This guide will walk you through how to install HAProxy on Rocky Linux 8. HAProxy is the current de-facto standard opensource load balancer. It offers high availability, load balancing and proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications.
While offering load balancing, HAProxy supports different algorithms for load balancing. Some of the commonly used ones include;
- Roundrobin – This is the default algorithm and it enables HAProxy to select each server to serve requests in turns according to their weights.
- leastconn – The server with the lowest number of connections receives the connections. It is recommended where very long sessions are expected, such as LDAP, SQL.
- source – With this algorithm, the source IP address is hashed and divided by the total weight of the running servers to designate which server will receive the request. This ensures that the same client IP address will always reach the same server as long as no server goes down or up. If the hash result changes due to the number of running servers changing, many clients will be directed to a different server.
Read more on HAProxy load balancing algorithms on the documentation page.
Installing HAProxy on Rocky Linux 8
For the purposes of demonstrating how HAProxy basically operates, this guide uses uses three virtual machines;
- one running as HAProxy load balancer
- two others running web servers serving basic html pages.
Install HAProxy from the Source on Rocky Linux 8
AS of this writing, HAProxy 2.4.2 is the current stable LTS version as HAProxy.org page.
The default Rocky Linux 8 repositories provides HAProxy 1.8;
dnf info haproxy
Available Packages
Name : haproxy
Version : 1.8.27
Release : 2.el8
Architecture : x86_64
Size : 1.4 M
Source : haproxy-1.8.27-2.el8.src.rpm
Repository : appstream
Summary : HAProxy reverse proxy for high availability environments
URL : http://www.haproxy.org/
License : GPLv2+
In order to install the current stable release version of HAProxy, you need to build from the source then.
Install Required Build Tools
Thus, begin by installing the required build tools.
dnf install gcc pcre-devel tar make openssl-devel readline-devel systemd-devel wget vimInstall LUA 5.3;
wget https://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.3.5.tar.gzcd /tmp/ && tar xzf lua-5.3.5.tar.gzcd lua-5.3.5 && make linux installCreate HAProxy system user
Run the command below to create HAProxy system user.
useradd -M -d /var/lib/haproxy -s /sbin/nologin -r haproxyDownload HAProxy Source Code
Navigate to HAProxy downloads page and grab HAProxy 2.4.2 source code. You can simply use the command below to download it.
wget http://www.haproxy.org/download/2.4/src/haproxy-2.4.2.tar.gz -P /tmpExtract the source code once the download is complete.
cd /tmp/ && tar xzf haproxy-2.4.2.tar.gzInstall HAProxy
cd haproxy-2.4.2make -j $(nproc) TARGET=linux-glibc USE_OPENSSL=1 USE_LUA=1 USE_PCRE=1 USE_SYSTEMD=1sudo make installConfiguring HAProxy on Rocky Linux 8
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg is the default HAProxy configuration file.
However, the directory and the config file are not created when installation is done from the source.
Hence, create the directory;
mkdir /etc/haproxy/Below is a sample HAProxy default configuration file;
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
ssl-default-bind-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
ssl-default-server-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
frontend main
bind *:5000
acl url_static path_beg -i /static /images /javascript /stylesheets
acl url_static path_end -i .jpg .gif .png .css .js
use_backend static if url_static
default_backend app
backend static
balance roundrobin
server static 127.0.0.1:4331 check
backend app
balance roundrobin
server app1 127.0.0.1:5001 check
server app2 127.0.0.1:5002 check
server app3 127.0.0.1:5003 check
server app4 127.0.0.1:5004 check
As you can see on the above configuration file, there are four HAProxy configuration sections;
- The
globalsettings which defines the parameters that apply to all servers running HAProxy - The
defaultsettings section defines the parameters that apply to all proxy subsections in a configuration (frontend,backend, andlisten). - The
frontendsettings section defines the servers’ listening sockets for client connection requests. - The
backendsettings section defines the real server IP addresses as well as the load balancer scheduling algorithm. - Sometimes, both
backendandfrontendcan be combined under thelistensection.
Read more about these sections on HAProxy essential sections or under doc/configuration.txt under the source code directory.
Defining Global HAProxy Settings
In our configuration, here are our global settings as it.
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
ssl-default-bind-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
ssl-default-server-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
Define HAProxy Default Settings
We use these defaults settings as is;
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
Defining HAProxy Frontend Settings
In this section, we will define how HAProxy is externally accessed to enable access to the backend servers. Since most options have been defined on defaults settings section, here is our frontend settings;
frontend lb01
bind 192.168.60.19:80
default_backend kifaruappsWhere;
- bind defines an given IP address and port on which HAProxy listens on.
default_backendgives the name of abackendserver to send traffic to.
Defining HAProxy Backend Settings
On Backend section, define the real backend server IP addresses as well as the load balancer scheduling algorithm.
backend kifaruapps
balance roundrobin
server webapp01 192.168.60.21:8080 check
server webapp02 192.168.59.23:80 check- balance setting defines the roundrobin load balancer scheduling algorithm.
- server setting specify the servers available in the back end.
