
This guide provides a foundational understanding of Kubernetes Kustomize. It will introduce you to Kustomize’s core concepts and the basics. With more organizations increasingly adopting the use of Kubernetes as the de facto standard for container orchestration, managing Kubernetes configurations across different environments such development, staging, production often requiring repetitive adjustments and configurations, can become cumbersome to manage. Kubernetes Kustomize addresses this challenge by offering a declarative approach to managing Kubernetes manifests. It simplifies the process of customizing configurations without the need for extensive templating or duplication of YAML files.
Table of Contents
Kubernetes Kustomize 101: Introduction and Basics
What is Kubernetes Kustomize?
Kubernetes Kustomize is a tool used to customize Kubernetes YAML configurations without the need to use templating engines like Helm. It provides a declarative way to manage Kubernetes manifests by overlaying patches on top of a base configuration, i.e without duplicating or modifying the base YAML files directly. It provides a way to manage configuration drifts hence maintaining consistency across deployments.
Key Concepts in Kustomize
Some of the key concepts that allows Kubernetes customize to simplify configuration management across different environments include:
- Base:
- This is the foundational directory in a Kustomize project where the original or default Kubernetes application manifests reside. It represents the base configuration of your application.
- Overlay:
- An
overlayis a directory that contains additional or modified Kubernetes manifests that overlay (or apply on top of) thebaseconfiguration. - They allow customization of the
baseconfiguration for different environments, regions, or specific use cases without modifying the originalbasefiles directly. - You can create separate overlay directories (e.g.,
overlays/dev,overlays/prod) where you can add or override resources, apply environment-specific configurations (like different resource limits, environment variables, etc.), and manage variations in configurations.
- An
- Patch:
- Patches are configurations that specifies the changes to apply to a resource. They provide a mechanism to modify or extend existing Kubernetes resources without directly modifying the original YAML files.
- Kustomization file:
- kustomization.yaml file is the recipe for building a customized deployment configuration in Kustomize. It tells Kustomize what resources to include (base manifests, overlays, additional YAMLs), how to modify them (patches), and where to deploy them (namespace) within your Kubernetes cluster.
Why use Kubernetes Kustomize?
Kubernetes Kustomize offers different benefits including:
- Makes it easy to manage configurations for different environments. With Kubernetes Kustomize, you can create a base manifest with common configurations and then use overlays to apply environment-specific updates, keeping your base manifests clean and reusable.
- Since Kubernetes Kustomize allows you to maintain a base manifest that can be customized whenever a need arises, it reduces the hussle of having to duplicate entire manifests for different environments.
- The flexibility of Kubernetes Kustomize provides easy configurations version control thus ensuring clear traceability and reproducibility of your deployments.
Common Use cases of Kubernetes Kustomize
Some of the common use cases of Kubernetes Kustomize include:
- Composing and Customizing resources.
- Generating ConfigMaps and Secrets
- Applying Cross-Cutting Fields for example to set common labels, annotations, or namespaces for all resources in a project.
Read more on Kustomize overview.
Getting Started with Kustomize
Installing Kubernetes Kustomize
From Kubernetes v1.14, Kustomize is integrated directly into kubectl, so you can use it without needing to install additional tools.
To check if Kustomize is installed, just check the version of kubectl;
kubectl versionClient Version: v1.30.2
Kustomize Version: v5.0.4-0.20230601165947-6ce0bf390ce3
Server Version: v1.30.2
Therefore, you can view resources available in a directory using the command;
kubectl kustomize <kustomization_file_directory>Or apply resources in a directory using the command;
kubectl apply [-k|--kustomize] <kustomization_directory>Running StandAlone Kustomize Tool
If you want, you can install a standalone Kustomize tool on your system.
The installation steps have been extensively described in the documentation, link given below.
Using Kustomize to Generate Resources from Other Sources
Kustomize can be used to dynamically generate Kubernetes resources from files or literals, simplifying resource management and avoiding hard-coded values.
