In this tutorial, we are going to learn how to install and setup Squid Proxy on Ubuntu 20.04.
Squid is a full-featured web proxy cache application which provides proxy and cache services for HTTP, FTP, SSL requests and DNS lookups. It also performs transparent caching that reduces bandwidth and improves response time by caching and reusing frequently requested web pages.
Installing Squid Proxy on Ubuntu 20.04
Run system update
To begin with, ensure that your system packages are up-to-date.
apt update
apt upgradeInstall Squid Proxy
Squid proxy is available on the default Ubuntu 20.04 repositories.
apt-cache policy squidsquid:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 4.10-1ubuntu1.1
Version table:
4.10-1ubuntu1.1 500
500 http://ke.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-updates/main amd64 Packages
500 http://ke.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal-security/main amd64 Packages
4.10-1ubuntu1 500
500 http://ke.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu focal/main amd64 PackagesTherefore, you can install it by running the command and can be installed by running the command;
apt install squidRunning Squid on Ubuntu 20.04
When installed, Squid is started and enabled to run on system boot;
systemctl status squid
● squid.service - Squid Web Proxy Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/squid.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2020-05-29 14:00:41 UTC; 10min ago
Docs: man:squid(8)
Main PID: 2237 (squid)
Tasks: 4 (limit: 2282)
Memory: 16.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/squid.service
├─2237 /usr/sbin/squid -sYC
├─2239 (squid-1) --kid squid-1 -sYC
├─2240 (logfile-daemon) /var/log/squid/access.log
└─2241 (pinger)
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Using Least Load store dir selection
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Set Current Directory to /var/spool/squid
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Finished loading MIME types and icons.
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: HTCP Disabled.
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Pinger socket opened on FD 14
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Squid plugin modules loaded: 0
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Adaptation support is off.
May 29 14:00:41 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: Accepting HTTP Socket connections at local=[::]:3128 remote=[::] FD 12 flags=9
May 29 14:00:42 ubuntu20 squid[2239]: storeLateRelease: released 0 objects
...
To check if enabled to run on system boot;
systemctl is-enabled squid.serviceenabledConfiguring Squid Proxy Server on Ubuntu 20.04
/etc/squid/squid.conf is the default Squid Proxy configuration. The configuration has the recommended minimum settings. However, we will modify this configuration to make a few changes. You can also have other configurations under /etc/squid/conf.d/ directory.
Make a backup of the default configuration file.
cp /etc/squid/squid.conf{,.old}By default, the Squid configuration file looks like as shown below (with comments removed);
acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN)
acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN)
acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range
acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines
acl SSL_ports port 443
acl Safe_ports port 80 # http
acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp
acl Safe_ports port 443 # https
acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher
acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais
acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports
acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt
acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http
acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker
acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http
acl CONNECT method CONNECT
http_access deny !Safe_ports
http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports
http_access allow localhost manager
http_access deny manager
include /etc/squid/conf.d/*
http_access allow localhost
http_access deny all
http_port 3128
coredump_dir /var/spool/squid
refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080
refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440
refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0
refresh_pattern \/(Packages|Sources)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/Release(|\.gpg)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/InRelease$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern \/(Translation-.*)(|\.bz2|\.gz|\.xz)$ 0 0% 0 refresh-ims
refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320
Configure Squid Access Control Policies
If you already noticed, the above configuration file has ACLs for specific networks and safe ports. You can modify them to include your safe ports as well as the your local networks whose Squid should proxy for.
When defining an ACL, each and every one of them must begin with an acl name and acl type followed by either type-specific arguments or a quoted filename that they are read from;
acl aclname acltype argument ...acl aclname acltype "file" ...When using “file“, the file should contain one item per line.
vim /etc/squid/squid.confIn this tutorial, we will create an ACL for our LAN network, 192.168.57.0/24. We append this line just above the SSL ports ACL. Replace the name of the ACL and the source network appropriately.
acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range
acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines
# My LAN network ACL
acl kifarunix-demo-net src 192.168.57.0/24
...Read more about ACL configuration directives on Squid Wiki page.
You can comment out (adding # at the beginning of the lines) the default ACLs.
