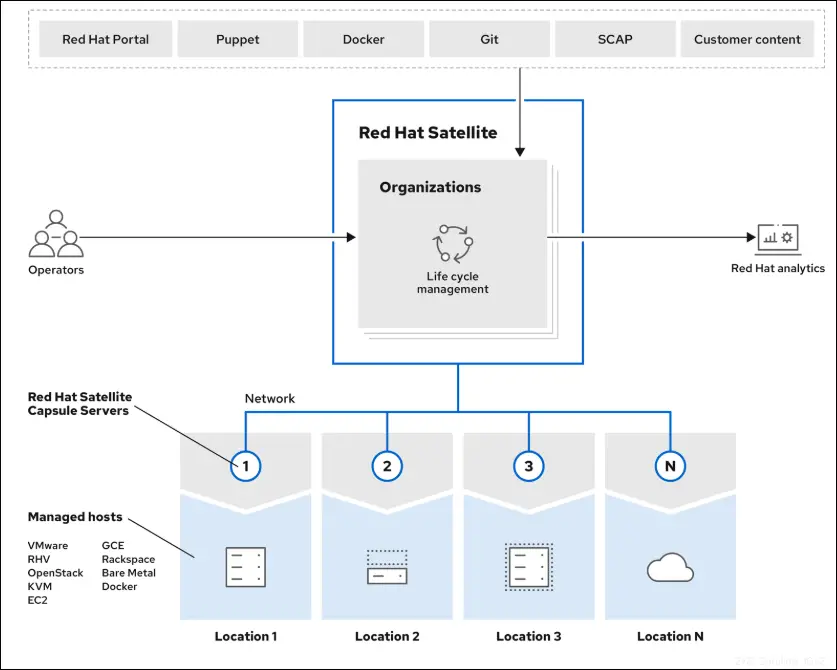
1. External Content Sources
External content sources are locations where Red Hat Satellite pulls software packages, errata, container images, and subscription management services from. These sources include:
- Primary Source : The Red Hat Customer Portal serves as the main source for official Red Hat content, including RPMs, security patches, container images, and subscription management services.
- Additional Sources : Organizations can also connect to custom repositories, such as Git repositories, Docker Hub, or private repositories for custom-built packages.
2. Satellite Server
The Satellite Server acts as the central hub of the architecture, managing the entire content lifecycle and serving as the primary point of administration. A typical Satellite deployment includes one Satellite Server and its responsibilities include:
- Content Lifecycle Management : Syncing content from external sources, organizing it into repositories, and distributing it to Capsule Servers or directly to managed hosts.
- Configuration of Capsule Servers: Setting up Capsule Servers for content distribution and proxying management services.
- Configuration of Hosts: Managing and configuring individual systems with templates and configuration settings.
- Host Provisioning: Automating the provisioning and installation of new systems.
- Patch Management: Applying patches and updates to systems in a controlled manner.
- Subscription Management: Managing Red Hat subscriptions, ensuring systems are properly registered and entitled.
- Multi-Org Support : Supporting multiple organizations, allowing isolation of lifecycle management for different groups of hosts (e.g., departments, teams, or environments).
3. Capsule Servers
Capsule Servers act as intermediaries between the Satellite Server and managed hosts. They mirror content locally to reduce latency and improve performance. Key functions of Capsule Servers include:
- Content Mirroring : Enabling hosts to pull content from a geographically closer location.
- Services Provided : Handling content distribution, host provisioning, and configuration management.
Satellite Server delegates content distribution, host provisioning, and communication to Capsule Servers. Satellite Server itself also includes a Capsule by default.
4. Managed Hosts
Managed hosts are the endpoints of the architecture—physical or virtual RHEL servers that receive content and configurations from the Satellite Server or Capsule Servers. These systems can be managed either directly by the Satellite Server or through remote Capsule Servers.
Key OpenSource Satellite Server Components
Red Hat Satellite integrates several open-source projects to deliver its functionality:
Foreman
A provisioning and lifecycle management tool that automates host configuration using kickstart scripts, Ansible Playbooks, and/or Puppet modules.
Katello
A Foreman plug-in focused on subscription and repository management. Katello organizes content into lifecycle stages, ensuring the right updates reach the right systems at the right time.
Candlepin
Handles subscription management, ensuring compliance with Red Hat licensing agreements.
Pulp
Manages repositories and content views, optimizing storage by avoiding duplicate RPM packages.
Hammer CLI & REST API
Provides command-line tools and programmatic access for automation enthusiasts who love scripting and integrating Satellite with custom workflows.
Conclusion
Red Hat Satellite is a game-changer for organizations managing large-scale RHEL deployments. By offering centralized control, automation, and scalability, it simplifies IT operations while enhancing security and compliance. Understanding its architecture and key features empowers IT teams to unlock its full potential and streamline their RHEL management processes.

