This step-by-step guide provides an easy way to install Kubernetes dashboard on Ubuntu 22.04/20.04. Installing Kubernetes Dashboard on Ubuntu 22.04/20.04 is a simple process that allows you to manage and monitor your Kubernetes clusters efficiently.
Table of Contents
Installing Kubernetes Dashboard on Ubuntu 22.04/20.04
Prerequisites
In order to install Kubernetes dashboard, you need to have a function Kubernetes cluster.
You can check our previous guide on how to setup a Kubernetes cluster on Ubuntu.
Setup Kubernetes Cluster on Ubuntu 22.04/20.04
Installing Kubernetes Dashboard on Cluster Master Node
If you have a multi-node cluster, it is recommended to install Kubernetes dashboard from the control plane.
Therefore, on the K8s cluster master node, run the command below to install Kubernetes dashboard.
Replace the value of the VER variable with the current release version of Kubernetes dashboard.
VER=2.7.0VER=2.7.0 && kubectl apply -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v${VER}/aio/deploy/recommended.yamlSample installation output;
namespace/kubernetes-dashboard created
serviceaccount/kubernetes-dashboard created
service/kubernetes-dashboard created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-certs created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-csrf created
secret/kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder created
configmap/kubernetes-dashboard-settings created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/kubernetes-dashboard created
deployment.apps/kubernetes-dashboard created
service/dashboard-metrics-scraper created
deployment.apps/dashboard-metrics-scraper created
Verify Dashboard Installation
The dashboard installation command will created Pods related to Kubernetes dashboard and dashboard metrics under a namespace called kubernetes-dashboard.
kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
calico-apiserver Active 17h
calico-system Active 17h
default Active 18h
kube-node-lease Active 18h
kube-public Active 18h
kube-system Active 18h
kubernetes-dashboard Active 3m33s
tigera-operator Active 17h
You can view the pods in this namespace as follows;
kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper-5cb4f4bb9c-k2fjk 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
kubernetes-dashboard-6967859bff-qtm52 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
If you want to find out on which node a pod is running, use -o wide option.
kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
dashboard-metrics-scraper-5cb4f4bb9c-qj4cx 1/1 Running 0 44m 10.100.196.133 node01 <none> <none>
kubernetes-dashboard-6967859bff-2ftjt 1/1 Running 0 44m 10.100.186.197 node03 <none> <none>
You can get more details about the Kubernetes dashboard by running the command below;
kubectl describe pod kubernetes-dashboard-6967859bff-qtm52 -n kubernetes-dashboard
Name: kubernetes-dashboard-6967859bff-qtm52
Namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
Priority: 0
Service Account: kubernetes-dashboard
Node: node01/192.168.56.120
Start Time: Sun, 21 May 2023 13:15:52 +0000
Labels: k8s-app=kubernetes-dashboard
pod-template-hash=6967859bff
Annotations: cni.projectcalico.org/containerID: 60184809005e6b9197f13b6587042b10ff659f6a55e5e56ff71c0d77aa5ab168
cni.projectcalico.org/podIP: 10.100.196.132/32
cni.projectcalico.org/podIPs: 10.100.196.132/32
Status: Running
SeccompProfile: RuntimeDefault
IP: 10.100.196.132
IPs:
IP: 10.100.196.132
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/kubernetes-dashboard-6967859bff
Containers:
kubernetes-dashboard:
Container ID: containerd://f6055806fbe4dcbcd94c30201b3c8bfab1c536e4b5ba5e5dc17cfbf247e8ae46
Image: kubernetesui/dashboard:v2.7.0
Image ID: docker.io/kubernetesui/dashboard@sha256:2e500d29e9d5f4a086b908eb8dfe7ecac57d2ab09d65b24f588b1d449841ef93
Port: 8443/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
Args:
--auto-generate-certificates
--namespace=kubernetes-dashboard
State: Running
Started: Sun, 21 May 2023 13:16:45 +0000
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Liveness: http-get https://:8443/ delay=30s timeout=30s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment:
Mounts:
/certs from kubernetes-dashboard-certs (rw)
/tmp from tmp-volume (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-667hl (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
kubernetes-dashboard-certs:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
Optional: false
tmp-volume:
Type: EmptyDir (a temporary directory that shares a pod's lifetime)
Medium:
SizeLimit:
kube-api-access-667hl:
Type: Projected (a volume that contains injected data from multiple sources)
TokenExpirationSeconds: 3607
ConfigMapName: kube-root-ca.crt
ConfigMapOptional:
DownwardAPI: true
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: kubernetes.io/os=linux
Tolerations: node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule
node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 6m6s default-scheduler Successfully assigned kubernetes-dashboard/kubernetes-dashboard-6967859bff-qtm52 to node01
Normal Pulling 6m4s kubelet Pulling image "kubernetesui/dashboard:v2.7.0"
Normal Pulled 5m13s kubelet Successfully pulled image "kubernetesui/dashboard:v2.7.0" in 50.912542693s (50.912558356s including waiting)
Normal Created 5m13s kubelet Created container kubernetes-dashboard
Normal Started 5m13s kubelet Started container kubernetes-dashboard
Expose Kubernetes Dashboard for External Access
The installation of Kubernetes dashboard also creates a service that is responsible for exposing Kubernetes dashboard application on the network.
