In this guide, you will learn how to install Nagios Server on Oracle Linux 9. Nagios provides enterprise-class Open Source IT monitoring, network monitoring, server and applications monitoring.
Install Nagios Server on Oracle Linux 9
Run System Update
Resynchronize your system packages to their latest versions.
dnf updateInstall Required Build Tools
The default Oracle Linux repositories do not provide Nagios Core packages. As a result, in this guide, we are going to build Nagios Core from the source code. As such there are packages and build tools that you need to install. Run the command below to install them.
dnf install gcc glibc glibc-common perl httpd php php-cli php-fpm wget net-snmp gd gd-devel openssl openssl-develDownload Nagios Core Source Code
Navigate to the Nagios Core downloads page and grab the latest Nagios core source code. Nagios v4.4.6 is the current stable release as of this guide.
Get the latest stable release version number and substitute the value of the $VER variable below and use wget to download the file.
VER=4.4.7wget https://assets.nagios.com/downloads/nagioscore/releases/nagios-$VER.tar.gzExtract the Nagios Source Code
Once the Nagios source is downloaded, extract it by running the command;
tar xzf nagios-$VER.tar.gzInstalling Nagios Core
Next, navigate to the Nagios source code directory.
cd nagios-$VER/Configure Nagios Core on Oracle Linux 9
Run the configuration script to adapt Nagios to your system and check if all required dependencies and build tools are in place.
./configureIf the configuration is successful, you will be provided with the summary;
Creating sample config files in sample-config/ ...
*** Configuration summary for nagios 4.4.7 2022-04-14 ***:
General Options:
-------------------------
Nagios executable: nagios
Nagios user/group: nagios,nagios
Command user/group: nagios,nagios
Event Broker: yes
Install ${prefix}: /usr/local/nagios
Install ${includedir}: /usr/local/nagios/include/nagios
Lock file: /run/nagios.lock
Check result directory: /usr/local/nagios/var/spool/checkresults
Init directory: /lib/systemd/system
Apache conf.d directory: /etc/httpd/conf.d
Mail program: /bin/mail
Host OS: linux-gnu
IOBroker Method: epoll
Web Interface Options:
------------------------
HTML URL: http://localhost/nagios/
CGI URL: http://localhost/nagios/cgi-bin/
Traceroute (used by WAP):
Review the options above for accuracy. If they look okay,
type 'make all' to compile the main program and CGIs.
Compile Nagios Core on Oracle Linux 9
Next, proceed to compile Nagios Main program and CGIs.
make allIf the main program and CGIs compiled without any errors, proceed to install Nagios Server on Oracle Linux, and its configurations.
Sample compilation output;
*** Compile finished ***
If the main program and CGIs compiled without any errors, you
can continue with testing or installing Nagios as follows (type
'make' without any arguments for a list of all possible options):
make test
- This runs the test suite
make install
- This installs the main program, CGIs, and HTML files
make install-init
- This installs the init script in /lib/systemd/system
make install-daemoninit
- This will initialize the init script
in /lib/systemd/system
make install-groups-users
- This adds the users and groups if they do not exist
make install-commandmode
- This installs and configures permissions on the
directory for holding the external command file
make install-config
- This installs *SAMPLE* config files in /usr/local/nagios/etc
You'll have to modify these sample files before you can
use Nagios. Read the HTML documentation for more info
on doing this. Pay particular attention to the docs on
object configuration files, as they determine what/how
things get monitored!
make install-webconf
- This installs the Apache config file for the Nagios
web interface
make install-exfoliation
- This installs the Exfoliation theme for the Nagios
web interface
make install-classicui
- This installs the classic theme for the Nagios
web interface
*** Support Notes *******************************************
If you have questions about configuring or running Nagios,
please make sure that you:
- Look at the sample config files
- Read the documentation on the Nagios Library at:
Nagios Library
before you post a question to one of the mailing lists.
Also make sure to include pertinent information that could
help others help you. This might include:
- What version of Nagios you are using
- What version of the plugins you are using
- Relevant snippets from your config files
- Relevant error messages from the Nagios log file
For more information on obtaining support for Nagios, visit:
Nagios Support Home
*************************************************************
Enjoy.
