Installing and setting up a Kubernetes cluster on RHEL 9 is essential for modern IT environments seeking efficient container orchestration. Whether you’re a DevOps professional or a Linux enthusiast, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the entire process—from preparing your Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9 environment to deploying a fully functional Kubernetes cluster on RHEL 9. By the end of this tutorial, you’ll know how to install Kubernetes on RHEL 9, configure kubeadm, kubelet, and kubectl, and set up master and worker nodes seamlessly.
Table of Contents
Install and Setup Kubernetes Cluster on RHEL 9
Kubernetes Cluster Architecture
In this tutorial, we are going install and setup a four node (one control plane and three worker nodes) Kubernetes cluster.
A Kubernetes cluster is composed a Master node which hosts the control plane and a Worker node which hosts Pods.
Check our guide on a high-level overview of Kubernetes cluster to understand more on this.
Kubernetes Architecture: A High-level Overview of Kubernetes Cluster Components
Below are our node details.
| Node | Hostname | IP Address | vCPUs | RAM (GB) | OS |
| Master | k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 | 192.168.233.181 | 2 | 4 | RHEL 9.4 |
| Worker 1 | k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 | 192.168.233.183 | 2 | 4 | RHEL 9.4 |
| Worker 2 | k8s-rhel-node-wk-02 | 192.168.233.8 | 2 | 4 | RHEL 9.4 |
| Worker 3 | k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 | 192.168.233.106 | 2 | 4 | RHEL 9.4 |
Run System Update on Cluster Nodes
To begin with, update system package cache on all the nodes;
sudo dnf update
Disable Swap on Cluster Nodes
Running Kubernetes requires that you disable swap.
Check if swap is enabled.
swapon --show
NAME TYPE SIZE USED PRIO
/dev/dm-1 partition 2G 0B -2
If there is no output, then swap is not enabled.
If it is enabled as shown in the output above, run the command below to disable it.
sudo swapoff -v /dev/dm-1
Or simply
sudo swapoff -a
To permanently disable swap, comment out or remove the swap line on /etc/fstab file.
sudo sed -i '/swap/s/^/#/' /etc/fstab
or Simply remove it;
sed "-i.bak" '/swap/d' /etc/fstab
Reload FSTAB;
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadEnable Kernel IP forwarding on Cluster Nodes
In order to permit the communication between Pods across different networks, the system should able to route traffic between them. This can be achieved by enabling IP forwarding. Without IP forwarding, containers won’t be able to communicate with resources outside of their network namespace, which would limit their functionality and utility.
To enable IP forwarding, set the value of net.ipv4.ip_forward to 1.
echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.d/99-sysctl.confSimilarly, enable Linux kernel’s bridge netfilter to pass bridge traffic to iptables for filtering. This means that the packets that are bridged between network interfaces can be filtered using iptables/ip6tables, just as if they were routed packets.
sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.d/99-sysctl.conf << 'EOL'
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
EOLApply the changes;
sudo sysctl -pLoad Some Required Kernel Modules on Cluster Nodes
overlay module provides support for the overlay filesystem. OverlayFS is type of union filesystem used by container runtimes to layer the container’s root filesystem over the host filesystem.
br_netfilter module provides support for packet filtering in Linux bridge networks based on various criteria, such as source and destination IP address, port numbers, and protocol type.
Check if these modules are enabled/loaded;
sudo lsmod | grep -E "overlay|br_netfilter"br_netfilter 32768 0
bridge 307200 1 br_netfilter
overlay 151552 9If not loaded, just load them as follows;
echo 'overlay
br_netfilter' | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/kubernetes.confsudo modprobe overlaysudo modprobe br_netfilterInstall Container Runtime on RHEL 9
Kubernetes uses container runtime to run containers in Pods. It supports multiple container runtimes including Docker Engine, containerd, CRI-O, Mirantis Container Runtime.
Install Containerd Runtime on all Cluster Nodes
In this guide, we will use containerd runtime. Therefore, on all nodes, master and workers, you need to install containerd runtime.
You can install containerd on RHEL using official binaries or from the Docker Engine RHEL repos. We will use the later in this guide, thus:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/rhel/docker-ce.repoInstall containerd;
sudo dnf install -y containerd.io
The kubelet automatically detects the container runtime present on the node and uses it to run the containers.
Configure Cgroup Driver for ContainerD
Cgroup (control groups) is a Linux kernel feature that allows for the isolation, prioritization, and monitoring of system resources like CPU, memory, and disk I/O for a group of processes. Kubernetes (kubelet and container runtime such as containerd) uses cgroup drivers to interface with control groups in order to manage and set limit for the resources allocated to the containers.
Kubernetes support two types of Cgroup drivers;
cgroupfs(control groups filesystem): This is the default cgroup driver used by Kubernetes kubelet to manage resources for containers.systemd: This is the default initialization system and service manager in some Linux systems. It offers functions such as starting of daemons, keeping track of processes using Linux cgroups etc.