- check – enables health checks on the server. By default, a server is always considered available. If set, the server is available when accepting periodic TCP connections, to ensure that it is really able to serve requests.
Define HAProxy Listen Settings
You can optionally add the listen section to enable HAProxy statistics. HAProxy provides a dashboard called the HAProxy Stats page that displays the metrics related to the health of your servers, current request rates, response times, and more that gives a granular data on a per-frontend, backend, and server basis.
The Stats page can be enabled as shown below;
listen stats
bind 192.168.60.19:8088 # Bind stats to port 8088
log global # Enable Logging
stats enable # enable statistics reports
stats hide-version # Hide the version of HAProxy
stats refresh 30s # HAProxy refresh time
stats show-node # Shows the hostname of the node
stats auth lbadmin:P@ssword # Authentication for Stats page
stats uri /lb_stats # Statistics URL
Ensure that the stats port is allowed on firewall.
firewall-cmd --add-port=8088/tcp --permanentfirewall-cmd --reloadBe sure to check SELinux logs just in case anything is not accessible.
Finally, this is how our HAProxy configuration file, /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg, is like;
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4000
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
ssl-default-bind-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
ssl-default-server-ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
frontend lb01
bind 192.168.60.19:80
default_backend kifarunixapps
backend kifarunixapps
balance roundrobin
server webapp01 192.168.60.21:8080 check
server webapp02 192.168.59.23:80 check
listen stats
bind 192.168.60.19:8088 # Bind stats to port 8088
stats enable # enable statistics reports
stats hide-version # Hide the version of HAProxy
stats refresh 30s # HAProxy refresh time
stats show-node # Shows the hostname of the node
stats auth lbadmin:P@ssword # Authentication for Stats page
stats uri /lb_stats # Statistics URL
Read more about the configuration options on HAProxy documentation page.
Create HAProxy chroot directory;
mkdir /var/lib/haproxy/Verify HAProxy Configuration
To check HAProxy config file for any syntax errors, run the command below;
haproxy -c -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgIf all is well, you should get such an output;
Configuration file is validOpen HAProxy port on firewall.
firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadRunning HAProxy on Rocky Linux 8
First off, you need to create HAProxy systemd configuration file.
cat > /etc/systemd/system/haproxy.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=HAProxy Load Balancer
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
[Service]
Environment="CONFIG=/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg" "PIDFILE=/run/haproxy.pid"
EnvironmentFile=/etc/sysconfig/haproxy
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/sbin/haproxy -f $CONFIG -c -q $OPTIONS
ExecStart=/usr/local/sbin/haproxy -Ws -f $CONFIG -p $PIDFILE $OPTIONS
ExecReload=/usr/local/sbin/haproxy -f $CONFIG -c -q $OPTIONS
ExecReload=/bin/kill -USR2 $MAINPID
SuccessExitStatus=143
KillMode=mixed
Type=notify
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
echo 'OPTIONS="-Ws"' > /etc/sysconfig/haproxyReload systemd configurations;
systemctl daemon-reloadTo start HAProxy to run the command below;
systemctl start haproxyTo enable it to run on boot;
systemctl enable haproxyCheck the status of HAProxy.
systemctl status haproxy
● haproxy.service - HAProxy Load Balancer
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/haproxy.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2021-07-25 09:57:36 EAT; 4s ago
Process: 39550 ExecStartPre=/usr/local/sbin/haproxy -f $CONFIG -c -q $OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 39552 (haproxy)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4938)
Memory: 3.6M
CGroup: /system.slice/haproxy.service
├─39552 /usr/local/sbin/haproxy -Ws -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg -p /run/haproxy.pid -Ws
└─39555 /usr/local/sbin/haproxy -Ws -f /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg -p /run/haproxy.pid -Ws
Jul 25 09:57:36 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: haproxy.service: Succeeded.
Jul 25 09:57:36 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Stopped HAProxy Load Balancer.
Jul 25 09:57:36 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Starting HAProxy Load Balancer...
Jul 25 09:57:36 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started HAProxy Load Balancer.
Jul 25 09:57:36 localhost.localdomain haproxy[39552]: [NOTICE] (39552) : New worker #1 (39555) forked
Configure HAProxy Logging on Rocky Linux 8
To configure HAProxy standard logging, edit /etc/rsyslog.conf and enable UDP syslog reception on port 514 by removing comments (#) on the lines, #module(load=”imudp”) and #input(type=”imudp” port=”514″) as shown below.
sed -i '/="imudp"/s/^#//g' /etc/rsyslog.confNext, disable logging of private authentication messages sent to local2 facility, (local2.none) on /var/log/messages and enable logging on /var/log/haproxy.log as shown below.
sed -i 's/*.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none/*.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none;local2.none/' /etc/rsyslog.confecho 'local2.* /var/log/haproxy.log' >> /etc/rsyslog.confSave the configuration file and run the command below to check for any errors.
rsyslogd -N1Next, restart Rsyslog and HAProxy
systemctl restart rsyslog haproxyYou should now be able to have HAProxy logs on /var/log/haproxy.log.
tail -f /var/log/haproxy.logConfigure Apache X-Forwarded-For Logging on Backend Servers
Since we have configured HAProxy to add HTTP header “X-Forwarded-For” to all requests sent to the backend server (option forwardfor), you can configure logging for the same on the backend server. This ensures the IP address of the requesting client is captured instead of the HAProxy load balancer.
