This guide will take you through how to install Redmine on CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9. Redmine is a cross-platform as well as cross-database flexible project management web application and we are using CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9 specifically on this blog post.
Redmine has quite a number of features that are described on Redmine features page.
Table of Contents
Installing Redmine on CentOS Stream
Create Redmine System User
In this guide, we will install Redmine on /opt/redmine directory and run it as non-privileged redmine system user.
As such, create a redmine system user (or any other non-privileged system user that Redmine will run as for that case) and assign the /opt/redmine as its home directory.
useradd -r -m -d /opt/redmine redmine
Consult man useradd to learn what the options used above means.
Install Apache HTTP Server
To install Apache HTTP server on CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9, simply execute;
dnf install httpd
Start and enable Apache HTTP server to run on system boot;
systemctl enable httpd --now
Next, since we will be using Apache as our HTTP server, add Apache to Redmine group.
usermod -aG redmine apache
Install MariaDB Database Backend
Redmine supports a number of database back-ends such as PostgreSQL, MySQL/MariaDB, MSSQL. In this demo, we are using MariaDB 10.x.
dnf install mariadb-serverrun the command below to start and enable MariaDB server on system boot;
systemctl enable --now mariadbRun initial MariaDB database secure script to remove default databases, test tables, disable remote root login;
mysql_secure_installationCreate Redmine Database and Database User
Once the database backend is installed, login and create the database and database user for Redmine. Replace the database name accordingly.
mysql -u root -p
create database redminedb;
Create and grant the user all privileges on the database created. Replace the database user and password accordingly.
grant all on redminedb.* to redmineadmin@localhost identified by 'P@ssWorD';
Reload privileges tables and quit.
flush privileges; quit
Installing Redmine on CentOS
Install Required Dependencies
Begin by installing the dependencies required to build Redmine.
Enable required repos;
CentOS Stream 8;
dnf install epel-releaseCentOS Stream 9;
dnf install epel-releasednf config-manager --enable crbEnable Ruby 3.1 modules on CentOS stream 8. This is enabled by default on CentOS stream 9 (confirm with the command, yum module list ruby).
dnf module reset ruby -ydnf module enable ruby:3.1Next, install required packages/dependencies.
dnf install ruby-devel \
rpm-build \
wget \
libxml2-devel \
vim \
make \
openssl-devel \
automake \
libtool \
ImageMagick \
ImageMagick-devel \
mariadb-devel \
gcc \
httpd-devel \
libcurl-devel \
gcc-c++ -y
Install Ruby on CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9
Redmine also requires Ruby interpreter which is installed automatically with the dependencies above.
Verify installed version.
ruby -v
Sample output on CentOS stream 8.
ruby 3.1.2p20 (2022-04-12 revision 4491bb740a) [x86_64-linux]Redmine version 5.1 supports upto Ruby 3.1 as of this post update!
Download and Install Redmine
In order to install the latest version of Redmine, navigate to the Download’s page and grab the latest stable release version.
You can simply download and extract the Redmine tarball to the Redmine install directory, /opt/redmine.
VER=5.1.0curl -s https://www.redmine.org/releases/redmine-$VER.tar.gz | \
sudo -u redmine tar xz -C /opt/redmine/ --strip-components=1You should now have redmine files under /opt/redmine.
ls -alh /opt/redmine
total 188K
drwx------. 17 redmine redmine 4.0K Nov 13 06:30 .
drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 21 Nov 13 05:32 ..