For systems that use Systemd as their default Init system, it is recommended to use systemd cgroup driver for Kubernetes instead of cgroupfs. systemd driver is also recommended for kubeadm based setups instead of the kubelet’s default cgroupfs driver, because kubeadm manages the kubelet as a systemd service.
The default configuration file for containerd is /etc/containerd/config.toml. When containerd is installed from Docker RHEL repos, this file is created with little configs. If installed from the official binaries, the containerd confguration file is not created.
Either way, update the containerd configuration file by executing the command below;
[ -d /etc/containerd ] || sudo mkdir /etc/containerdcontainerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.tomlSample configuration.
disabled_plugins = []
imports = []
oom_score = 0
plugin_dir = ""
required_plugins = []
root = "/var/lib/containerd"
state = "/run/containerd"
temp = ""
version = 2
[cgroup]
path = ""
[debug]
address = ""
format = ""
gid = 0
level = ""
uid = 0
[grpc]
address = "/run/containerd/containerd.sock"
gid = 0
max_recv_message_size = 16777216
max_send_message_size = 16777216
tcp_address = ""
tcp_tls_ca = ""
tcp_tls_cert = ""
tcp_tls_key = ""
uid = 0
[metrics]
address = ""
grpc_histogram = false
[plugins]
[plugins."io.containerd.gc.v1.scheduler"]
deletion_threshold = 0
mutation_threshold = 100
pause_threshold = 0.02
schedule_delay = "0s"
startup_delay = "100ms"
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri"]
cdi_spec_dirs = ["/etc/cdi", "/var/run/cdi"]
device_ownership_from_security_context = false
disable_apparmor = false
disable_cgroup = false
disable_hugetlb_controller = true
disable_proc_mount = false
disable_tcp_service = true
drain_exec_sync_io_timeout = "0s"
enable_cdi = false
enable_selinux = false
enable_tls_streaming = false
enable_unprivileged_icmp = false
enable_unprivileged_ports = false
ignore_deprecation_warnings = []
ignore_image_defined_volumes = false
image_pull_progress_timeout = "5m0s"
image_pull_with_sync_fs = false
max_concurrent_downloads = 3
max_container_log_line_size = 16384
netns_mounts_under_state_dir = false
restrict_oom_score_adj = false
sandbox_image = "registry.k8s.io/pause:3.8"
selinux_category_range = 1024
stats_collect_period = 10
stream_idle_timeout = "4h0m0s"
stream_server_address = "127.0.0.1"
stream_server_port = "0"
systemd_cgroup = false
tolerate_missing_hugetlb_controller = true
unset_seccomp_profile = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".cni]
bin_dir = "/opt/cni/bin"
conf_dir = "/etc/cni/net.d"
conf_template = ""
ip_pref = ""
max_conf_num = 1
setup_serially = false
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd]
default_runtime_name = "runc"
disable_snapshot_annotations = true
discard_unpacked_layers = false
ignore_blockio_not_enabled_errors = false
ignore_rdt_not_enabled_errors = false
no_pivot = false
snapshotter = "overlayfs"
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.default_runtime]
base_runtime_spec = ""
cni_conf_dir = ""
cni_max_conf_num = 0
container_annotations = []
pod_annotations = []
privileged_without_host_devices = false
privileged_without_host_devices_all_devices_allowed = false
runtime_engine = ""
runtime_path = ""
runtime_root = ""
runtime_type = ""
sandbox_mode = ""
snapshotter = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.default_runtime.options]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc]
base_runtime_spec = ""
cni_conf_dir = ""
cni_max_conf_num = 0
container_annotations = []
pod_annotations = []
privileged_without_host_devices = false
privileged_without_host_devices_all_devices_allowed = false
runtime_engine = ""
runtime_path = ""
runtime_root = ""
runtime_type = "io.containerd.runc.v2"
sandbox_mode = "podsandbox"
snapshotter = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.runtimes.runc.options]
BinaryName = ""
CriuImagePath = ""
CriuPath = ""
CriuWorkPath = ""
IoGid = 0
IoUid = 0
NoNewKeyring = false
NoPivotRoot = false
Root = ""
ShimCgroup = ""
SystemdCgroup = false
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.untrusted_workload_runtime]
base_runtime_spec = ""
cni_conf_dir = ""
cni_max_conf_num = 0
container_annotations = []
pod_annotations = []
privileged_without_host_devices = false
privileged_without_host_devices_all_devices_allowed = false
runtime_engine = ""
runtime_path = ""
runtime_root = ""
runtime_type = ""
sandbox_mode = ""