# Example rule allowing access from your local networks.
# Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing
# should be allowed
#acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN)
#acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
#acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN)
#acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines
#acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
#acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN)
#acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range
#acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines
# My LAN network ACL
acl kifarunix-demo-net src 192.168.57.0/24
...
Allow or Deny Access Based on defined ACL
Once you have the ACL in place, you can then use the http_access directive to define the ACL allowed or denied to use the proxy to access external network. Therefore, to allow our network, defined by our ACL, kifarunix-demo-net, external access, add the line below;
...
#http_access allow localnet
http_access allow localhost
# Allow kifarunix-demo-net
http_access allow kifarunix-demo-net
# And finally deny all other access to this proxy
http_access deny allThe last entry should always be http_access deny all.
Deny Access to Specific Websites
Access to specific websites can be restricted using Squid Proxy. For example to block access to youtube, facebook, netflix;
- you would have to create a file that defines the domains of these websites as shown below;
- or you would list the domain names, space separated on the ACL statement.
vim /etc/squid/denied-sites.squid.youtube.com
.facebook.com
.netflix.comNext, create an ACL for the restricted sites above in the squid configuration file and set the deny rule for the defined ACL.
acl deniedsites dstdomain "/etc/squid/denied-sites.squid"Or you can list the sites domain;
acl deniedsites dstdomain youtube.com facebook.com netflix.comUpdate squid configuration file.
...
#
# My LAN network ACL
acl kifarunix-demo-net src 192.168.57.0/24
## Sites to Block access to ###
acl deniedsites dstdomain "/etc/squid/denied-sites.squid"
...
...
# Deny access to facebook, youtube, netflix
http_access deny deniedsites
# Allow kifarunix-demo-net
http_access allow kifarunix-demo-net
# And finally deny all other access to this proxy
http_access deny all
Block Sites based on Specific Keywords
You can also restrict access to a website by the use of a keyword. Create a file with specific keywords as shown below;
vim /etc/squid/banned-keywords.squidporn
ads
movie
gambleMake the necessary changes on squid configuration file.
...
#
# My LAN network ACL
acl kifarunix-demo-net src 192.168.57.0/24
...
acl CONNECT method CONNECT
# ACL for Sites to Block Access to
acl deniedsites dstdomain "/etc/squid/denied-sites.squid"
acl keyword-ban url_regex -i "/etc/squid/keyword-ban.squid"
...
# http_access allow localnet
http_access allow localhost
# Deny access to facebook, youtube, netflix
http_access deny deniedsites
# Deny access based on keywords
http_access deny keyword-ban
# Allow kifarunix-demo-net
http_access allow kifarunix-demo-net
# And finally deny all other access to this proxy
http_access deny all
NOTE: http_access entries are processed from top to bottom and depending on which occurs first, access is allowed or denied.
Masking Outgoing Traffic
As much as you use proxy server to anonymize your IP addresses by presenting the IP address of the proxy to other web servers, proxy servers may expose your IP addresses on the outgoing HTTP requests. You can however disable this by including the following directives at the end of your squid configuration file.
Disable Via headers in requests and replies by locating the line, # via on, uncomment and set its value to off.
#Default:
# via on
via offConfigure Squid not to append your client’s IP address in the HTTP requests it forwards by uncommenting the line, # forwarded_for on, and setting the value to off.
#Default:
# forwarded_for on
forwarded_for offRemove Squid proxy headers to avoid revealing identity of Squid proxy server. You can add the lines below under the section, # TAG: request_header_access.
request_header_access From deny all
request_header_access Server deny all
request_header_access WWW-Authenticate deny all
request_header_access Link deny all
request_header_access Cache-Control deny all
request_header_access Proxy-Connection deny all
request_header_access X-Cache deny all
request_header_access X-Cache-Lookup deny all
request_header_access Via deny all
request_header_access X-Forwarded-For deny all
request_header_access Pragma deny all
request_header_access Keep-Alive deny all
Change Squid Default Port
Squid proxy listens on TCP port 3128 by default. To change this port, open the /etc/squid/squid.conf configuration file and replace the value of the http_port with your desired port number.
For example, to change the default port to 8888, as long as no other application is listening on the same port;
...
# Squid normally listens to port 3128
# http_port 3128 << Comment the line by adding #
http_port 8888
...You can also set it to listen on a specific IP (Replace the IP address accordingly)
http_port 192.168.57.8:3128Save and exit the configuration file once you are done with the configuration.
