In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Nikto web scanner on Rocky Linux 8.
Nikto is a Perl based open-source web vulnerability scanner that can unearth every other potential threat on your web server including but not limited to;
- Insecure files and programs
- Outdated servers and programs
- Server and software misconfigurations
- Default files and programs
Nikto can run on almost any Operating system with Perl interpreter installed. It supports SSL, proxies, host authentication, attack encoding, IDS evation etc.
Installing Nikto Web Scanner on Rocky Linux 8
There are two ways in which you can install Nikto web scanner.
- Clone the Nikto GitHub repo and run Nikto perl
- Install Nikto on Rocky Linux 8 from Third Party Repositories
Clone the Nikto GitHub Repo and run Nikto perl program
The easiest and the most recommended way to run Nikto on Rocky Linux is to clone its GitHub repository to your system and run Nikto perl program from the repository directory.
Since this is a perl program, you need to install perl on your system before you can run Nikto.
dnf install perlOnce you have Perl installed, clone the Nikto repository;
git clone https://github.com/sullo/niktoOnce you have cloned the repository, you can now change into program directory;
cd nikto/programand run nikto.pl program.
The syntax is;
./nikto.pl [options...]When run without any command line options, it shows basic description of various command options;
./nikto.pl
Sample output;
- Nikto v2.1.6
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ ERROR: No host (-host) specified
Options:
-ask+ Whether to ask about submitting updates
yes Ask about each (default)
no Don't ask, don't send
auto Don't ask, just send
-Cgidirs+ Scan these CGI dirs: "none", "all", or values like "/cgi/ /cgi-a/"
-config+ Use this config file
-Display+ Turn on/off display outputs:
1 Show redirects
2 Show cookies received
3 Show all 200/OK responses
4 Show URLs which require authentication
D Debug output
E Display all HTTP errors
P Print progress to STDOUT
S Scrub output of IPs and hostnames
V Verbose output
-dbcheck Check database and other key files for syntax errors
-evasion+ Encoding technique:
1 Random URI encoding (non-UTF8)
2 Directory self-reference (/./)
3 Premature URL ending
4 Prepend long random string
5 Fake parameter
6 TAB as request spacer
7 Change the case of the URL
8 Use Windows directory separator (\)
A Use a carriage return (0x0d) as a request spacer
B Use binary value 0x0b as a request spacer
-Format+ Save file (-o) format:
csv Comma-separated-value
json JSON Format
htm HTML Format
nbe Nessus NBE format
sql Generic SQL (see docs for schema)
txt Plain text
xml XML Format
(if not specified the format will be taken from the file extension passed to -output)
-Help This help information
If you want to see more details about the options above, run the command below;
./nikto -HUsing Nikto to Perform Web Scanning
In this section, we are going to see how Nikto is used with various command line options shown above to perform web scanning.