snapshotter = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd.untrusted_workload_runtime.options]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".image_decryption]
key_model = "node"
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry]
config_path = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.auths]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.configs]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.headers]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".registry.mirrors]
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".x509_key_pair_streaming]
tls_cert_file = ""
tls_key_file = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.internal.v1.opt"]
path = "/opt/containerd"
[plugins."io.containerd.internal.v1.restart"]
interval = "10s"
[plugins."io.containerd.internal.v1.tracing"]
[plugins."io.containerd.metadata.v1.bolt"]
content_sharing_policy = "shared"
[plugins."io.containerd.monitor.v1.cgroups"]
no_prometheus = false
[plugins."io.containerd.nri.v1.nri"]
disable = true
disable_connections = false
plugin_config_path = "/etc/nri/conf.d"
plugin_path = "/opt/nri/plugins"
plugin_registration_timeout = "5s"
plugin_request_timeout = "2s"
socket_path = "/var/run/nri/nri.sock"
[plugins."io.containerd.runtime.v1.linux"]
no_shim = false
runtime = "runc"
runtime_root = ""
shim = "containerd-shim"
shim_debug = false
[plugins."io.containerd.runtime.v2.task"]
platforms = ["linux/amd64"]
sched_core = false
[plugins."io.containerd.service.v1.diff-service"]
default = ["walking"]
[plugins."io.containerd.service.v1.tasks-service"]
blockio_config_file = ""
rdt_config_file = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.aufs"]
root_path = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.blockfile"]
fs_type = ""
mount_options = []
root_path = ""
scratch_file = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.devmapper"]
async_remove = false
base_image_size = ""
discard_blocks = false
fs_options = ""
fs_type = ""
pool_name = ""
root_path = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.native"]
root_path = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.overlayfs"]
mount_options = []
root_path = ""
sync_remove = false
upperdir_label = false
[plugins."io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.zfs"]
root_path = ""
[plugins."io.containerd.tracing.processor.v1.otlp"]
[plugins."io.containerd.transfer.v1.local"]
config_path = ""
max_concurrent_downloads = 3
max_concurrent_uploaded_layers = 3
[[plugins."io.containerd.transfer.v1.local".unpack_config]]
differ = ""
platform = "linux/amd64"
snapshotter = "overlayfs"
[proxy_plugins]
[stream_processors]
[stream_processors."io.containerd.ocicrypt.decoder.v1.tar"]
accepts = ["application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+encrypted"]
args = ["--decryption-keys-path", "/etc/containerd/ocicrypt/keys"]
env = ["OCICRYPT_KEYPROVIDER_CONFIG=/etc/containerd/ocicrypt/ocicrypt_keyprovider.conf"]
path = "ctd-decoder"
returns = "application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar"
[stream_processors."io.containerd.ocicrypt.decoder.v1.tar.gzip"]
accepts = ["application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip+encrypted"]
args = ["--decryption-keys-path", "/etc/containerd/ocicrypt/keys"]
env = ["OCICRYPT_KEYPROVIDER_CONFIG=/etc/containerd/ocicrypt/ocicrypt_keyprovider.conf"]
path = "ctd-decoder"
returns = "application/vnd.oci.image.layer.v1.tar+gzip"
[timeouts]
"io.containerd.timeout.bolt.open" = "0s"
"io.containerd.timeout.metrics.shimstats" = "2s"
"io.containerd.timeout.shim.cleanup" = "5s"
"io.containerd.timeout.shim.load" = "5s"
"io.containerd.timeout.shim.shutdown" = "3s"
"io.containerd.timeout.task.state" = "2s"
[ttrpc]
address = ""
gid = 0
uid = 0
Once you generate the default config, you need to enable systemd cgroup for the containerd low-level container runtime, runc by changing the value of SystemdCgroup from false to true.
sudo sed -i '/SystemdCgroup/s/false/true/' /etc/containerd/config.tomlAlso, as of this writing, it is recommended to use “registry.k8s.io/pause:3.10” as the CRI sandbox image. pause container image is a minimalistic container image that enables containerd to provide network isolation for pods in Kubernetes. Containerd uses pause:3.8.
grep sandbox_image /etc/containerd/config.toml sandbox_image = "registry.k8s.io/pause:3.8"To change this to pause:3.10;
sudo sed -i '/pause:3.8/s/3.8/3.10/' /etc/containerd/config.tomlIf the default version is other than 3.8, then adjust the number accordingly.