Check Squid Configuration File for Errors
squid -k parseIf there is any syntax error, the erroneous lines will be displayed. Be sure to run this command every time you modify your configuration.
Restart Squid
Once you are done with the configuration, save the file and restart squid.
systemctl restart squidCheck that Squid is listening on defined port. In this case, we didn’t change the default.
ss -altnp | grep 3128LISTEN 0 256 192.168.57.8:3128 0.0.0.0:* users:(("squid",pid=3808,fd=12))Allow Squid Port on Firewall
If UFW is running, allow open squid proxy port;
ufw allow 3128/tcpConfigure Clients to Connect Through Proxy server
To configure end points to connect to internet via Squid proxy server, you can either set system wide proxy configurations, configure client to use the Squid proxy as the gateway or set the proxy settings on the browser.
System Wide proxy configuration on Ubuntu 20.04
To set system wide proxy configurations, create a configuration file under /etc/profile.d with environment variables defining squid proxy server details as follows;
vim /etc/profile.d/squid.shReplace the IP address of the Squid server accordingly.
PROXY_URL="192.168.57.8:3128"
HTTP_PROXY=$PROXY_URL
HTTPS_PROXY=$PROXY_URL
FTP_PROXY=$PROXY_URL
http_proxy=$PROXY_URL
https_proxy=$PROXY_URL
ftp_proxy=$PROXY_URL
export HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY FTP_PROXY http_proxy https_proxy ftp_proxyAfter that, source the new configuration file.
source /etc/profile.d/squid.shTo test this, try to download anything from the clients terminal while tailing access logs on squid proxy server.
On the client’s terminal, run;
wget google.com--2020-06-02 21:24:08-- http://google.com/
Connecting to 192.168.57.8:3128... connected.
Proxy request sent, awaiting response... 301 Moved Permanently