drwxr-xr-x. 8 redmine redmine 97 Oct 31 00:50 app
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 863 Oct 31 00:50 appveyor.yml
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 18 Jul 19 00:00 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 144 Jul 19 00:00 .bash_profile
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 522 Jul 19 00:00 .bashrc
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 78 Oct 31 00:50 bin
drwxr-xr-x. 5 redmine redmine 4.0K Oct 31 00:50 config
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 129 Oct 31 00:50 config.ru
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 538 Oct 31 00:50 CONTRIBUTING.md
drwxr-xr-x. 3 redmine redmine 21 Oct 31 00:50 db
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 113 Oct 31 00:50 doc
drwxr-xr-x. 5 redmine redmine 58 Oct 31 00:50 extra
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 23 Oct 31 00:50 files
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 3.5K Oct 31 00:50 Gemfile
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 38 Oct 31 00:50 .github
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 823 Oct 31 00:50 .gitignore
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 694 Oct 31 00:50 .hgignore
drwxr-xr-x. 6 redmine redmine 85 Oct 31 00:50 lib
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 23 Oct 31 00:50 log
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 81 Oct 31 00:50 package.json
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 20 Oct 31 00:50 plugins
drwxr-xr-x. 8 redmine redmine 4.0K Oct 31 00:50 public
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 redmine redmine 275 Oct 31 00:50 Rakefile
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 205 Oct 31 00:50 README.rdoc
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 56K Oct 31 00:50 .rubocop_todo.yml
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 5.3K Oct 31 00:50 .rubocop.yml
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 42 Oct 31 00:50 .stylelintignore
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 1009 Oct 31 00:50 .stylelintrc
drwxr-xr-x. 15 redmine redmine 4.0K Oct 31 00:50 test
drwxr-xr-x. 8 redmine redmine 95 Oct 31 00:50 tmp
drwxr-xr-x. 2 redmine redmine 6 Oct 31 00:50 vendor
-rw-r--r--. 1 redmine redmine 51K Oct 31 00:50 yarn.lock
Configure Redmine Database Connection Settings
First switch to Redmine’s user account.
su - redmine
Rename the sample Redmine configuration.
cp config/configuration.yml{.example,}
Rename the sample dispatch CGI configuration file under the public folder as shown below;
cp public/dispatch.fcgi{.example,}
Rename the sample the database configuration file.
cp config/database.yml{.example,}
Next, open the database configure file for editing and and configure it to set the Redmine database connection details.
vim config/database.yml
Replace the database name, database user and the password accordingly.
...
production:
adapter: mysql2
database: redminedb
host: localhost
username: redmineadmin
password: "P@ssWorD"
# Use "utf8" instead of "utfmb4" for MySQL prior to 5.7.7
encoding: utf8mb4
...
Save and exit the file.
Install Ruby Dependencies
Next, install required Ruby dependencies. Note that this step should be executed as Redmine user created above. If you are still logged in as Redmine user, proceed. Otherwise, switch to redmine user.
su - redmine
Install Bundler for managing gem dependencies.
gem install bundlerOnce the bundler installation is done, you can now install required gems dependencies.
bundle config set --local path 'vendor/bundle'bundle config set --local without 'development test'
bundle install
Generate Secret Session Token
To prevent tempering of the cookies that stores session data, you need to generate a random secret key that Rails uses to encode them.
bundle exec rake generate_secret_token
Create Database Schema Objects
Create Rails database structure by running the command below;
RAILS_ENV=production bundle exec rake db:migrate
Once the database migration is done, insert default configuration data (optional) into the database by executing;
RAILS_ENV=production REDMINE_LANG=en bundle exec rake redmine:load_default_data
Configure FileSystem Permissions
Ensure that the following directories are available on Redmine directory, /opt/redmine.
- tmp and tmp/pdf
- public and public/plugin_assets
- log
- files
If they do not exist, simply create them and ensure that they are owned by the user used to run Redmine.
for i in tmp tmp/pdf public/plugin_assets; do [ -d $i ] || mkdir -p $i; done
chown -R redmine:redmine files log tmp public/plugin_assets
chmod -R 755 /opt/redmine/
Testing Redmine Installation
The setup of Redmine on CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9 is now done. You can test Redmine using WEBrick by executing the command below;
You can now test Redmine using WEBrick by executing the command below;
su - redmineAdd webrick to Gemfile;
echo 'gem "webrick"' >> GemfileInstall webrick gem and test the installation;
bundle installbundle exec rails server -u webrick -e productionSample output;
=> Booting WEBrick
=> Rails 6.1.7.6 application starting in production http://0.0.0.0:3000
=> Run `bin/rails server --help` for more startup options
[2023-11-13 15:31:55] INFO WEBrick 1.8.1
[2023-11-13 15:31:55] INFO ruby 3.1.2 (2022-04-12) [x86_64-linux]
[2023-11-13 15:31:55] INFO WEBrick::HTTPServer#start: pid=25649 port=3000
You can now access Redmine via the browser using the address, http://Server-IP:3000/.