Verify the changes again;
grep sandbox_image /etc/containerd/config.toml sandbox_image = "registry.k8s.io/pause:3.10"Start and enable containerd to run on system boot;
sudo systemctl enable --now containerdConfirm the status;
systemctl status containerd● containerd.service - containerd container runtime
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2025-01-18 09:36:37 EST; 10s ago
Docs: https://containerd.io
Process: 14372 ExecStartPre=/sbin/modprobe overlay (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 14373 (containerd)
Tasks: 8
Memory: 17.2M
CPU: 71ms
CGroup: /system.slice/containerd.service
└─14373 /usr/bin/containerd
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.913234967-05:00" level=info msg="Start subscribing containerd event"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.913348866-05:00" level=info msg="Start recovering state"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.913489170-05:00" level=info msg="Start event monitor"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.913523637-05:00" level=info msg="Start snapshots syncer"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.913539340-05:00" level=info msg="Start cni network conf syncer for default"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.913551774-05:00" level=info msg="Start streaming server"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.914433160-05:00" level=info msg=serving... address=/run/containerd/containerd.sock.ttrpc
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.914537159-05:00" level=info msg=serving... address=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 containerd[14373]: time="2025-01-18T09:36:37.915181878-05:00" level=info msg="containerd successfully booted in 0.039538s"
Jan 18 09:36:37 k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 systemd[1]: Started containerd container runtime.
Install Kubernetes on RHEL 9
There are a number of node components required to provide Kubernetes runtime environment that needs to be installed on each node. These include:
- kubelet: runs as an agent on each worker node and ensures that containers are running in a Pod.
- kubeadm: Bootstraps Kubernetes cluster
- kubectl: Used to run commands against Kubernetes clusters.
These components are not available on the default RHEL repos. Thus, you need to install Kubernetes repos to install them.
Install Kubernetes Repository on RHEL 9 (All nodes)
Replace the value of the VER variable below with the release number of Kubernetes you need to run! In this guide, I will be using the current latest minor release version (as of this writing), v1.32.
VER=1.32Then run the command below to install Kubernetes repository on RHEL 9;
sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/k8s.repo << EOF
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v$VER/rpm/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v$VER/rpm/repodata/repomd.xml.key
exclude=kubelet kubeadm kubectl
EOF
Note the exclude=kubelet kubeadm kubectl. This specifies a list of packages to exclude from being installed or updated from this repository. This is to help ensure that there are no unintended or unexpected upgrades to critical Kubernetes components like kubelet, kubeadm, and kubectl!
Install Kubernetes components on all the nodes
The components that need to be installed are kubeadm, kubelet and kubectl. To install them form the repository just created, you need to pass the --disableexcludes=REPO-ID. Remember, they were excluded!
sudo dnf install kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes -y
Ensure that kubelet service is up and running;
sudo systemctl enable --now kubeletInitialize Kubernetes Cluster on Control Plane using Kubeadm
Once the above steps are completed, initialize the Kubernetes cluster on the master node. The Kubernetes master node is responsible for maintaining the desired state for your cluster.
We will be using kubeadm tool to deploy our K8S cluster.
The cluster can be initiated using the kubeadm tool by passing the init command argument;
kubeadm init <args>Some of the common arguments/options include;
- --apiserver-advertise-address: Defines the IP address the API Server will listen on. If not defined, the default network interface will be used. An example usage is
--apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.233.181. - --pod-network-cidr: Specify range of IP addresses for the pod network. If set, the control plane will automatically allocate CIDRs for every node from that network. You use this to define your preferred network range if there is a chance for collision between your network plugin’s preferred Pod network addon and some of your host networks to happen e.g
--pod-network-cidr=10.100.0.0/16. - --control-plane-endpoint: Specifies the hostname and port that the API server will listen on. This is recommended over the use of
--apiserver-advertise-addressbecause it enables you to define a shared endpoint such as load balance DNS name or an IP address that can be used when you upgrade single master node to highly available node. For example,--control-plane-endpoint=cluster.kifarunix-demo.com:6443.
Since we are just running a single master node Kubernetes cluster in this guide (for demo purposes), with no plans to upgrade to highly available cluster, then we will specify just the IP address of the control plane while bootstrapping our cluster.
Thus, run the command below on the master node to bootstrap the Kubernetes control-plane node.
Be sure to run the commands as regular user (recommended), with sudo rights.
Thus, if you are root, then switch to regular user with sudo rights (kifarunix is our regular, it could be a different user for you)
su - kifarunix
sudo kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.233.181 --pod-network-cidr=10.100.0.0/16
The command will start by pre-pulling (kubeadm config images pull) the required container images for a Kubernetes cluster before initializing the cluster.