Create Nagios User and Group
Nagios runs as non-privileged nagios user. As such, you need to create a Nagios system user and group.
make install-groups-usersAdd Apache user to the Nagios group.
usermod -aG nagios apacheInstall Nagios Core on Oracle Linux 9
Install Nagios main program, CGIs, and HTML files.
make installInstall Nagios Systemd Service
Install Nagios Systemd initialization scripts.
make install-daemoninitInstall Nagios Commands
Install and configure the external command file as well as the permissions on the directory holding the external commands file.
make install-commandmodeInstall Nagios Configuration Files
Install Nagios Sample configuration file.
make install-configThis command installs Nagios sample configuration files in /usr/local/nagios/etc.
Install Nagios Apache Configuration files
Next, install the Apache HTTP server configuration files for Nagios.
make install-webconfSetup Nagios Apache Authentication
To setup Nagios Web authentication, you need to create an Apache user for authentication. This can be done using the htpasswd command.
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadminThe user, nagiosadmin, is used by default.
If you need to use a different user, you need to replace all the occurences of nagiosadmin on the /usr/local/nagios/etc/cgi.cfg file with the user you created.
For example, if you use a user like monadmin, replace nagiosadmin as shown below.
sed -i 's/nagiosadmin/monadmin/g' /usr/local/nagios/etc/cgi.cfgIf you also want to use a different authentication user file instead of, /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users, ensure you edit the Nagios Apache configuration file, /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf and change the value of AuthUserFile.
Set the ownership of the Nagios Apache authentication configuration file to web-server user, apache.
chown apache:apache /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.usersAdjust the file permissions appropriately such that the owner (apache) have read write access, the group has read access.
chmod 640 /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.usersStart Apache Web server
Once you are done with configuration, start and enable Apache to run on system boot.
systemctl enable httpd --nowIf firewallD is running on your system, be sure to enable external access to Apache.
firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadStart Nagios Core service
Start and enable Nagios service to run on system boot.
systemctl enable nagios --nowTo check the status
systemctl status nagios● nagios.service - Nagios Core 4.4.7
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nagios.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2022-09-14 19:25:36 EAT; 2min 37s ago
Docs: https://www.nagios.org/documentation
Process: 775 ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 782 ExecStart=/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 790 (nagios)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 15848)