Before that, open port 3000/tcp on firewalld. Run the commands below as privileged user.
firewall-cmd --add-port=3000/tcp --permanent firewall-cmd --reload
Once the port is opened, navigate to the browser and access Redmine. You should see a welcome page.

Click sign in at the top right corner and use the credentials:
- User:
admin - Password:
admin
To stop Redmine foreground run, just press CTRL+C.
Configure Apache for Redmine
Once you have confirmed that Redmine is working fine after the testing, you need to configure Apache HTTP server for Redmine.
Install Apache Passenger Module on CentOS Stream 8
Phusion Passenger is a web application server that can be used to server Redmine on production environments.
Therefore, switch to Redmine user created above to install the Phusion Passenger Apache module;
su - redminegem install passenger --no-documentNext, install Passenger Apache module. Replace the version of the Passenger accordingly.
passenger-install-apache2-moduleFollow through the installation guide to install Phusion Passenger. You maybe prompted to reinstall Passenger through the RPMs. However, press Enter to continue using this installer anyway.
Similarly, when prompted to choose a language, select Ruby and press Enter.
Welcome to the Phusion Passenger Apache 2 module installer, v6.0.18.
This installer will guide you through the entire installation process. It
shouldn't take more than 3 minutes in total.
Here's what you can expect from the installation process:
1. The Apache 2 module will be installed for you.
2. You'll learn how to configure Apache.
3. You'll learn how to deploy a Ruby on Rails application.
Don't worry if anything goes wrong. This installer will advise you on how to
solve any problems.
Press Enter to continue, or Ctrl-C to abort.
--------------------------------------------
Installation through RPMs recommended
It looks like you are on a Red Hat or CentOS operating system, with SELinux
enabled. SELinux is a security mechanism for which special Passenger-specific
configuration is required. We supply this configuration as part of
our Passenger RPMs.
However, Passenger is currently installed through gem or tarball and does not
include any SELinux configuration. Therefore, we recommend that you:
1. Uninstall your current Passenger install.
2. Reinstall Passenger through the RPMs that we provide:
https://www.phusionpassenger.com/library/install/apache/yum_repo/
What would you like to do?
Press Ctrl-C to exit this installer so that you can install RPMs (recommended)
-OR-
Press Enter to continue using this installer anyway
--------------------------------------------
Which languages are you interested in?
Use to select.
If the menu doesn't display correctly, press '!'
‣ ⬢ Ruby
⬡ Python
⬡ Node.js
⬡ Meteor
--------------------------------------------
Checking for required software...
* Checking for C compiler...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/bin/cc
* Checking for C++ compiler...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/bin/c++
* Checking for Curl development headers with SSL support...
Found: yes
curl-config location: /usr/bin/curl-config
Header location: /usr/include/curl/curl.h
Version: libcurl 7.61.1
Usable: yes
Supports SSL: yes
* Checking for Zlib development headers...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/include/zlib.h
* Checking for Apache 2...
Found: yes
Location of httpd: /usr/sbin/httpd
Apache version: 2.4.37
* Checking for Rake (associated with /usr/bin/ruby)...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/bin/ruby /opt/redmine/bin/rake
* Checking for OpenSSL support for Ruby...
Found: yes
* Checking for RubyGems...
Found: yes
* Checking for Ruby development headers...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/include/ruby.h
* Checking for rack...
Found: yes
* Checking for OpenSSL development headers...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/include/openssl/ssl.h
* Checking for Apache 2 development headers...
Found: yes
Location of apxs2: /usr/bin/apxs
* Checking for Apache Portable Runtime (APR) development headers...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/bin/apr-1-config
Version: 1.6.3
* Checking for Apache Portable Runtime Utility (APU) development headers...
Found: yes
Location: /usr/bin/apu-1-config
Version: 1.6.1
--------------------------------------------
Checking whether there are multiple Apache installations...
Only a single installation detected. This is good.
--------------------------------------------
Compiling and installing Apache 2 module...
You could as well install Phusion Passenger from the RPM repos but I hit a snag with ruby-libs!!
Once the module compilation is done, you are provided with how configure the module on Apache,
...
Almost there!