Once the initialization is done, you should be able to see an output similar to the one below;
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING Firewalld]: firewalld is active, please ensure ports [6443 10250] are open or your cluster may not function correctly
[WARNING Service-Kubelet]: kubelet service is not enabled, please run 'systemctl enable kubelet.service'
[preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster
[preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection
[preflight] You can also perform this action beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull'
[certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki"
[certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key
[certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.233.181]
[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 localhost] and IPs [192.168.233.181 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key
[certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 localhost] and IPs [192.168.233.181 127.0.0.1 ::1]
[certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key
[certs] Generating "sa" key and public key
[kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes"
[kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "super-admin.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file
[kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file
[etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager"
[control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests"
[kubelet-check] Waiting for a healthy kubelet at http://127.0.0.1:10248/healthz. This can take up to 4m0s
[kubelet-check] The kubelet is healthy after 501.071226ms
[api-check] Waiting for a healthy API server. This can take up to 4m0s
[api-check] The API server is healthy after 3.500982906s
[upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace
[kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster
[upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers]
[mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule]
[bootstrap-token] Using token: cksg7l.su9fsi574cr9sd53
[bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token
[bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster
[bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace
[kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key
[addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS
[addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy
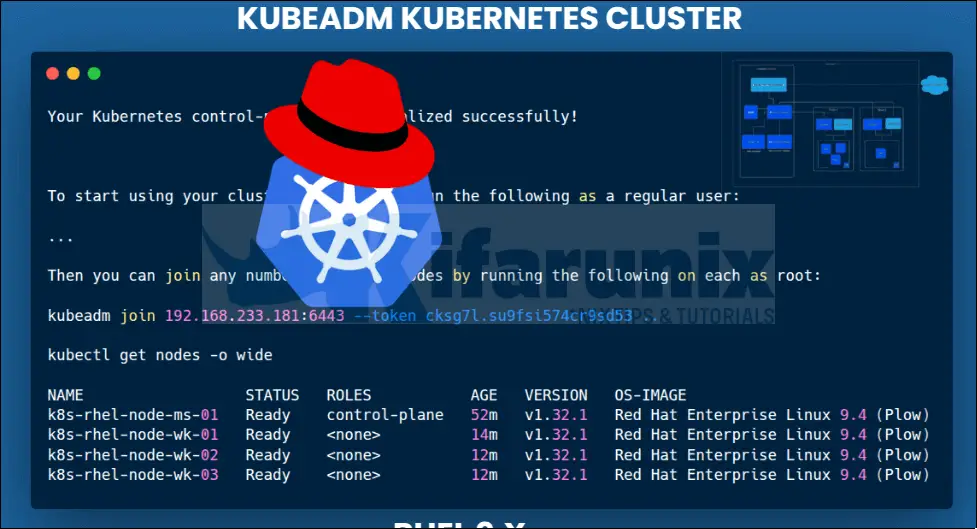
Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully!
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run:
export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 192.168.233.181:6443 --token cksg7l.su9fsi574cr9sd53 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:065a2927d6b3503633e94e9ba68dd8e55b6d41344d0394e5476aea1125888502
Next, create a Kubernetes cluster directory.
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
Copy Kubernetes admin configuration file to the cluster directory created above.
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
Set the proper ownership for the cluster configuration file.
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Verify the status of the Kubernetes cluster;
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 NotReady control-plane 4m30s v1.32.1
As you can see, the cluster is not ready yet.
You can also get the address of the control plane and cluster services;
kubectl cluster-infoKubernetes control plane is running at https://192.168.233.181:6443
CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.233.181:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
Install Pod Network Addon on Master Node
A Pod is a group of one or more related containers in a Kubernetes cluster. They share the same lifecycle, storage/network. For Pods to communicate with one another, you must deploy a Container Network Interface (CNI) based Pod network add-on.
There are multiple Pod network addons that you can choose from. Refer to Addons page for more information.
To deploy a CNI Pod network, run the command below on the master node;
kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml
Where [podnetwork].yaml is the path to your preferred CNI YAML file. In this demo, we will use Calico network plugin.
Install Calico Pod network addon Operator by running the command below. Execute the command as the user with which you created the Kubernetes cluster.
Current release version is v3.28.0.
Get the current release version from releases page and replace the value of CNI_VER below.
CNI_VER=3.29.1kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v${CNI_VER}/manifests/tigera-operator.yamlnamespace/tigera-operator created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpfilters.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/caliconodestatuses.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ippools.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipreservations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networksets.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/tiers.crd.projectcalico.org created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/adminnetworkpolicies.policy.networking.k8s.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/apiservers.operator.tigera.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/imagesets.operator.tigera.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/installations.operator.tigera.io created
customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/tigerastatuses.operator.tigera.io created
serviceaccount/tigera-operator created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tigera-operator created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tigera-operator created
deployment.apps/tigera-operator created
Next, download the custom resources definition file necessary to configure Calico. The default network for Calico plugin is 192.168.0.0/16. If you used custom pod CIDR as defined above (--pod-network-cidr=10.100.0.0/16), download the custom resource file and modify the network to match your custom one.
We will the manifest of the same version of CNI above.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/projectcalico/calico/v${CNI_VER}/manifests/custom-resources.yamlcat custom-resources.yaml# This section includes base Calico installation configuration.