In its basic functionality, Nikto requires just an host an to scan. The target host can be specified with the -h or -host option. For example, to scan a web server whose IP address is 192.168.60.20, run Nikto as follows;
./nikto.pl -host 192.168.60.20
- Nikto v2.1.6
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ Target IP: 192.168.60.20
+ Target Hostname: 192.168.60.20
+ Target Port: 80
+ Start Time: 2021-07-13 22:17:01 (GMT3)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
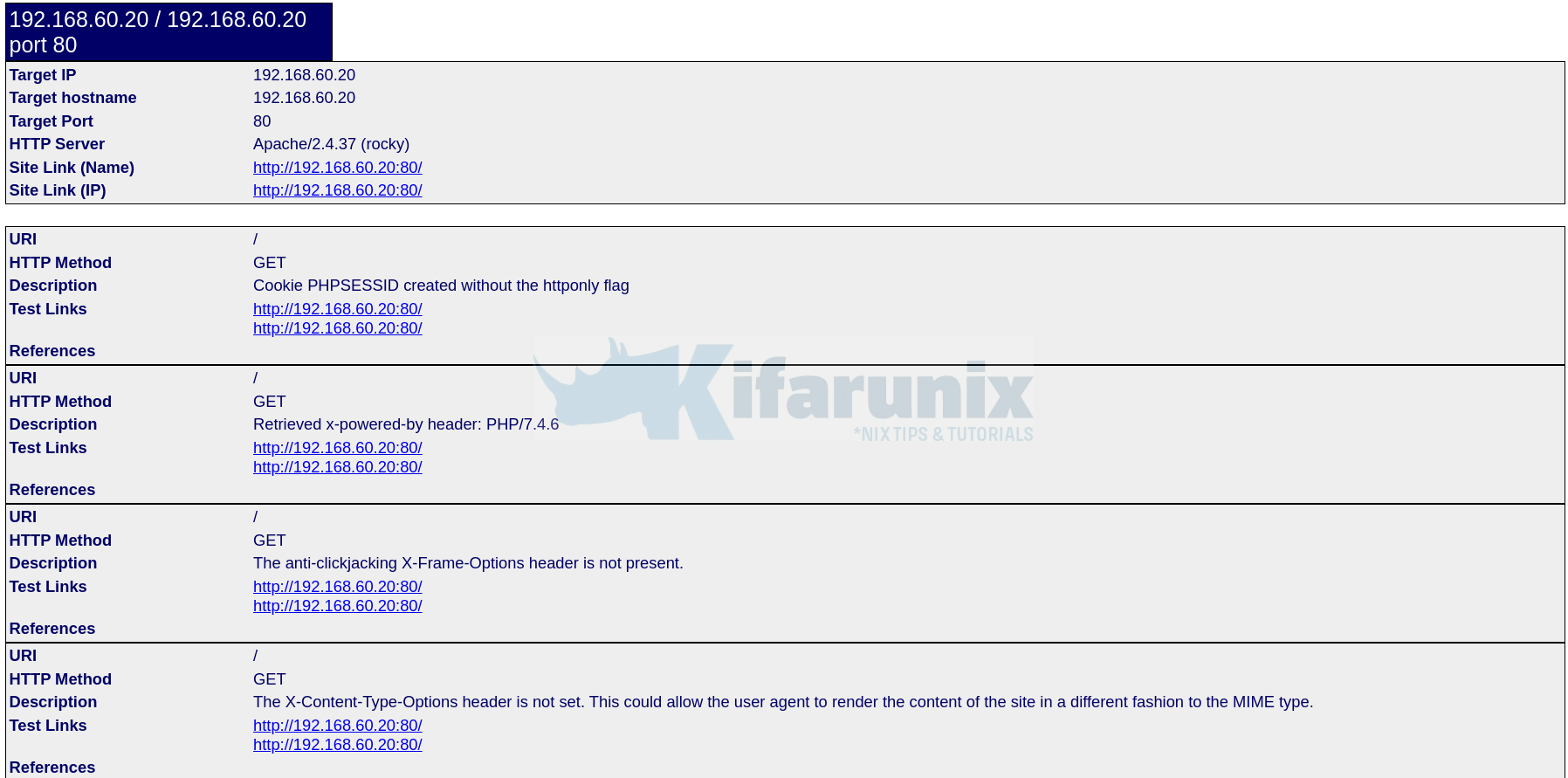
+ Server: Apache/2.4.37 (rocky)
+ Cookie PHPSESSID created without the httponly flag
+ Retrieved x-powered-by header: PHP/7.4.6
+ The anti-clickjacking X-Frame-Options header is not present.
+ The X-Content-Type-Options header is not set. This could allow the user agent to render the content of the site in a different fashion to the MIME type.
+ Root page / redirects to: login.php
+ Apache/2.4.37 appears to be outdated (current is at least Apache/2.4.46). Apache 2.2.34 is the EOL for the 2.x branch.
