In this guide, we are going to learn how to install and setup GlusterFS storage cluster on CentOS 8. GlusterFS is an opensource distributed and scalable network file system that clusters various disk storage resources into a single global namespace. It is suitable for data-intensive tasks such as cloud storage and media streaming. Some of the common features for GlusterFS include;
- Can scale to several petabytes thus can handle thousands of clients.
- Provides high availability through data mirroring. It also supports self healing mechanism that restores data to the correct state following recovery with nearly no overhead.
- Provides a unified global namespace that clusters disk and memory resources into a single pool that ensures load balanced I/O.
- Uses elastic hash algorithm to locate data in the storage pool hence linear performance scaling.
- Provides elastic volume manager in which data is stored in logical volumes that are abstracted from the hardware and logically partitioned from each other. This ensures that storage can be added or removed while data continues to be online with no application interruption.
- Gluster is fully POSIX-compliant and does not require any unique APIs for data access.
- Supports industry standard protocols like NFS, SMB, CIFS, HTTP and FTP.
Install and Setup GlusterFS Storage Cluster on CentOS 8
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have at least three storage nodes. Check our deployment architecture below.
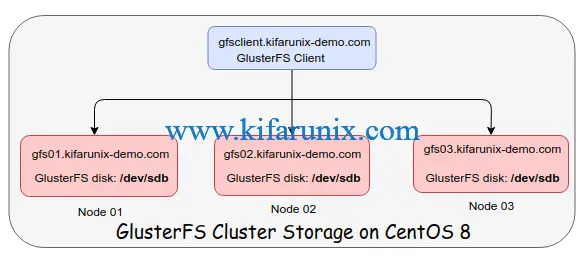
Also, ensure that you have an extract virtual disk apart from the root disk where the OS is installed. In our case above, we have an extra disk, /dev/sdb.
lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 8G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─sda2 8:2 0 7G 0 part
├─cl-root 253:0 0 6.2G 0 lvm /
└─cl-swap 253:1 0 820M 0 lvm [SWAP]
sdb 8:16 0 2G 0 disk
└─sdb1 8:17 0 2G 0 part
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
If using hostnames, ensure that they are resolvable.
Ensure that time is tightly synchronized between the three nodes. If you need to setup your NTP server on a CentOS 8 system, simply follow the link below;
Setup NTP Server using Chrony on CentOS 8
Partition and Format the GlusterFS Storage Drives
On each GlusterFS node, format and create a file system on the storage drive. You can use any partitioning method.
Format and create a primary partition on the disk.
parted /dev/sdb mklabel msdosparted -a opt /dev/sdb mkpart primary xfs 0% 100%Create a Filesystem on the disk. XFS is used here.
mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb1 -L gfsdiskMount GlusterFS Storage Drives (Bricks)
On each node, create a mount point for the GlusterFS storage drive, here in called bricks. A brick is a basic unit of GlusterFS storage.
mkdir -p /export/gfsbrickMount the GlusterFS storage drive on the bricks directory created above.
mount /dev/sdb1 /export/gfsbrick/To automount the drive on system boot, simply update the /etc/fstab configuration file as follows;
echo "/dev/sdb1 /export/gfsbrick/ xfs defaults 1 2" >> /etc/fstabCheck the mounting;
df -hTP /dev/sdb1Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sdb1 xfs 2.0G 47M 2.0G 3% /export/gfsbrickInstall GlusterFS 7 on CentOS 8
Install GlusterFS Repo
Now that the prerequisites part is done, proceed to install GlusterFS on all nodes. GlusterFS is not available on the default repos. Hence, run the command below to create the repo.
dnf install centos-release-glusterEnable PowerTools repos in order to be able to install other required GlusterFS dependencies.
dnf config-manager --set-enabled PowerToolsInstall GlusterFS server package on CentOS 8 by running the command below;
dnf install glusterfs-serverRunning GlusterFS on CentOS 8
Start and enable GlusterFS daemon to run on system boot by executing the command below;
systemctl enable --now glusterdTo check the status of GlusterFS daemon;
systemctl status glusterd
● glusterd.service - GlusterFS, a clustered file-system server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/glusterd.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2020-03-20 19:51:37 EAT; 12s ago
Docs: man:glusterd(8)
Process: 2739 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/glusterd -p /var/run/glusterd.pid --log-level $LOG_LEVEL $GLUSTERD_OPTIONS (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 2740 (glusterd)
Tasks: 9 (limit: 5047)
Memory: 3.9M
CGroup: /system.slice/glusterd.service
└─2740 /usr/sbin/glusterd -p /var/run/glusterd.pid --log-level INFO
Mar 20 19:51:37 gfs01.kifarunix-demo.com systemd[1]: Starting GlusterFS, a clustered file-system server...