# For more information, see: https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/reference/installation/api#operator.tigera.io/v1.Installation
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: Installation
metadata:
name: default
spec:
# Configures Calico networking.
calicoNetwork:
ipPools:
- name: default-ipv4-ippool
blockSize: 26
cidr: 192.168.0.0/16
encapsulation: VXLANCrossSubnet
natOutgoing: Enabled
nodeSelector: all()
---
# This section configures the Calico API server.
# For more information, see: https://docs.tigera.io/calico/latest/reference/installation/api#operator.tigera.io/v1.APIServer
apiVersion: operator.tigera.io/v1
kind: APIServer
metadata:
name: default
spec: {}
The network section of the custom resource file will now look like below by default;
- blockSize: 26
cidr: 192.168.0.0/16Update the network subnet to match your subnet.
sed -i 's/192.168/10.100/' custom-resources.yamlThe CIDR should be changed now;
grep cidr custom-resources.yaml cidr: 10.100.0.0/16Apply the changes.
kubectl create -f custom-resources.yamlSample output;
installation.operator.tigera.io/default created
apiserver.operator.tigera.io/default createdGet Running Pods in the Kubernetes cluster
Once the command completes, you can list the Pods in the namespaces by running the command below;
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
calico-apiserver calico-apiserver-5d4b86bbc5-9lrhg 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 25s
calico-apiserver calico-apiserver-5d4b86bbc5-hbrk5 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 25s
calico-system calico-kube-controllers-5568c67b5-tr2sd 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 25s
calico-system calico-node-m5clj 0/1 Running 0 26s
calico-system calico-typha-67f9f69d47-mstbb 1/1 Running 0 26s
calico-system csi-node-driver-hgg7l 0/2 ContainerCreating 0 25s
kube-system coredns-668d6bf9bc-5pn78 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system coredns-668d6bf9bc-cls2n 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system etcd-k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system kube-apiserver-k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system kube-proxy-6tw49 1/1 Running 0 14m
kube-system kube-scheduler-k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 1/1 Running 0 14m
tigera-operator tigera-operator-7d68577dc5-vxzwk 1/1 Running 0 3m37s
You can list Pods on specific namespaces;
kubectl get pods -n calico-systemNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
calico-kube-controllers-5568c67b5-tr2sd 1/1 Running 0 68s
calico-node-m5clj 1/1 Running 0 69s
calico-typha-67f9f69d47-mstbb 1/1 Running 0 69s
csi-node-driver-hgg7l 2/2 Running 0 68s
As can be seen, all Pods on calico-system namespace are running.
Open Kubernetes Cluster Ports on Firewall
If firewall is running on the nodes, then there are some ports that needs to be opened to ensure a functional cluster.
Control Plane ports;
| Protocol | Direction | Port Range | Purpose | Used By |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | Inbound | 6443 | Kubernetes API server | All |
| TCP | Inbound | 2379-2380 | etcd server client API | kube-apiserver, etcd |
| TCP | Inbound | 10250 | Kubelet API | Self, Control plane |
| TCP | Inbound | 10259 | kube-scheduler | Self |
| TCP | Inbound | 10257 | kube-controller-manager | Self |
So the ports that should be open and accessible from outside the master node are:
6443- Kubernetes API Server (secure port)2379-2380- etcd server client API10250- Kubelet API10251- kube-scheduler10252- kube-controller-manager
As a result, we have disabled and stopped our Firewalld. Please be aware of the repercussions of this before you can proceed!
sudo systemctl disable --now firewalldWorker Nodes ports that should be opened if using a system firewall to control access;
| Protocol | Direction | Port Range | Purpose | Used By |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCP | Inbound | 10250 | Kubelet API | Self, Control plane |
| TCP | Inbound | 30000-32767 | NodePort Services | All |
Add Worker Nodes to Kubernetes Cluster
You can now add Worker nodes to the Kubernetes cluster using the kubeadm join command as follows.
Before that, ensure that container runtime is installed, configured and running. We are using containerd CRI;
systemctl status containerdSample output from worker01 node;
● containerd.service - containerd container runtime
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/containerd.service; enabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2025-01-18 09:58:47 EST; 35min ago
Docs: https://containerd.io
Process: 14564 ExecStartPre=/sbin/modprobe overlay (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 14566 (containerd)
Tasks: 8
Memory: 20.3M
CPU: 2.842s
CGroup: /system.slice/containerd.service
└─14566 /usr/bin/containerd
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169496832-05:00" level=info msg="Start subscribing containerd event"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169572239-05:00" level=info msg="Start recovering state"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169653754-05:00" level=info msg="Start event monitor"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169696562-05:00" level=info msg="Start snapshots syncer"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169743305-05:00" level=info msg="Start cni network conf syncer for default"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169774730-05:00" level=info msg="Start streaming server"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169769921-05:00" level=info msg=serving... address=/run/containerd/containerd.sock.ttrpc
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169864423-05:00" level=info msg=serving... address=/run/containerd/containerd.sock
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 containerd[14566]: time="2025-01-18T09:58:47.169906043-05:00" level=info msg="containerd successfully booted in 0.021092s"
Jan 18 09:58:47 k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 systemd[1]: Started containerd container runtime.