As an example, Kustomize can be used to generate ConfigMaps and Secrets using Kustomize configMapGenerator and secretGenerator features respectively. Similarly, it can be used to generate other Kubernetes resources such as deployments, services, etc
We will be creating our resources on our custom namespace, kube-kustomize-base.
kubectl create namespace kube-kustomize-baseThen, let’s create our base configuration file.
mkdir baseWithin the directory, we will create the Kustomization file and config directory for storing configMaps and Secrets.
mkdir base/configIn our example, we will be using a simple Nginx app serving the following content;
cat base/config/index.html<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
text-align: center; /* Centers text and inline elements */
font-family: Arial, sans-serif; /* Optional: sets a nicer font */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Kube Kustomize Base Environment!</h1>
<p>This is the base version of our web app.</p>
<p>Feel free to explore and innovate!</p>
</body>
</html>
And Nginx configuration with basic authentication.
cat base/config/nginx.confserver {
listen 80;
location / {
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
}
}
So, we will store the basic authentication password in a file (base/config/.htpasswd);
htpasswd -c base/config/.htpasswd adminNext, let’s create Kubernetes kustomization file in the base directory. The Kustomization file defines how to use the configMapGenerator and secretGenerator to generate the configMap and Secrets.
cat base/kustomization.yamlnamespace: kube-kustomize-base
configMapGenerator:
- name: nginx-config
files:
- config/nginx.conf
- config/index.html
secretGenerator:
- name: nginx-auth
files:
- htpasswd=config/.htpasswd
generatorOptions:
disableNameSuffixHash: true
The:
configMapGenerator Section:
name: nginx-config: Creates a ConfigMap namednginx-config.files:: Includesnginx.confandindex.htmlin the ConfigMap. Note that you can also generate the configmaps from the environment variables file or from literals.
secretGenerator Section:
name: nginx-auth: Creates a Secret namednginx-auth.files:: Readsconfig/.htpasswdand adds it to the Secret under the keyhtpasswd.- Note that you can also generate the secrets from the environment variables file or from literals.
- You can also specify the type of the secret you are generating.
generatorOptions:
- The option
disableNameSuffixHashis used to avoid adding a hash suffix to the names of generated ConfigMaps and Secrets. This is useful if you want to keep the names consistent and predictable.
Thus, this is our basic base directory structure;
tree -a basebase
├── config
│ ├── .htpasswd
│ ├── index.html
│ └── nginx.conf
└── kustomization.yaml
2 directories, 4 files
You can examine the configMap and Secret to be generated using the command;
kubectl kustomize baseSample output;
apiVersion: v1
data:
index.html: |
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
text-align: center; /* Centers text and inline elements */
font-family: Arial, sans-serif; /* Optional: sets a nicer font */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Kube Kustomize Base Environment!</h1>
<p>This is the base version of our web app.</p>
<p>Feel free to explore and innovate!</p>
</body>
</html>
nginx.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
location / {
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
}
}
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
namespace: kube-kustomize-base
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
.htpasswd: |
YWRtaW46JDJ5JDEwJG5uc25kTFozSTYzWENNOVRxbFF2bi45LzRWVC8vbGxWajRKSWY1UW
M4RlFGYmEwS1JOSlptCg==
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: nginx-auth
namespace: kube-kustomize-base
type: Opaque
To create the configMap and Secrets, simply apply using kustomize;
kubectl apply [-k|--kustomize] <path to directory containing kustomization yaml>E.g
kubectl apply -k baseSample output;
configmap/nginx-config created
secret/nginx-auth createdYou can customize how the resources are generated with generator options.