+ OSVDB-877: HTTP TRACE method is active, suggesting the host is vulnerable to XST
+ OSVDB-3268: /config/: Directory indexing found.
+ /config/: Configuration information may be available remotely.
+ OSVDB-3268: /tests/: Directory indexing found.
+ OSVDB-3092: /tests/: This might be interesting.
+ OSVDB-3268: /icons/: Directory indexing found.
+ OSVDB-3268: /docs/: Directory indexing found.
+ OSVDB-3233: /icons/README: Apache default file found.
+ OSVDB-3092: /.git/index: Git Index file may contain directory listing information.
+ /.git/HEAD: Git HEAD file found. Full repo details may be present.
+ /.git/config: Git config file found. Infos about repo details may be present.
+ /.gitignore: .gitignore file found. It is possible to grasp the directory structure.
+ 8916 requests: 0 error(s) and 17 item(s) reported on remote host
+ End Time: 2021-07-13 22:17:16 (GMT3) (15 seconds)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ 1 host(s) tested
As you can see from the output, when the target host is specified without a port, Nikto scans port 80 by default.
However, if your web server is running on a different port, you have to specify the port using the -p or -port option.
See example below;
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.60.15 -p 8080If you have multiple virtualhosts on the same host server listening on different ports, you can specify multiple ports by separating them with comma.
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.60.20 -p 8080,8888You can also specify a range of ports in the format port1-portN for example,
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.60.20 -p 8080-8888Instead of using the IP address to specify the target host, URLs can also be used for example;
./nikto.pl -h mydvwa.example.com
./nikto.pl -h https://mydvwa.example.comYou can also specify the port when you use URL;
./nikto.pl -h mydvwa.example.com -p 8080
./nikto.pl -h https://mydvwa.example.com -p 8443or
./nikto.pl -h mydvwa.example.com:8080./nikto.pl -h https://mydvwa.example.com:8443/
As much as target hosts can be specified using the -p option, it is also possible to specify a file containing a list of target hosts one per line. For instance, you file should should contains the targets in the format;
cat scan-targets
https://mydvwa.example.com:443/
192.168.60.20:8888
192.168.43.101To scan these hosts at the same time, run the command below;
./nikto.pl -h scan-targetsIt is also possible to scan the hosts in a network listening on web server ports using Nmap and pass the output to ./nikto.pl. For example to scan for open port 80 in a network, 192.168.43.0/24,
nmap -p80 192.168.60.0/24 -oG - | ./nikto.pl -h -If you are going through a proxy server, you can ask ./nikto.pl to use proxy by using the -useproxy option. You can set the proxy details on the ./nikto.pl configuration file, /etc/./nikto.pl/config.txt or you can it on the command line as shown below;
To define the proxy server details in the /etc/./nikto.pl/config.txt file, use the format;
PROXYHOST=192.168.20.45
PROXYPORT=3128
PROXYUSER=username
PROXYPASS=passwordWhen you have defined the proxy details as shown above, then run ./nikto.pl as follows;
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.20.128 -useproxyTo specify the proxy connection details on the command line;
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.20.128 -useproxy http://id:[email protected]:3128/./nikto.pl -h 192.168.20.128 -useproxy http://@192.168.20.23:3128/Nikto can export scan results in different formats; CSV, HTML, XML, NBE, text. To save the results in a specific output format, you need to specify the -o/-output option as well as the -Format option to define the output format. See examples below to save the scan results in html format.
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.60.20 -o /var/www/html/test.html -F htmlYou can therefore access the report via web browser. See screenshot below;
Nikto can also be fine tuned to perform specific scans. Below is a description of the tuning options that can be used to achieve this functionality.