kubectl get services -n kubernetes-dashboardNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.109.231.10 <none> 8000/TCP 12m
kubernetes-dashboard ClusterIP 10.110.200.227 <none> 443/TCP 12mThere are different ways in which Kubernetes service can expose an application on the network. The most common ones;
ClusterIP– This is the default type of service and exposes the application on an internal IP address in the cluster. This type of service is only reachable from within the cluster.NodePort– This type of service exposes the application on the same port of each selected Node in the cluster using NAT. This makes the service accessible from outside the cluster using<NodeIP>:<NodePort>. The default NodePort range is 30000-32767.LoadBalancer– This type of service creates an external load balancer in the current cloud (if supported) and assigns a fixed, external IP to the service. This makes the service accessible from outside the cluster using the external IP address. The external IP address is assigned by the cloud provider and is not managed by Kubernetes.
By default, Kubernetes dashboard is exposed via ClusterIP service type and hence, can only be accessed within the cluster.
In order for use to easily access Kubernetes dashboard, I will reconfigure the service to expose the application via the NodePort service type.
kubectl edit service kubernetes-dashboard -n kubernetes-dashboardBy default, this is how the Kubernetes dashboard is set;
# Please edit the object below. Lines beginning with a '#' will be ignored,
# and an empty file will abort the edit. If an error occurs while saving this file will be
# reopened with the relevant failures.
#
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"v1","kind":"Service","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"k8s-app":"kubernetes-dashboard"},"name":"kubernetes-dashboard","namespace":"kubernetes-dashboard"},"spec":{"ports":[{"port":443,"targetPort":8443}],"selector":{"k8s-app":"kubernetes-dashboard"}}}
creationTimestamp: "2023-05-21T13:15:52Z"
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
resourceVersion: "28313"
uid: c70844c4-3795-4491-9986-3dab8c1090d2
spec:
clusterIP: 10.110.200.227
clusterIPs:
- 10.110.200.227
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8443
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
We will update this service and change the service type from ClusterIP to NodePort and bind it to static Node port.
Under spec: section, we added;
nodePort: 30001under ports.- changed
type: ClusterIPtotype: NodePort.
...
spec:
clusterIP: 10.110.200.227
clusterIPs:
- 10.110.200.227
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8443
nodePort: 30001
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
status:
loadBalancer: {}
Be sure not to assign a node port that is already being used by a service in the cluster.
You can check which Node ports are currently in use using the command below;
kubectl get services --all-namespaces -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.spec.ports[*].nodePort}{"\n"}{end}'Save and exit the service.
The changes will be applied automatically. You can confirm by checking the service again;
kubectl get services -n kubernetes-dashboard
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.109.231.10 <none> 8000/TCP 44m
kubernetes-dashboard NodePort 10.110.200.227 <none> 443:30001/TCP 44m
The type has now changed to NodePort and the internal port 443 is mapped to port 30001/tcp which can be accessed via any cluster nodes’ IPs.