View the created configMap and Secret;
kubectl get configmap,secrets -n kube-kustomize-baseNAME DATA AGE
configmap/kube-root-ca.crt 1 7m26s
configmap/nginx-config 1 104s
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
secret/nginx-auth Opaque 1 104s
Now, let’s add a deployment that will utilize the configMap and Secrets above, as well a service that exposes the Deployment.
cat base/deployment.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: nginx-auth
mountPath: /etc/nginx/.htpasswd
subPath: .htpasswd
readOnly: true
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
subPath: nginx.conf
- name: nginx-config
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
subPath: index.html
volumes:
- name: nginx-auth
secret:
secretName: nginx-auth
- name: nginx-config
configMap:
name: nginx-config
And the service to expose our deployment via the NodePort.
cat base/service.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: NodePort
At this point, these are all the files in my base directory;
tree -a basebase
├── config
│ ├── .htpasswd
│ ├── index.html
│ └── nginx.conf
├── deployment.yaml
├── kustomization.yaml
└── service.yaml
2 directories, 6 files
Next, include the Deployment and Service resources in the kustomization file.
cat base/kustomization.yamlnamespace: kube-kustomize-base
configMapGenerator:
- name: nginx-config
files:
- config/nginx.conf
- config/index.html
secretGenerator:
- name: nginx-auth
files:
- config/.htpasswd
generatorOptions:
disableNameSuffixHash: true
resources:
- deployment.yaml
- service.yaml
To see what the final YAML output would look like after all customizations are applied.
kubectl kustomize base/To apply the customizations into Kubernetes cluster;
kubectl apply -k base/You can check the Deployment and Service created.
kubectl get deployment,svc -n kube-kustomize-baseNAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment 1/1 1 1 31s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-service NodePort 10.110.182.223 <none> 80:32169/TCP 31s
Your basic Nginx app is now running.
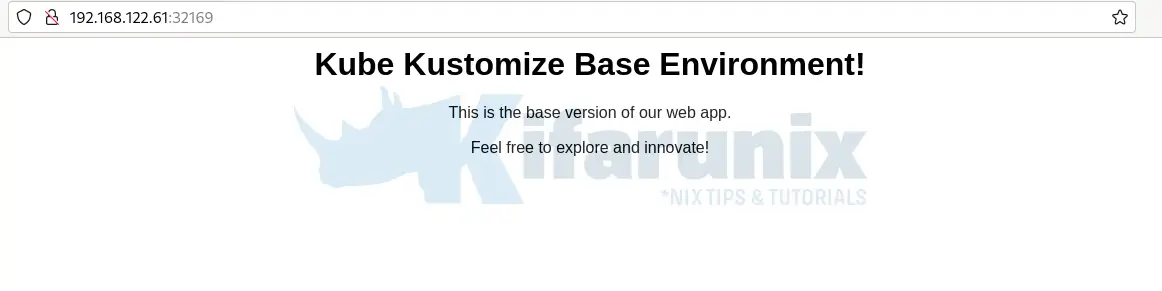
Customizing Kubernetes Resources with Kustomize Overlays
To update the above Nginx app to reflect different environments (dev, staging, production) using Kustomize overlays, you can create a configuration that includes patches to modify the content served by Nginx or any specific configuration that reflects specific environment of the app.
Base Configuration
In the base configuration above, we have the app configuration directory which contains the Secrets, ConfigMap, the deployment and service manifest and the kustomization file. We have used Kubernetes Kustomize to generate Secrets, ConfigMaps, and our Nginx deployment and service.
Base Directory Structure:
tree -a basebase
├── config
│ ├── .htpasswd
│ ├── index.html
│ └── nginx.conf
├── deployment.yaml
├── kustomization.yaml
└── service.yaml
2 directories, 6 files
Overlay Configuration
To demonstrate how you can use Kustomize to customize/patch the app for each environment (dev, staging, production), we will update our ConfigMap using patches to customize the base configuration without altering the original files.
We already have a base directory with base configurations. Next, let’s create overlays directory for the three environments:
mkdir -p overlays/{dev,staging,production}Each overlay will provide a patch to modify the index.html content for that environment.
Similarly, I will put each environment under its own namespace. So, let’s create three namespaces.
kubectl create ns kube-kustomize-devkubectl create ns kube-kustomize-stagingkubectl create ns kube-kustomize-productionIn summary, this is what we want to try out:
- Customize the
nginxdefault page for each environment. - Set different replica counts for development, staging, and production.
- Deploy to different namespaces for each environment.