Please edit your Apache configuration file, and add these lines:
LoadModule passenger_module /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18/buildout/apache2/mod_passenger.so
PassengerRoot /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18
PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/bin/ruby
After you restart Apache, you are ready to deploy any number of web
applications on Apache, with a minimum amount of configuration!
Press ENTER when you are done editing.
Before you can press Enter to complete the Module installation and setup, open a new login session as privileged user and create/update the Redmine Apache configuration file.
Create Apache virtual host configuration for Redmine with the following content and configure it to load the passenger modules. Replace the Server Name accordingly and ensure it is resolvable if using domain name. You can as well change the default port if you want.
vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/redmine.confListen 3000
LoadModule passenger_module /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18/buildout/apache2/mod_passenger.so
<IfModule mod_passenger.c>
PassengerRoot /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18
PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/bin/ruby
</IfModule>
<VirtualHost *:3000>
ServerName redmine.kifarunix-demo.com
DocumentRoot "/opt/redmine/public"
CustomLog logs/redmine_access.log combined
ErrorLog logs/redmine_error_log
LogLevel warn
<Directory "/opt/redmine/public">
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
AllowOverride all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Verify Apache configuration syntax.
httpd -t
Syntax OK
Once the installation and setup of Apache Passenger module is complete, restart Apache
systemctl restart httpd
Press ENTER on the Passenger module installation shell to validate the configurations.
Press ENTER when you are done editing.
--------------------------------------------
Validating installation...
* Checking whether this Passenger install is in PATH... (!)
Please add /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18/bin to PATH.
Otherwise you will get "command not found" errors upon running
any Passenger commands.
Learn more at about PATH at:
https://www.phusionpassenger.com/library/indepth/environment_variables.html#the-path-environment-variable
* Checking whether there are no other Passenger installations... (!)
You are currently validating against Phusion Passenger(R) 6.0.18, located in:
/opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18/bin/passenger
Besides this Passenger installation, the following other
Passenger installations have also been detected:
/opt/redmine/bin/passenger
Please uninstall these other Passenger installations to avoid
confusion or conflicts.
* Checking whether Apache is installed... ✓
* Checking whether the Passenger module is correctly configured in Apache... ✓
Detected 0 error(s), 2 warning(s).
Press ENTER to continue.
--------------------------------------------
Deploying a web application
To learn how to deploy a web app on Passenger, please follow the deployment
guide:
https://www.phusionpassenger.com/library/deploy/apache/deploy/
Enjoy Phusion Passenger, a product of Phusion® (www.phusion.nl) :-)
https://www.phusionpassenger.com
Passenger® is a registered trademark of Phusion Holding B.V.
Check if anything is listening on Port 3000.
ss -altnp
That is awesome.
Install Apache Passenger Module on CentOS Stream 9
Phusion Passenger is a web application server that can be used to server Redmine on production environments.
Install the passenger repo;
curl --fail -sSLo \
/etc/yum.repos.d/passenger.repo \
https://oss-binaries.phusionpassenger.com/yum/definitions/el-passenger.repoInstall the module;
yum install -y mod_passengerWhen installed, it should be enabled by default.
httpd -M | grep passengerpassenger_module (shared)Create Apache virtual host configuration for Redmine with the following content. Replace the server name accordingly. You can as well change the default port if you want.
cat > /etc/httpd/conf.d/redmine.conf << 'EOL'
Listen 3000
<VirtualHost *:3000>
ServerName redmine.kifarunix-demo.com
DocumentRoot "/opt/redmine/public"
CustomLog logs/redmine_access.log combined
ErrorLog logs/redmine_error_log
LogLevel warn
<Directory "/opt/redmine/public">
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
AllowOverride all
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
EOL
Verify Apache configuration syntax.
httpd -tSyntax OKOnce the installation and setup of Apache Passenger module is complete, restart Apache
systemctl restart httpdCheck if anything is listening on Port 3000.
lsof -i :3000COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
httpd 28283 root 6u IPv6 74009 0t0 TCP *:hbci (LISTEN)
httpd 28323 apache 6u IPv6 74009 0t0 TCP *:hbci (LISTEN)
httpd 28325 apache 6u IPv6 74009 0t0 TCP *:hbci (LISTEN)
httpd 28326 apache 6u IPv6 74009 0t0 TCP *:hbci (LISTEN)
That is awesome.