Once you have confirmed that, get the cluster join command that was output during cluster boot strapping and execute on each node.
Note that this command is displayed after initializing the control plane above and it should be executed as a privileged user.
sudo kubeadm join 192.168.233.181:6443 --token cksg7l.su9fsi574cr9sd53 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:065a2927d6b3503633e94e9ba68dd8e55b6d41344d0394e5476aea1125888502
If you didn't save the Kubernetes Cluster joining command, you can at any given time print using the command below on the Master or control plane;
kubeadm token create --print-join-command
Once the command runs, you will get an output similar to below;
[sudo] password for kifarunix:
[preflight] Running pre-flight checks
[WARNING Service-Kubelet]: kubelet service is not enabled, please run 'systemctl enable kubelet.service'
[preflight] Reading configuration from the "kubeadm-config" ConfigMap in namespace "kube-system"...
[preflight] Use 'kubeadm init phase upload-config --config your-config.yaml' to re-upload it.
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml"
[kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env"
[kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet
[kubelet-check] Waiting for a healthy kubelet at http://127.0.0.1:10248/healthz. This can take up to 4m0s
[kubelet-check] The kubelet is healthy after 501.497956ms
[kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap
This node has joined the cluster:
* Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received.
* The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details.
Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
On the Kubernetes control plane (master, as the regular user with which you created the cluster as), run the command below to verify that the nodes have joined the cluster.
kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-rhel-node-ms-01 Ready control-plane 40m v1.32.1
k8s-rhel-node-wk-01 Ready <none> 2m8s v1.32.1
k8s-rhel-node-wk-02 Ready <none> 40s v1.32.1
k8s-rhel-node-wk-03 Ready <none> 21s v1.32.1
There are different node stati;
- NotReady: The node has been added to the cluster but is not yet ready to accept workloads.
- SchedulingDisabled: The node is not able to receive new workloads because it is marked as unschedulable.
- Ready: The node is ready to accept workloads.
- OutOfDisk: Indicates that the node is running out of disk space.
- MemoryPressure: Indicates that the node is running out of memory.
- PIDPressure: indicates that there are too many processes on the node
- DiskPressure: Indicates that the node is running out of disk space.
- NetworkUnavailable: Indicates that the node is not reachable via the network.
- Unschedulable: Indicates that the node is not schedulable for new workloads.
- ConditionUnknown: Indicates that the node status is unknown due to an error.
Role of the Worker nodes may show up as <none>. This is okay. No role is assigned to the node by default. It is only until the control plane assign a workload on the node then it shows up the correct role.
You can however update this ROLE using the command;
kubectl label node <worker-node-name> node-role.kubernetes.io/worker=trueGet Kubernetes Cluster Information
As you can see, we now have a cluster. Run the command below to get cluster information.
kubectl cluster-info
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://192.168.233.181:6443
CoreDNS is running at https://192.168.233.181:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxy
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
List Kubernetes Cluster API Resources
You can list all Kubernetes cluster resources using the command below;
kubectl api-resourcesNAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
bindings v1 true Binding
componentstatuses cs v1 false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm v1 true ConfigMap
endpoints ep v1 true Endpoints
events ev v1 true Event
limitranges limits v1 true LimitRange
namespaces ns v1 false Namespace
nodes no v1 false Node
persistentvolumeclaims pvc v1 true PersistentVolumeClaim
persistentvolumes pv v1 false PersistentVolume
pods po v1 true Pod
podtemplates v1 true PodTemplate
replicationcontrollers rc v1 true ReplicationController
resourcequotas quota v1 true ResourceQuota
secrets v1 true Secret
serviceaccounts sa v1 true ServiceAccount
services svc v1 true Service
mutatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false MutatingWebhookConfiguration
validatingadmissionpolicies admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false ValidatingAdmissionPolicy
validatingadmissionpolicybindings admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false ValidatingAdmissionPolicyBinding
validatingwebhookconfigurations admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 false ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
customresourcedefinitions crd,crds apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 false CustomResourceDefinition
apiservices apiregistration.k8s.io/v1 false APIService
controllerrevisions apps/v1 true ControllerRevision
daemonsets ds apps/v1 true DaemonSet
deployments deploy apps/v1 true Deployment
replicasets rs apps/v1 true ReplicaSet
statefulsets sts apps/v1 true StatefulSet
selfsubjectreviews authentication.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectReview
tokenreviews authentication.k8s.io/v1 false TokenReview
localsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 true LocalSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectAccessReview
selfsubjectrulesreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SelfSubjectRulesReview
subjectaccessreviews authorization.k8s.io/v1 false SubjectAccessReview
horizontalpodautoscalers hpa autoscaling/v2 true HorizontalPodAutoscaler
cronjobs cj batch/v1 true CronJob
jobs batch/v1 true Job
certificatesigningrequests csr certificates.k8s.io/v1 false CertificateSigningRequest
leases coordination.k8s.io/v1 true Lease
bgpconfigurations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BGPConfiguration
bgpfilters crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BGPFilter
bgppeers crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BGPPeer
blockaffinities crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false BlockAffinity
caliconodestatuses crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false CalicoNodeStatus
clusterinformations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false ClusterInformation
felixconfigurations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false FelixConfiguration
globalnetworkpolicies crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false GlobalNetworkPolicy
globalnetworksets crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false GlobalNetworkSet
hostendpoints crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false HostEndpoint
ipamblocks crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPAMBlock
ipamconfigs crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPAMConfig
ipamhandles crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPAMHandle
ippools crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPPool
ipreservations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false IPReservation
kubecontrollersconfigurations crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false KubeControllersConfiguration
networkpolicies crd.projectcalico.org/v1 true NetworkPolicy
networksets crd.projectcalico.org/v1 true NetworkSet
tiers crd.projectcalico.org/v1 false Tier
endpointslices discovery.k8s.io/v1 true EndpointSlice
events ev events.k8s.io/v1 true Event
flowschemas flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1 false FlowSchema
prioritylevelconfigurations flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1 false PriorityLevelConfiguration
ingressclasses networking.k8s.io/v1 false IngressClass
ingresses ing networking.k8s.io/v1 true Ingress
networkpolicies netpol networking.k8s.io/v1 true NetworkPolicy
runtimeclasses node.k8s.io/v1 false RuntimeClass
apiservers operator.tigera.io/v1 false APIServer
imagesets operator.tigera.io/v1 false ImageSet
installations operator.tigera.io/v1 false Installation
tigerastatuses operator.tigera.io/v1 false TigeraStatus
poddisruptionbudgets pdb policy/v1 true PodDisruptionBudget
adminnetworkpolicies anp policy.networking.k8s.io/v1alpha1 false AdminNetworkPolicy
bgpconfigurations bgpconfig,bgpconfigs projectcalico.org/v3 false BGPConfiguration
bgpfilters projectcalico.org/v3 false BGPFilter
bgppeers projectcalico.org/v3 false BGPPeer
blockaffinities blockaffinity,affinity,affinities projectcalico.org/v3 false BlockAffinity
caliconodestatuses caliconodestatus projectcalico.org/v3 false CalicoNodeStatus
clusterinformations clusterinfo projectcalico.org/v3 false ClusterInformation
felixconfigurations felixconfig,felixconfigs projectcalico.org/v3 false FelixConfiguration
globalnetworkpolicies gnp,cgnp,calicoglobalnetworkpolicies projectcalico.org/v3 false GlobalNetworkPolicy
globalnetworksets projectcalico.org/v3 false GlobalNetworkSet
hostendpoints hep,heps projectcalico.org/v3 false HostEndpoint
ipamconfigurations ipamconfig projectcalico.org/v3 false IPAMConfiguration
ippools projectcalico.org/v3 false IPPool
ipreservations projectcalico.org/v3 false IPReservation
kubecontrollersconfigurations kcconfig projectcalico.org/v3 false KubeControllersConfiguration
networkpolicies cnp,caliconetworkpolicy,caliconetworkpolicies projectcalico.org/v3 true NetworkPolicy
networksets netsets projectcalico.org/v3 true NetworkSet
profiles projectcalico.org/v3 false Profile
tiers projectcalico.org/v3 false Tier
clusterrolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 false ClusterRoleBinding
clusterroles rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 false ClusterRole
rolebindings rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 true RoleBinding
roles rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 true Role
priorityclasses pc scheduling.k8s.io/v1 false PriorityClass
csidrivers storage.k8s.io/v1 false CSIDriver
csinodes storage.k8s.io/v1 false CSINode
csistoragecapacities storage.k8s.io/v1 true CSIStorageCapacity
storageclasses sc storage.k8s.io/v1 false StorageClass
volumeattachments storage.k8s.io/v1 false VolumeAttachment
You are now ready to deploy an application on Kubernetes cluster.
Step-by-Step Guide on Deploying an Application on Kubernetes Cluster
Remove Worker Nodes from Cluster
You can gracefully remove a node from Kubernetes cluster as described in the guide below;
Gracefully Remove Worker Node from Kubernetes Cluster
Inspect SELinux
Note that we haven't disabled SELinux. It is running in enforcing mode. In case you notice some issues, please be sure to check the logs.
sudo dnf install setroubleshoot-serversudo sealert -a /var/log/audit/audit.logsudo ausearch -m AVC -ts recentsudo grep denied /var/log/audit/audit.logIf any issue, fix accordingly.
Install Kubernetes Dashboard
You can manage your cluster from the dashboard using Kubernetes. See the guide below;
How to Install Kubernetes Dashboard