Location: http://www.google.com/ [following]
--2020-06-02 21:24:08-- http://www.google.com/
Reusing existing connection to 192.168.57.8:3128.
Proxy request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: unspecified [text/html]
Saving to: ‘index.html.4’
index.html.4 [ <=> ] 12.36K --.-KB/s in 0.01s
2020-06-02 21:24:08 (971 KB/s) - ‘index.html.4’ saved [12657]On the Squid proxy server;
tail -f /var/log/squid/access.log1591122302.356 0 192.168.57.10 TCP_MEM_HIT/301 629 GET http://google.com/ - HIER_NONE/- text/html
1591122302.642 282 192.168.57.10 TCP_MISS/200 13538 GET http://www.google.com/ - HIER_DIRECT/216.58.223.100 text/htmlConfigure Proxy settings on Firefox browser.
On your Firefox, configure it to connect external network via your Squid server. Preferences > General > Network Settings > Manual Proxy Configuration. Check Use this proxy server for all protocols.
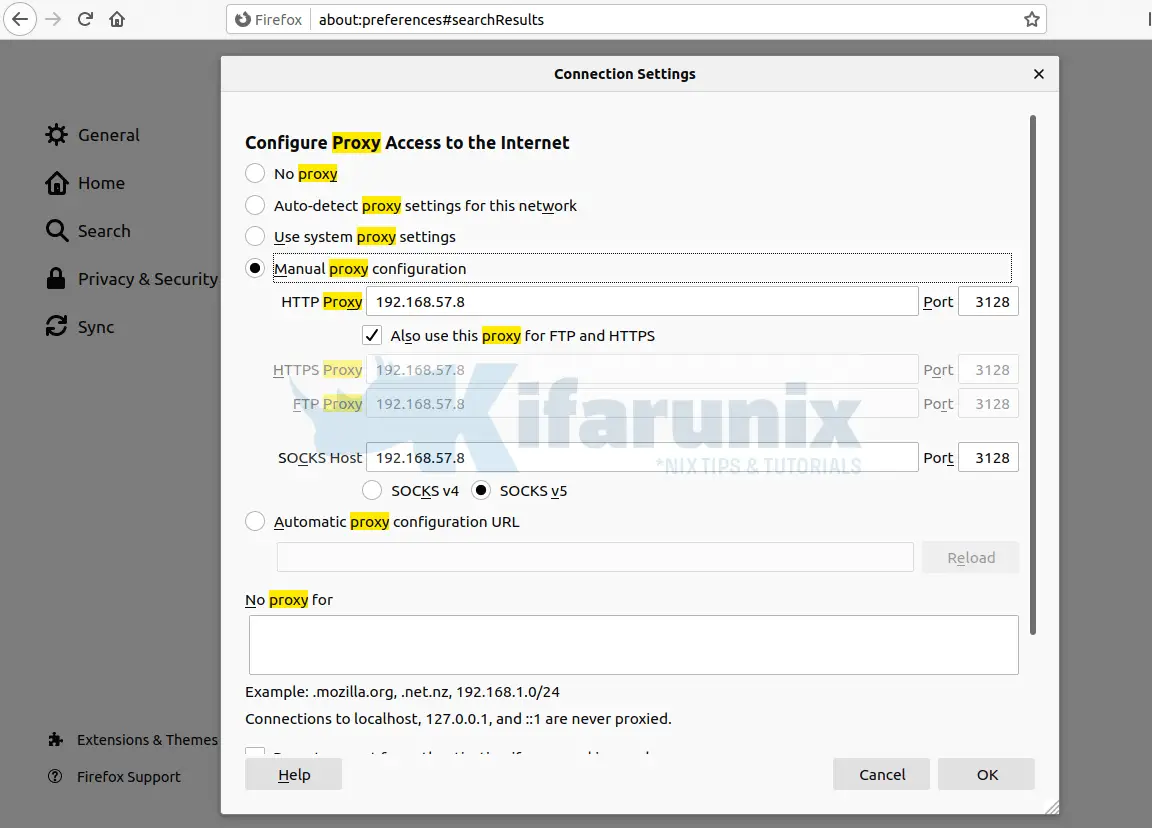
Try to access blocked sites on your browser;
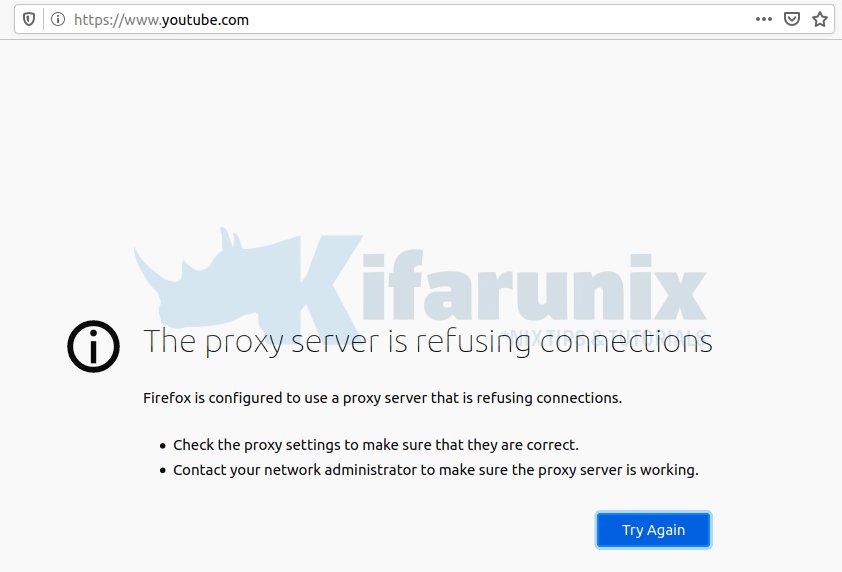
Check the logs.
tail -f /var/log/squid/access.log1591126191.919 0 192.168.57.11 TCP_DENIED/403 3963 CONNECT www.youtube.com:443 - HIER_NONE/- text/htmlAnd that how to basically configure squid proxy to block or deny access to external resources. That marks the end of our tutorial on how to install and configure Squid Proxy on Ubuntu 20.04.
Related Tutorials
Install and Configure Squid Proxy on CentOS 8
Monitor Squid logs with Grafana and Graylog
Create Squid Logs Extractors on Graylog Server
Monitor Squid Access Logs with Graylog Server
Setup Squid Proxy Authentication on Ubuntu 18.04/Fedora 29/28/CentOS 7


Yes. Only one very big problem
Max open files 1024 (must be 65536) /for proc
There is not possible to change this value. Very poor. Ten simultaneously users and squid not responding.