Memory: 19.4M
CPU: 101ms
CGroup: /system.slice/nagios.service
├─790 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
├─792 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios --worker /usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.qh
├─793 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios --worker /usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.qh
├─794 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios --worker /usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.qh
├─795 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios --worker /usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.qh
└─810 /usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Sep 14 19:25:36 localhost nagios[790]: wproc: Registry request: name=Core Worker 792;pid=792
Sep 14 19:25:36 localhost nagios[790]: wproc: Registry request: name=Core Worker 793;pid=793
Sep 14 19:25:36 localhost nagios[790]: Successfully launched command file worker with pid 810
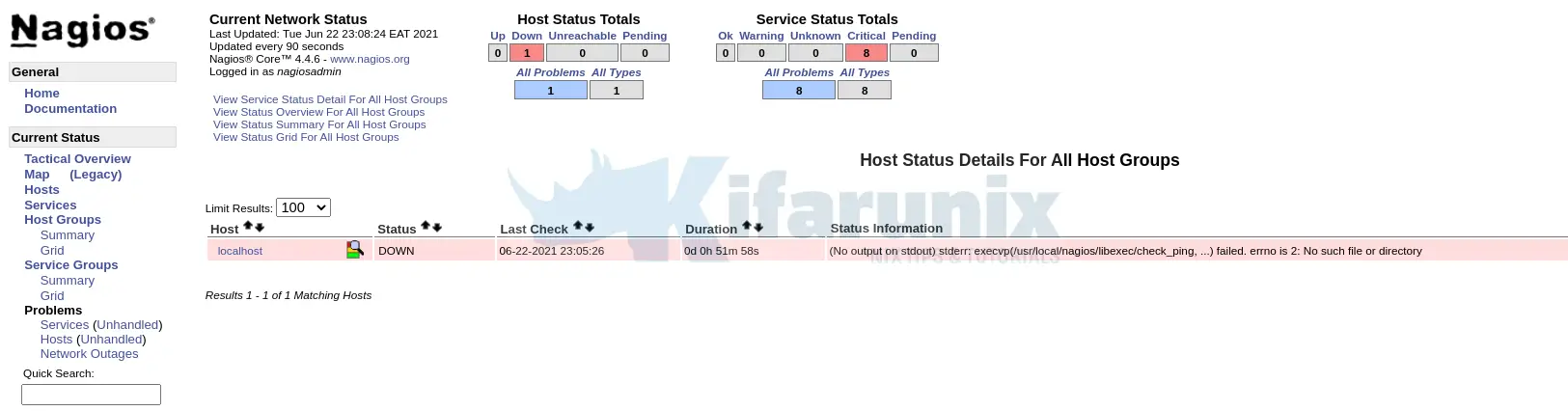
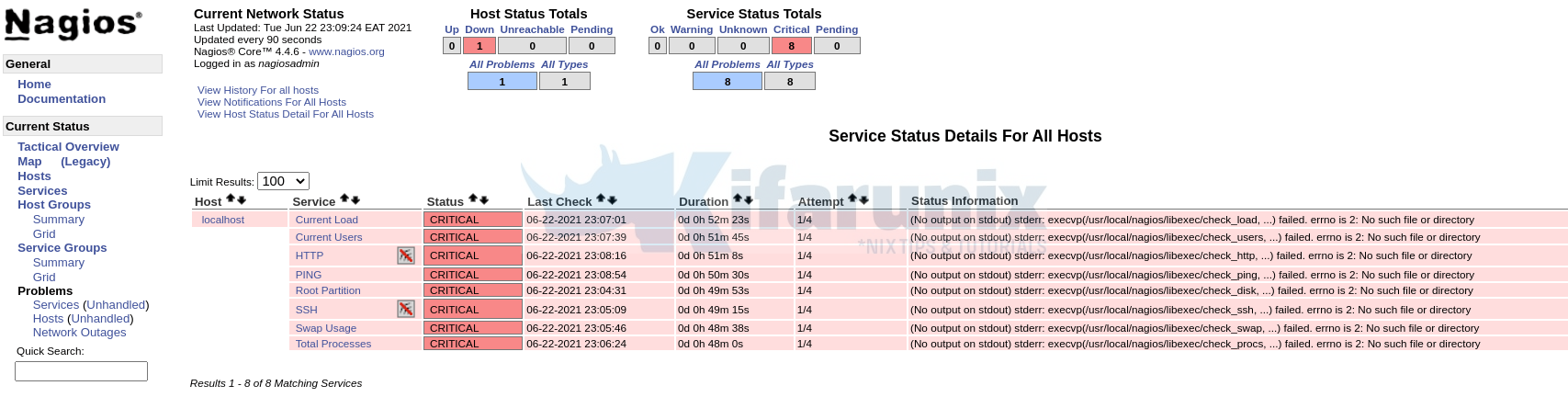
Sep 14 19:25:36 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: HOST ALERT: localhost;DOWN;SOFT;1;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_ping, ...) failed>
Sep 14 19:26:13 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: SERVICE ALERT: localhost;Current Load;CRITICAL;HARD;1;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/che>
Sep 14 19:26:36 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: HOST ALERT: localhost;DOWN;SOFT;2;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_ping, ...) failed>
Sep 14 19:26:51 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: SERVICE ALERT: localhost;Current Users;CRITICAL;HARD;1;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/ch>
Sep 14 19:27:28 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: SERVICE ALERT: localhost;HTTP;CRITICAL;HARD;1;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_http,>
Sep 14 19:27:36 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: HOST ALERT: localhost;DOWN;SOFT;3;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_ping, ...) failed>
Sep 14 19:28:06 localhost.localdomain nagios[790]: SERVICE ALERT: localhost;PING;CRITICAL;HARD;1;(No output on stdout) stderr: execvp(/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_ping
You can check Nagios logs at /usr/local/nagios/var/nagios.log.
If the service fails with the error;
Caught SIGSEGV, shutting down...- Either check to ensure that your system is not running out of memory
- or disable updates check by editing the file,
/usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfgand setting the value ofcheck_for_updatesto 0 and restart the service.
If for some reasons you want to configure Apache to server Nagios on a different port apart from port 80, then insert the following lines in the Nagios Apache configuration file, /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.conf.