Mar 20 19:51:37 gfs01.kifarunix-demo.com systemd[1]: Started GlusterFS, a clustered file-system server.
Allow GlusterFS on Firewall
In order for the GlusterFS nodes to be able to communicate, you need to open certain GlusterFS ports or services on a firewall. The 24007-24008/TCP are used for the communication between nodes, while 24009-24108/TCP are required for client communication. To make this easy, simply use the service, glusterfs.
firewall-cmd --add-service=glusterfs --permanentfirewall-cmd --reloadConfigure GlusterFS Trusted Storage Pool
To configure GlusterFS storage cluster, you first need to create a trusted storage pool (TSP) which basically is a network of storage servers. TSP can be created by adding storage nodes to the TSP using the gluster peer probe command as shown below.
To probe other nodes, eg gfs02 and gfs03 from gfs01 in our case, run the command below. Replace the names of the nodes accordingly. You can probe other nodes from any node.
gluster peer probe gfs02gluster peer probe gfs03To verify cluster peering status, run the command below from any node. Eg from node 1, gfs01;
gluster peer status
Number of Peers: 2
Hostname: gfs01.kifarunix-demo.com
Uuid: b2003be4-4bc9-4125-a2a1-0d46e4b2476f
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: gfs02
Uuid: 6bc3b730-b7bb-4d24-865a-c33a3db4489d
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
To list all nodes in a TSP, eg from GlusterFS node 02, gfs01;
gluster pool list
UUID Hostname State
6bc3b730-b7bb-4d24-865a-c33a3db4489d gfs02 Connected
26cdb6a4-ad15-41e7-bb72-2da0a9906fa6 gfs03 Connected
b2003be4-4bc9-4125-a2a1-0d46e4b2476f localhost Connected
You can be able to add more serves or remove servers from the GlusterFS storage pool;
For example, to add a new server, you need to probe it from a node already in the pool. Replace the server-name accordingly.
gluster peer probe server-nameTo detach a server from the pool;
gluster peer detach server-nameSetup GlusterFS Storage Volume
A GlusterFS storage volume can be created from the bricks that were created above. In this case, we have created bricks mounted on /export/gfsbrick on each node.
GlusterFS Storage Volume Types
There are different configuration settings to consider while creating GlusterFS storage volume depending on various operational needs.
Distributed: Files are distributed across the bricks in the volume.Replicated: Files are replicated across the bricks in the volume. It ensures high storage availability and reliability.Distributed Replicated: Files are distributed across the replicated bricks in the volume. Ensures high-reliability, scalability and improved read performance.Arbitrated Replicated: Files are replicated across two bricks in a replica set and only the metadata is replicated to the third brick. Ensures data consistency.Dispersed: Files are dispersed across the bricks in the volume.Distributed Dispersed: Data is distributed across the dispersed sub-volume.
The GlusterFS volume can be created using the command;
gluster volume create <NEW-VOLNAME> [stripe <COUNT>] [[replica <COUNT> [arbiter <COUNT>]]|[replica 2 thin-arbiter 1]] [disperse [<COUNT>]] [redundancy <COUNT>] [transport <tcp|rdma|tcp,rdma>] <NEW-BRICK> ...<TA-BRICK>Consult man gluster for more details.
Setup Replicated GlusterFS Storage Volume
In this demo, we are going to learn how to setup replicated glusterfs storage volume.
Create a mount point for the volume on the brick on each cluster node. In our case, our brick is mounted on /export/gfsbrick.
mkdir /export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01Next, created a replicated storage volume. For example, to create a replicated GlusterFS storage volume with three nodes called gfsvol01;
gluster volume create gfsvol01 replica 3 transport tcp gfs01:/export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01 gfs02:/export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01 gfs03:/export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01You can run the command from any node, replacing the names of the other peers and the associated bricks accordingly.
If everything goes well, you should get an output like;
volume create: gfsvol01: success: please start the volume to access dataAfter that, start the GlusterFS volume. Replace gfsvol01 with the name of your volume.
gluster volume start gfsvol01Verify GlusterFS Volumes
Once you have created and started the volumes, you can verify by running the command below from any node in the cluster.
gluster volume info all
Volume Name: gfsvol01
Type: Replicate
Volume ID: 9361067e-da82-411c-9c83-2ab1c2b888aa
Status: Started
Snapshot Count: 0
Number of Bricks: 1 x 3 = 3
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: gfs01:/export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01
Brick2: gfs02:/export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01
Brick3: gfs03:/export/gfsbrick/gfsvol01
Options Reconfigured:
transport.address-family: inet
storage.fips-mode-rchecksum: on
nfs.disable: on
performance.client-io-threads: off
There you go. You have successfully installed and setup replicated GlusterFS storage cluster.