If lsof command is not installed, install it as follows;
yum install lsof -yAccess Redmine from Browser
Since we have already opened port 3000/tcp on firewallD, you should be able to access Redmine web interface now.
Replace the server-IP-or-Hostname accordingly.
http://server-IP-or-Hostname:3000
Ensure the port is opened on the firewall.
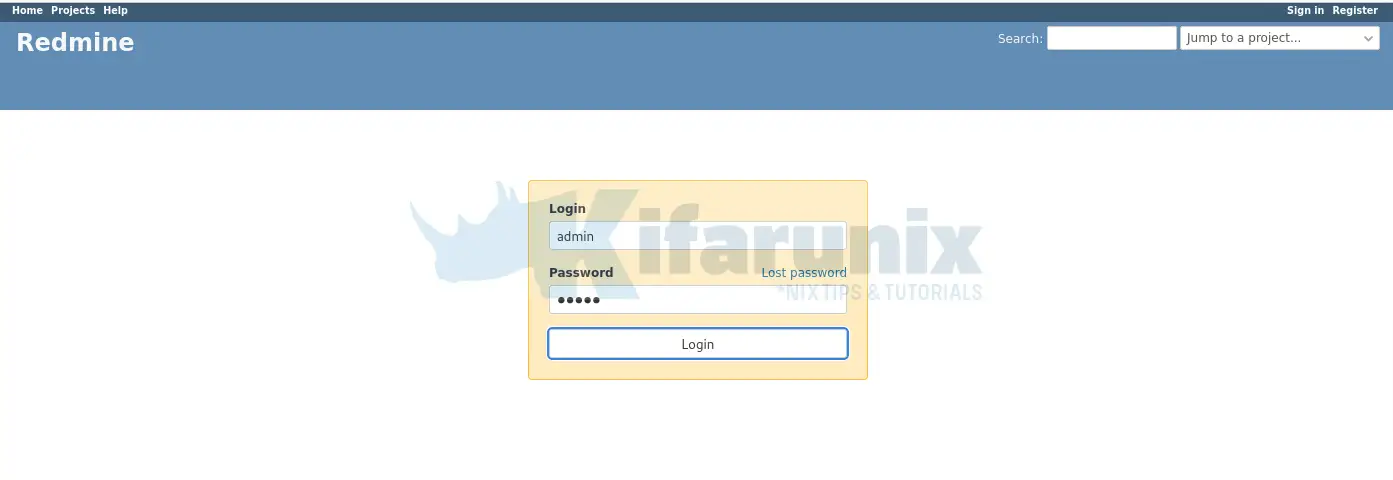
Default login credentials given above.
If you get the error below;
We're sorry, but something went wrong.
The issue has been logged for investigation. Please try again later.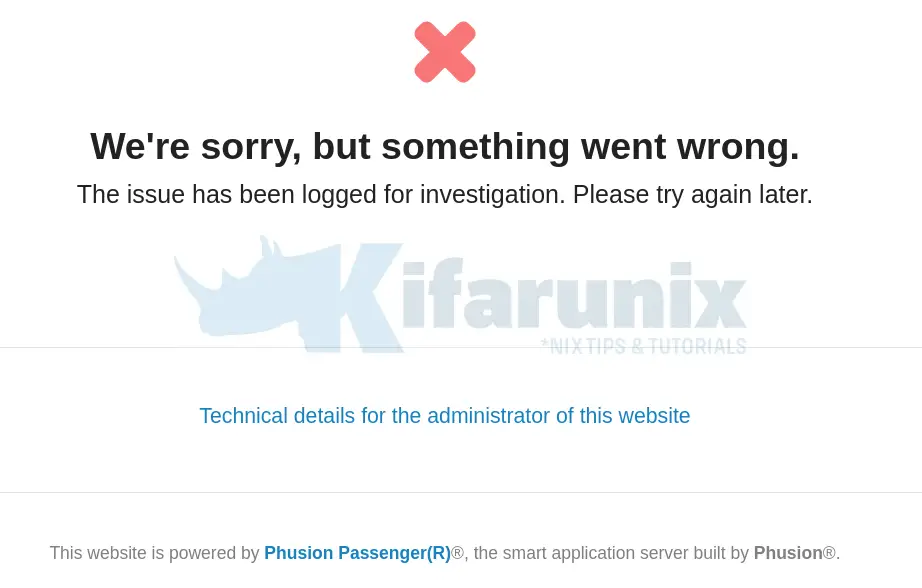
You may also come across such errors in Apache logs;
tail -f /var/log/httpd/error_log[ pid=20914 ] **************** LOOK ABOVE FOR CRASH DETAILS ****************
[ W 2023-11-13 08:45:56.7052 20325/T4 age/Wat/AgentWatcher.cpp:94 ]: Passenger core (pid=20914) crashed with signal SIGABRT, restarting it...