Configs can be;
- /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Therefore, login to the backend servers and configure Apache to log X-Forwarded-For headers. The default line we are changing is;
...
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
...Hence, edit this line such that it looks like;
...
LogFormat "\"%{X-Forwarded-For}i\" %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
...Save the file and run Apache configuration file syntax check command.
apachectl configtestSyntax OKRestart Apache
systemctl restart httpdor
systemctl restart apache2Testing HAProxy Load Balancer on Rocky Linux 8
To verify that HAProxy is able to load balance the http requests, navigate to browser and access HAProxy using either the hostname or IP address.
Since it is using the roundrobin algorithm, when you refresh the page, you should be able to get content from both backend servers served.

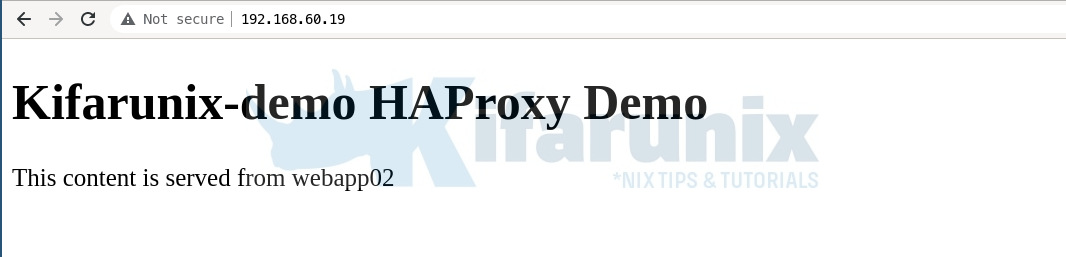
Checking HAProxy Statistics
To check the statistics of your frontend and backend servers, simply navigate to stats url defined on the listen section; http://server-IP_OR_hostname:8088/lb_stats. Set the appropriate URL.
When prompted, authentication using the credentials defined by the stats auth on the listen section, in this demo, lbadmin:P@ssword, for username and password.
HAProxy statistics
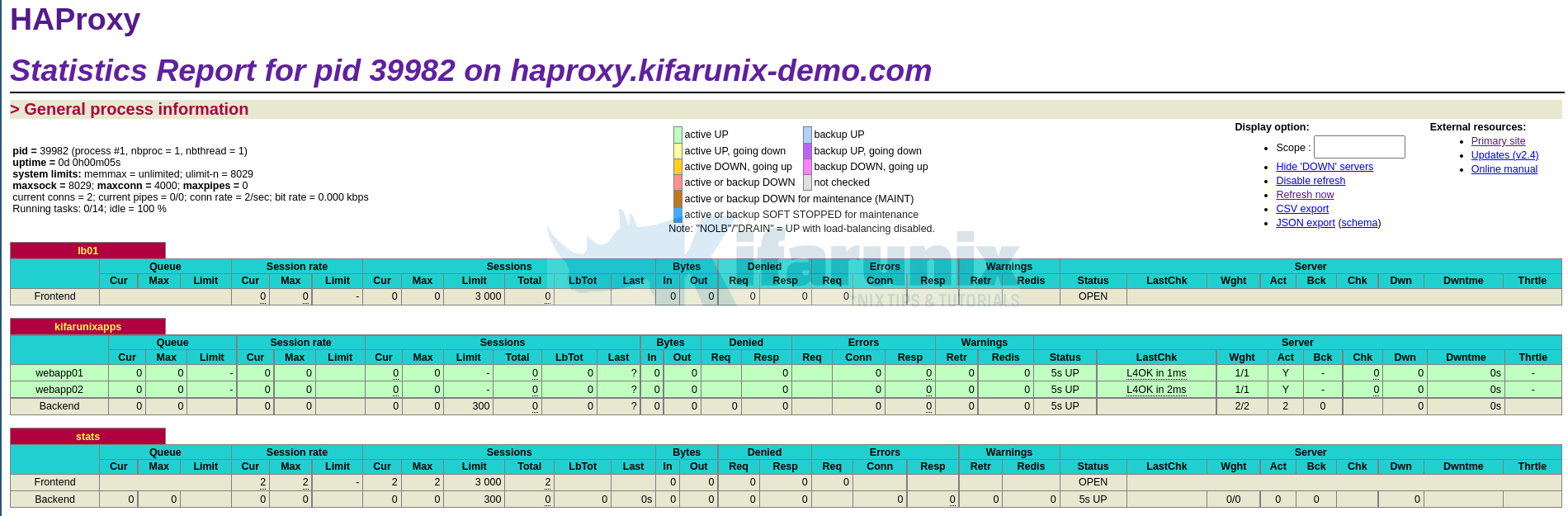
That marks the end of our guide on how to installing HAProxy on Rocky Linux 8.
Read more on HAProxy Documentations.
Related Tutorials
Configure Highly Available HAProxy with Keepalived on Ubuntu 20.04