Want to set a different type of GlusterFS volume? Consult GlusterFS documentation on setting up volume types.
Learn how to setup GlusterFS distributed replicated storage volume by following the link below;
Setup GlusterFS Distributed Replicated Volume on CentOS 8
If anything, you can always check the log file, /var/log/glusterfs/glusterd.log for any would be issues.
Install and Setup GlusterFS client on CentOS 8
Now that you have a GlusterFS storage cluster running, you can setup a client to be able to utilize this storage. Gluster volumes can be accessed using the Gluster Native Client or via NFS v3.
In this demo, we are going to learn how to use the native GlusterFS client on CentOS 8.
Install the GlusterFS repositories on CentOS 8
dnf install centos-release-glusterRun system update;
dnf updateInstall Gluster Native Client on CentOS 8
dnf install glusterfs glusterfs-fuseMounting Gluster Storage Volumes on Client
To manually mount the Gluster storage volumes on a client, use the command;
mount -t glusterfs HOSTNAME-OR-IPADDRESS:/VOLNAME MOUNTDIRWhere:
-t glusterfsspecifies the GlusterFS filesystem.HOSTNAME-OR-IPADDRESSis any gluster node eg, gfs01, gf02 or gfs03. Ensure hostnames are resolvable./VOLNAMEis the name of the GlusterFS storage volume e.ggfsvol01in this demo.MOUNTDIRis the mount point on the client.
Thus, to mount the Gluster storage volume from glusterfs node 01, gfs01, our mount command would be like;
mkdir /media/gfsmount -t glusterfs gfs01:/gfsvol01 /media/gfs/Confirm the mounting;
df -hT
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs devtmpfs 1.4G 0 1.4G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 1.4G 0 1.4G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 1.4G 9.9M 1.4G 1% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 1.4G 0 1.4G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/cl-root xfs 8.0G 5.7G 2.4G 71% /
/dev/sda1 ext4 976M 244M 666M 27% /boot
...
gfs01:/gfsvol01 fuse.glusterfs 2.0G 67M 2.0G 4% /media/gfs
To automatically mount the GlusterFS storage volume, you can update the /etc/fstab with the line;
gfs01:/gfsvol01 /media/gfs/ glusterfs defaults,_netdev 0 0Where _netdev ensures that the filesystem is not mounted until when the network is enabled and running.
In our next guide, we will discuss how to mount GlusterFS storage volume on a client using NFS.
That marks the end of our guide on how to install and setup GlusterFS storage cluster on CentOS 8.
Reference
Related Tutorials
Setup Three Node Ceph Storage Cluster on Ubuntu 18.04
Install and Setup GlusterFS on Ubuntu 18.04
How to Configure NFS Server on Ubuntu 18.04 Server


Hi Koromicha,
I can’t access to this link: https://download.gluster.org/pub/gluster/glusterfs/7/LATEST/CentOS/glusterfs-rhel8.repo
Thanks,
Do
Thank you Do for the feedback. This has been updated. Enjoy
Hi Koromicha,
Thank you very much for your consider,
I will wait for your update.
Thanks,
Do
Hi Koromicha,
I haven’t still access:The requested URL /pub/gluster/glusterfs/7/LATEST/CentOS/glusterfs-rhel8.repo was not found on this server.
Please check again,
Thanks,
Do
Apologies Do, please check again.
Hi Koromicha,
I am sorry for my late response,
I installed again ok, thank you very much.
Can Koromicha guide command (gluster volume create) Distributed & Replicate ?
//Command Replicate, I already setting ok as your guide.
Thanks,
Do
Hi Koromicha,
I am sorry for my late response,
I installed again ok, thank you very much.
And can you guide command create gluster volume: Distributed Replicated ?
//command replicated: I already installed ok as your guide ?
Thanks,
Do
Hello Koromicha,
first of all, thanks for the comprehensive tutorial.
I was following the steps here, and everything went well till when I tried to create Gluster Volume, here is the command I ran and the error I got:
$gluster volume create gfsvol01 replica 3 transport tcp virthost01:/gfsPool/gBricks/gfsvol01 virthost02:/gfsPool/gBricks/gfsvol01 virthost03:/gfsPool/gBricks/gfsvol01
volume create: gfsvol01: failed: Multiple bricks of a replicate volume are present on the same server. This setup is not optimal. Bricks should be on different nodes to have best fault tolerant configuration. Use ‘force’ at the end of the command if you want to override this behavior.
When I used force, the following error occurred:
volume create: gfsvol01: failed: Commit failed on localhost. Please check the log file for more details.
I appreciate your support.