[ N 2023-11-13 08:45:56.7285 21003/T1 age/Cor/CoreMain.cpp:1340 ]: Starting Passenger core...
[ N 2023-11-13 08:45:56.7287 21003/T1 age/Cor/CoreMain.cpp:256 ]: Passenger core running in multi-application mode.
[ W 2023-11-13 08:45:56.7352 21003/T1 age/Cor/CoreMain.cpp:1007 ]: WARNING: potential privilege escalation vulnerability detected. Phusion Passenger(R) is running as root, and part(s) of the Passenger root path (/opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18) can be changed by non-root user(s):
- /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.18 is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
- /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby/gems is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
- /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem/ruby is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
- /opt/redmine/.local/share/gem is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
- /opt/redmine/.local/share is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
- /opt/redmine/.local is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
- /opt/redmine is not secure: it can be modified by user redmine
Please either fix up the permissions for the insecure paths, or install Passenger in a different location that can only be modified by root.
[ N 2023-11-13 08:45:56.7352 21003/T1 age/Cor/CoreMain.cpp:1015 ]: Passenger core online, PID 21003
[ N 2023-11-13 08:45:58.7776 21003/T4 age/Cor/SecurityUpdateChecker.h:519 ]: Security update check: no update found (next check in 24 hours)
You need to sort your SELinux permissions.
Phusion Passenger when not installed from the repositories does not come with SELinux policy modules and thus may not work well with SELinux enabled.
To make this simple, just disable SELinux and reboot your system and then access Redmine again on browser.
setenforce 0sed -i 's/=enforcing/=disabled/' /etc/selinux/configOtherwise if you want to keep SELinux running, generate a custom SELinux module for Phusion Passenger for any denied entry in /var/log/audit/audit.log and install it. For example;
dnf install policycoreutils-python-utils
grep -i denied /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep -iE "Passenger|httpd" | audit2allow -a -M passenger
This command generated a policy package that can be installed by running;
semodule -i passenger.pp
With SELinux issues fixed, login to Redmine using admin for both user and password.
You are prompted to reset the password. Do reset and proceed to login to Redmine web interface.
After login, reset the password and proceed to setup your Redmine profile on CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9.
Once your profile is setup, you can jump to new project.
That marks the end of our guide on how to install Redmine on CentOS Stream 8|CentOS Stream 9. You can now explore this awesome tool.
Reference
Other CentOS Guides
Install Robo 3T MongoDB GUI Tool on CentOS 8
Install MongoDB Community Edition on CentOS 8


thank you for your tutorial, I mashed them together (with the mariadb) into a script
here you go
https://pastebin.com/Bz44101C
echo “LoadModule passenger_module /opt/redmine/.gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.4/buildout/apache2/mod_passenger.so” \ > /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-passenger.conf
Create Apache virtual host configuration for Redmine with the following content. Replace the server name accordingly. You can as well change the default port if you want.
Listen 3000
PassengerRoot /opt/redmine/.gem/ruby/gems/passenger-6.0.4
PassengerDefaultRuby /usr/bin/ruby
ServerName redmine.kifarunix-demo.com
DocumentRoot “/opt/redmine/public”
CustomLog logs/redmine_access.log combined
ErrorLog logs/redmine_error_log
LogLevel warn
Options Indexes ExecCGI FollowSymLinks
Require all granted
AllowOverride all
How do i add this ?
Can be done on the Apache configuration file for Redmine.