Overlay directory structure:
tree -a overlaysoverlays/
├── dev
│ ├── configmap-patch.yaml
│ ├── deployment-patch.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
├── production
│ ├── configmap-patch.yaml
│ ├── deployment-patch.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── staging
├── configmap-patch.yaml
├── deployment-patch.yaml
└── kustomization.yaml
4 directories, 9 files
In general, this is how our custom app directory structure is like;
tree -a kustomize-app/kustomize-app/
├── base
│ ├── config
│ │ ├── .htpasswd
│ │ ├── index.html
│ │ └── nginx.conf
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── service.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ ├── configmap-patch.yaml
│ ├── deployment-patch.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
├── production
│ ├── configmap-patch.yaml
│ ├── deployment-patch.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── staging
├── configmap-patch.yaml
├── deployment-patch.yaml
└── kustomization.yaml
7 directories, 15 files
- Strategic merge patches: These are partial representations of a resource that merge with the existing resource, specified by a list of file paths. Each file should be resolved to a strategic merge patch. The names inside the patches must match Resource names that are already loaded. Small patches that do one thing are recommended
- JSON6902 patches: These are JSON patches that can modify specific fields in a resource.
Development Overlays:
cat overlays/dev/kustomization.yamlnamespace: kube-kustomize-dev
resources:
- ../../base
patches:
- path: deployment-patch.yaml
- path: configmap-patch.yaml
cat overlays/dev/deployment-patch.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
cat overlays/dev/configmap-patch.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
data:
index.html: |
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Kube Kustomize Dev Environment!</h1>
<p>This is the Development version of our web app.</p>
<p>Feel free to explore and innovate!</p>
</body>
</html>
Now, you can review your patches;
kubectl kustomize overlays/devapiVersion: v1
data:
index.html: |
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Kube Kustomize Dev Environment!</h1>
<p>This is the Development version of our web app.</p>
<p>Feel free to explore and innovate!</p>
</body>
</html>
nginx.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
location / {
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
}
}
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
namespace: kube-kustomize-dev
---
apiVersion: v1
data:
.htpasswd: |
YWRtaW46JDJ5JDEwJG5uc25kTFozSTYzWENNOVRxbFF2bi45LzRWVC8vbGxWajRKSWY1UW
M4RlFGYmEwS1JOSlptCg==
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: nginx-auth
namespace: kube-kustomize-dev
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
namespace: kube-kustomize-dev
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
type: NodePort
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
namespace: kube-kustomize-dev
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:latest
name: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/nginx/.htpasswd
name: nginx-auth
readOnly: true
subPath: .htpasswd
- mountPath: /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
name: nginx-config
subPath: nginx.conf
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
name: nginx-config
subPath: index.html
volumes:
- name: nginx-auth
secret:
secretName: nginx-auth
- configMap:
name: nginx-config
name: nginx-config
The apply if all is good.
kubectl apply -k overlays/devList all resources in the Development namespace.
kubectl get all -n kube-kustomize-devNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-deployment-85c575f57-kjn24 1/1 Running 0 53s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-service NodePort 10.105.39.168 <none> 80:32056/TCP 53s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment 1/1 1 1 53s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-deployment-85c575f57 1 1 1 53s
You can access your app via port 32056. Remember we didnt change the basic auth password. So use the one set in the base configuration.
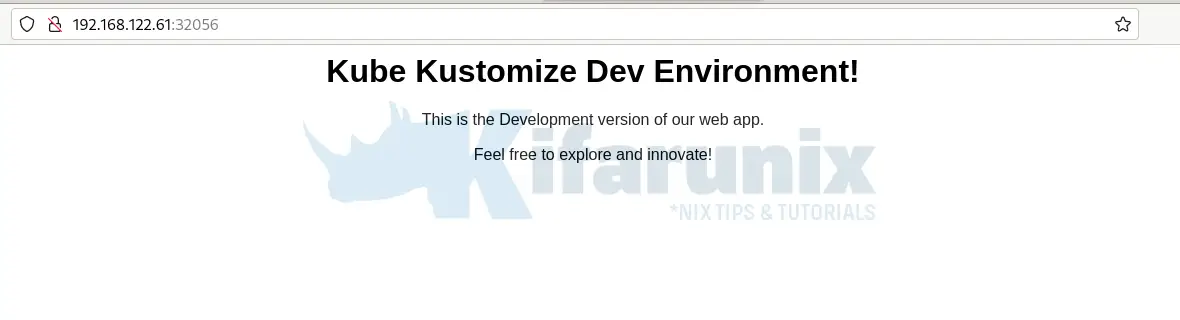
If you want, you can update other settings as you see fit.