Create Kubernetes Dashboard Admin User Account
Create user and assign admin riles
Kubernetes dashboard doesn’t come with default user account. To create an admin user account, create a service account manifest file as follows;
vim kubernetes-dashboard-admin-user.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
Create the account;
kubectl apply -f kubernetes-dashboard-admin.ymlYou can list service accounts using the command below;
kubectl get serviceaccounts -n kubernetes-dashboardGenerate Access Token
A service account requires a token that can be used to login to Kubernetes dashboard. To generate a token for the dashadmin service account we created above, run the command below;
kubectl create token admin-user -n kubernetes-dashboardYou will get get such a string;
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IkVad2xuTHZFb0RSZ3VxazJObHRUeUpTV1cya0l6a21KRERvSmZTNG9aQzgifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiXSwiZXhwIjoxNjg0NzM3MjYzLCJpYXQiOjE2ODQ3MzM2NjMsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZCIsInNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Ijp7Im5hbWUiOiJhZG1pbi11c2VyIiwidWlkIjoiOGJhZWVkYjQtMGMyOC00MDY1LTgxZDctZjY4MTk2YzBiNWFjIn19LCJuYmYiOjE2ODQ3MzM2NjMsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDprdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZDphZG1pbi11c2VyIn0.u_rFMGQPfWKybODPMfnZNnB8HeycXo5cTfB1ga4RXNE4YMZcmRv6nTseNtz4CvgQEvAMAGdgG0BaZSdUPMx1aiUTNwf4mxF3O8n9E4P7z_6kE0NnbWDg14j9jJpAKfN7G_EIY7fngTQ4_5L94teLWKBYKnwlSL2aZCVPtTQ5IlCcO8YHM8AZaoHxMdBICMY_doiWwxLRsXVMNc3FcdQN6W88ALupB9r8RPIEkqyxFcQLK0pofCsX2QImSyV4VNxyiMhQ9x-ONJIYyz0pVehiXQUGqWHUI8y05VAYZzjWIMOEEjn3oA00zc3gvp01Z17t-vAh9JMYfqE92zBruSFc2wAccessing Kubernetes Dashboard
You can now access your Kubernetes dashboard from your browser using any node IP in the cluster on port 30001/tcp and HTTPS, https://Node-IP:30001.
Of course accept the use of insecure SSL cert and proceed.
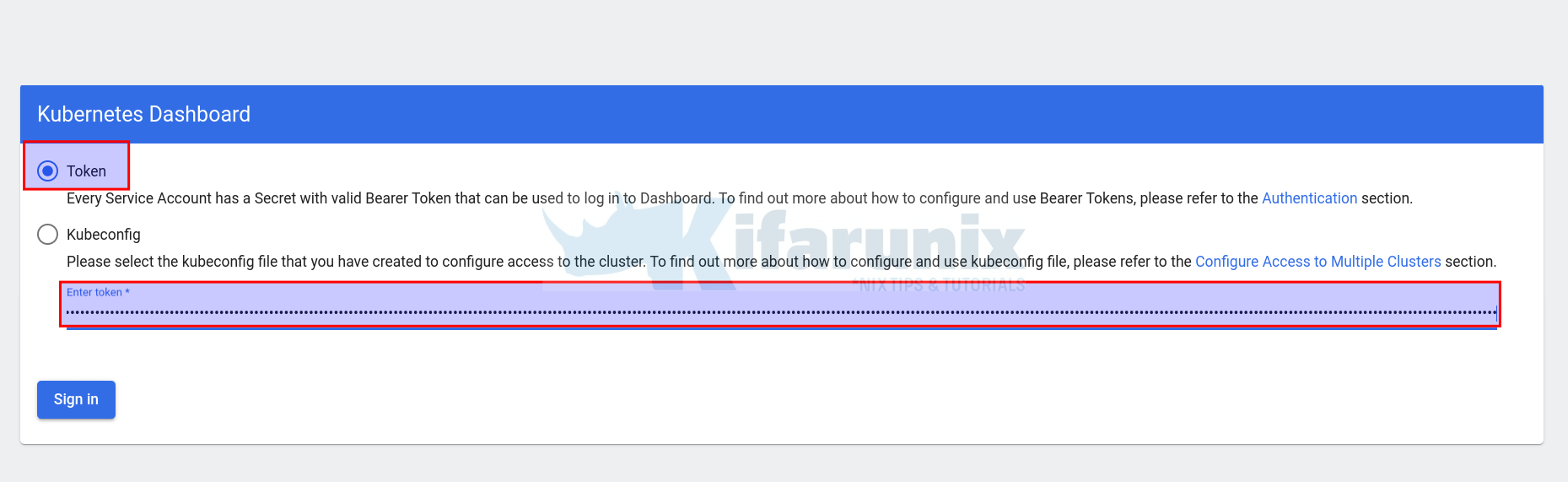
Select Token and paste the token generated above and proceed to sign in.