1 - Interesting File / Seen in logs
2 - Misconfiguration / Default File
3 - Information Disclosure
4 - Injection (XSS/Script/HTML)
5 - Remote File Retrieval - Inside Web Root
6 - Denial of Service
7 - Remote File Retrieval - Server Wide
8 - Command Execution / Remote Shell
9 - SQL Injection
0 - File Upload
a - Authentication Bypass
b - Software Identification
c - Remote Source Inclusion
x - Reverse Tuning Options (i.e., include all except specified)
For example, to test for SQL Injection and Remote File Retrieval – Server Wide, you would use ./nikto.pl like;
./nikto.pl -h 192.168.60.20 -Tuning 79 -o /var/www/html/test.html -F htmlSample command output;
- Nikto v2.1.6
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ Target IP: 192.168.60.20
+ Target Hostname: 192.168.60.20
+ Target Port: 80
+ Start Time: 2021-07-13 22:27:33 (GMT3)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ Server: Apache/2.4.37 (rocky)
+ Cookie PHPSESSID created without the httponly flag
+ Retrieved x-powered-by header: PHP/7.4.6
+ The anti-clickjacking X-Frame-Options header is not present.
+ The X-Content-Type-Options header is not set. This could allow the user agent to render the content of the site in a different fashion to the MIME type.
+ Root page / redirects to: login.php
+ Apache/2.4.37 appears to be outdated (current is at least Apache/2.4.46). Apache 2.2.34 is the EOL for the 2.x branch.
+ OSVDB-877: HTTP TRACE method is active, suggesting the host is vulnerable to XST
+ 717 requests: 0 error(s) and 6 item(s) reported on remote host
+ End Time: 2021-07-13 22:27:35 (GMT3) (2 seconds)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ 1 host(s) tested
Install Nikto on Rocky Linux 8 from Third Party Repositories
Nikto can be installed from EPEL repos but also, there are some other required dependencies that can be provided by third party GetPageSpeed repository.
dnf install https://extras.getpagespeed.com/release-el8-latest.rpm epel-releaseOnce the repos are in place, install Nikto on Rocky Linux 8.
dnf install nikto
============================================================================================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
============================================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
nikto noarch 1:2.1.6-8.el8 epel 352 k
Installing dependencies:
perl-JSON-PP noarch 1:2.97.001-3.el8 appstream 67 k
perl-Math-BigRat noarch 0.2614-1.el8 appstream 39 k
perl-Time-HiRes x86_64 4:1.9758-2.el8 appstream 60 k
perl-bignum noarch 0.49-2.el8 appstream 42 k
perl-libwhisker2 noarch 2.5-29.el8 getpagespeed-extras-noarch 95 k
Transaction Summary
============================================================================================================================================================================
Install 6 Packages
Total download size: 655 k
Installed size: 2.8 M
Is this ok [y/N]: y
You can then use Nikto from the command line like above, except that for this you just run nikto instead of ./nikto.pl.
nikto
- ***** RFIURL is not defined in nikto.conf--no RFI tests will run *****
- Nikto v2.1.6
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ ERROR: No host specified
-config+ Use this config file
-Display+ Turn on/off display outputs
-dbcheck check database and other key files for syntax errors
-Format+ save file (-o) format
-Help Extended help information
-host+ target host
-id+ Host authentication to use, format is id:pass or id:pass:realm
-list-plugins List all available plugins
-output+ Write output to this file
-nossl Disables using SSL
-no404 Disables 404 checks
-Plugins+ List of plugins to run (default: ALL)
-port+ Port to use (default 80)
-root+ Prepend root value to all requests, format is /directory
-ssl Force ssl mode on port
-Tuning+ Scan tuning
-timeout+ Timeout for requests (default 10 seconds)
-update Update databases and plugins from CIRT.net
-Version Print plugin and database versions
-vhost+ Virtual host (for Host header)
+ requires a value
Note: This is the short help output. Use -H for full help text.
Feel free to explore the basic usage of other command line options from Nikto Documentation page.
Other Tutorials
Detecting Malicious Files with Wazuh and VirusTotal