For our production, this is how we customized the app: 4 replicas and updated web page.
cat overlays/production/kustomization.yamlnamespace: kube-kustomize-production
resources:
- ../../base
patches:
- path: deployment-patch.yaml
- path: configmap-patch.yaml
cat overlays/production/deployment-patch.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 4
overlays/production/configmap-patch.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
data:
index.html: |
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
padding: 50px;
}
h1 {
color: #009688;
}
p {
color: #607d8b;
}
.container {
margin-top: 30px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.kube-logo {
width: 150px;
height: 150px;
margin-right: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to Kubernetes Kustomize Basics!</h1>
<div class="container">
<img class="kube-logo" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/master/logo/logo.png" alt="Kubernetes Logo">
<p>This is the Production Kustomize Overlay with an updated web page and with four replicas!</p>
</div>
<p>Feel free to explore and innovate!</p>
</body>
</html>
You can review the changes;
kubectl kustomize overlays/productionThen apply;
kubectl apply --kustomize overlays/productionView resources;
kubectl get all -n kube-kustomize-productionNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-deployment-85c575f57-2rl9k 1/1 Running 0 13s
pod/nginx-deployment-85c575f57-2vt49 1/1 Running 0 13s
pod/nginx-deployment-85c575f57-4x656 1/1 Running 0 13s
pod/nginx-deployment-85c575f57-t9ggv 1/1 Running 0 13s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx-service NodePort 10.107.20.199 80:31487/TCP 13s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx-deployment 4/4 4 4 13s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-deployment-85c575f57 4 4 4 13s
And there you go!
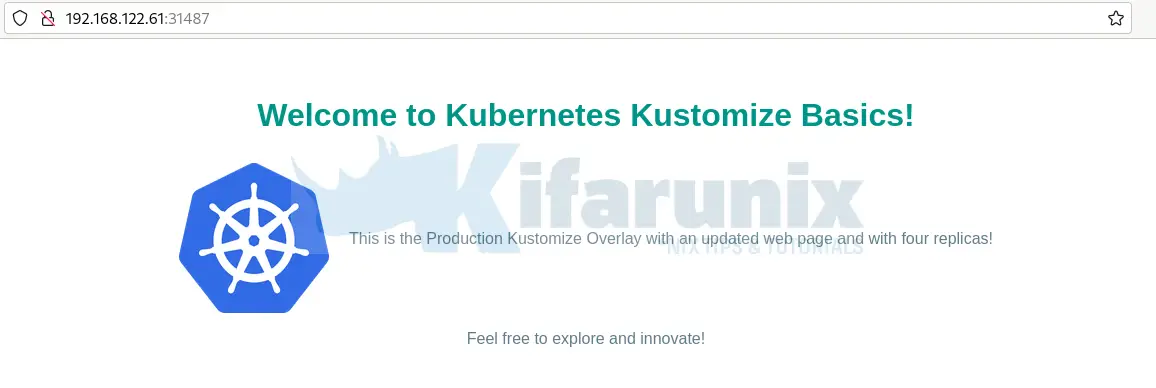
And that closes our basic guide on Kubernetes Kustomize 101.
Conclusion
Kustomize provides robust features for managing Kubernetes configurations, including:
- Generating Resources from Other Sources: Combine and reuse configurations to create complex deployments.
- Setting Cross-Cutting Fields for Resources: Apply consistent settings such as labels and annotations across multiple resources.
- Composing and Customizing Collections of Resources: Build and manage complex configurations in a modular and flexible manner.
Read more on Kustomize page.