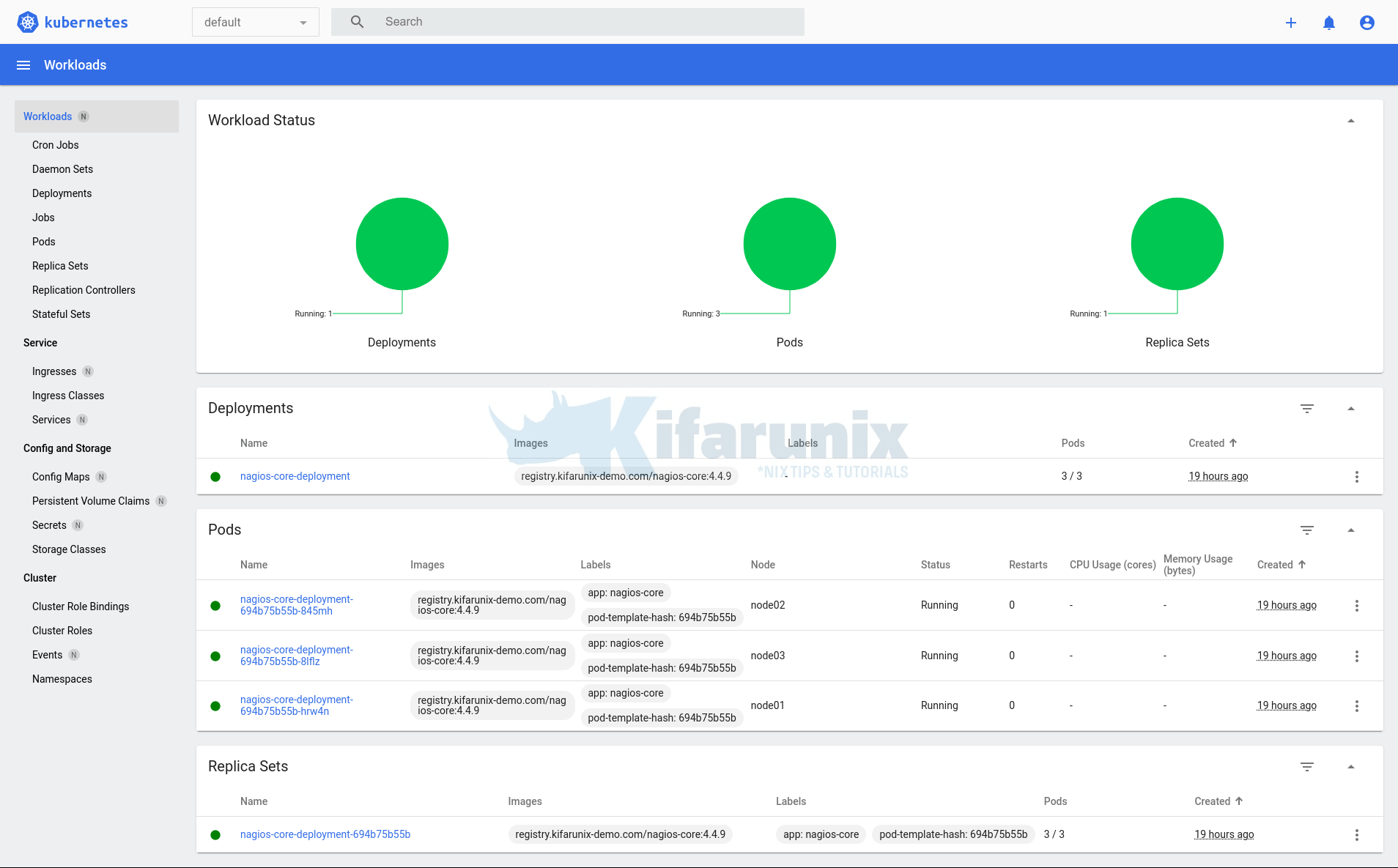
And there you go! landing on Kubernetes dashboard,
You should now be able to manage your cluster from the Kubernetes dashboard. Explore further!
Install Metrics Server
You can see how to integrate Kubernetes dashboard with metrics server to be able to view graphs of the metrics on the dashboard.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Install Metrics Server on Kubernetes
That marks the end of our tutorial on how to installing Kubernetes dashboard on Ubuntu.
Read more on the documentation page.