Insert the lines below at the top of the configuration file;
Listen 8888
<VirtualHost *:8888>And the line below at the end of the configuration file;
</VirtualHost>Such that the configuration file looks like below, without comment lines;
grep -Ev "^#|^$" /etc/httpd/conf.d/nagios.confListen 8888
<VirtualHost *:8888>
ScriptAlias /nagios/cgi-bin "/usr/local/nagios/sbin"
<Directory "/usr/local/nagios/sbin">
Options ExecCGI
AllowOverride None
<IfVersion >= 2.3>
<RequireAll>
Require all granted
AuthName "Nagios Access"
AuthType Basic
AuthUserFile /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users
Require valid-user
</RequireAll>
</IfVersion>
<IfVersion < 2.3>
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
AuthName "Nagios Access"
AuthType Basic
AuthUserFile /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users
Require valid-user
</IfVersion>
</Directory>
Alias /nagios "/usr/local/nagios/share"
<Directory "/usr/local/nagios/share">
Options None
AllowOverride None
<IfVersion >= 2.3>
<RequireAll>
Require all granted
AuthName "Nagios Access"
AuthType Basic
AuthUserFile /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users
Require valid-user
</RequireAll>
</IfVersion>
<IfVersion < 2.3>
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
AuthName "Nagios Access"
AuthType Basic
AuthUserFile /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users
Require valid-user
</IfVersion>
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Check Apache configuration syntax;
httpd -tIf SELinux is running, execute the commands below to allow Apache to bind to the new port;
setsebool -P nis_enabled 1Restart both Nagios service and Apache service;
systemctl restart httpd nagiosOpen new port on firewall;
firewall-cmd --add-port=8888/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadAccessing Nagios on Oracle Linux 9
You can now access your Nagios server from the browser using the address http://<server-IP or HOSTNAME>/nagios.
If you changed the port, access it as http://<server-IP or HOSTNAME>:PORT/nagios
You will be prompted to enter username and password created above to login.
Enter the authentication credentials and proceed to Nagios web interface.
You have successfully installed Nagios on Oracle Linux 9.
You can now start monitoring your end points with Nagios.
If you can check, even the status of the localhost and services are down since no Nagios plugins are installed by default.
To start to monitor your hosts with Nagios, you need to install Nagios plugins and the NRPE plugins.
Install Nagios Plugins on Oracle Linux
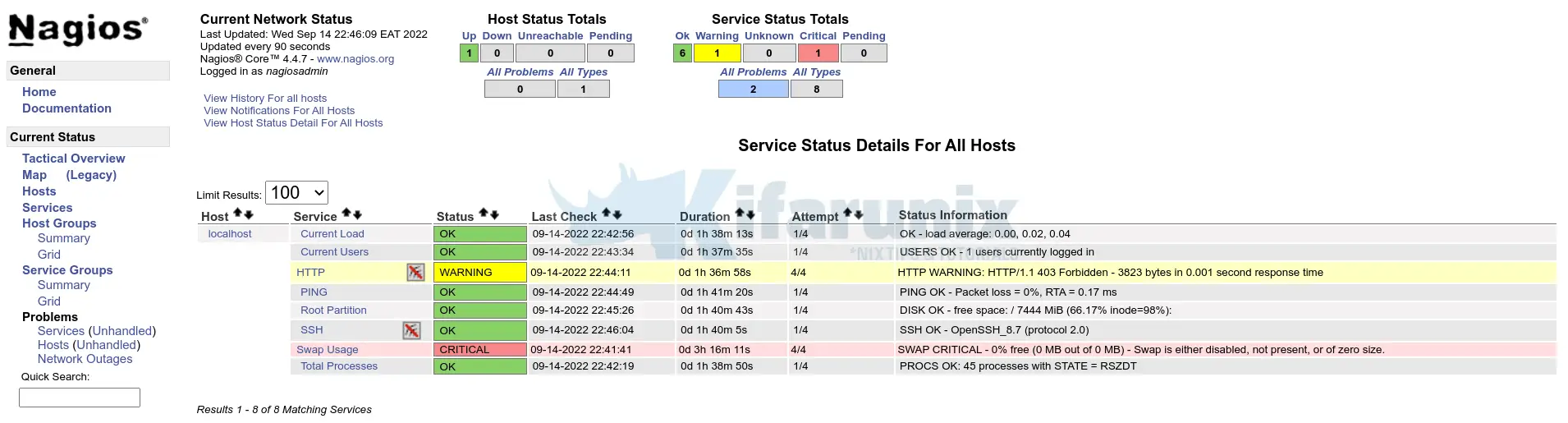
Once you install plugins, services should be ok now;
That marks the end of our tutorial on how to install Nagios Server on Oracle Linux.
You can also check other Nagios Tutorials by following the links below;
Monitor SSL/TLS Certificates Expiry with Nagios