Follow through this guide to learn how to install Cockpit on Debian 11/Ubuntu 22.04. Cockpit is Web Console enables users to administer GNU/Linux servers using a web browser. It offers network configuration, log inspection, diagnostic reports, interactive command-line sessions, and more. You will learn how to install Cockpit on Debian 11 and how to install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04.
Install Cockpit on Debian 11/Ubuntu 22.04
Cockpit is available on the default Debian/Ubuntu repositories. However, in order to get the latest version releases installed, you need to install the Backports repositories on Ubuntu/Debian systems.
Install Cockpit on Debian 11
To install the latest version of Cockpit on Debian 11, you need to install the backports repository as follows;
. /etc/os-releaseecho "deb http://deb.debian.org/debian ${VERSION_CODENAME}-backports main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/backports.listOnce the backports repositories are installed, then, run system package cache update;
apt updateNext, execute the command below to install Cockpit on Debian 11;
apt install -t ${VERSION_CODENAME}-backports cockpitInstall Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04
Fortunately, Ubuntu 22.04 has got the latest release version of Cockpit in its repositories;
Thus, you can install Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04 by executing the command below;
apt install cockpitRunning Cockpit on Ubuntu 22.04/Debian 11
Once the installation is done, Cockpit sets up its systemd service unit for easy management.
Start Cockpit service;
systemctl start cockpitChecking the status;
systemctl status cockpit
● cockpit.service - Cockpit Web Service
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/cockpit.service; static)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2022-03-10 13:01:51 EST; 2s ago
TriggeredBy: ● cockpit.socket
Docs: man:cockpit-ws(8)
Process: 11906 ExecStartPre=/usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-certificate-ensure --for-cockpit-tls (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 11921 (cockpit-tls)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 2324)
Memory: 2.0M
CPU: 155ms
CGroup: /system.slice/cockpit.service
└─11921 /usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-tls
Mar 10 13:01:50 debian11 systemd[1]: Starting Cockpit Web Service...
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 cockpit-certificate-ensure[11913]: /usr/lib/cockpit/cockpit-certificate-helper: line 32: sscg: command not found
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 cockpit-certificate-ensure[11914]: Generating a RSA private key
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 cockpit-certificate-ensure[11914]: ........................+++++
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 cockpit-certificate-ensure[11914]: ..................+++++
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 cockpit-certificate-ensure[11914]: writing new private key to '0-self-signed.key'
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 cockpit-certificate-ensure[11914]: -----
Mar 10 13:01:51 debian11 systemd[1]: Started Cockpit Web Service.
Cockpit listens on TCP Port 9090;
ss -altnp | grep 9090Sample output;
LISTEN 0 4096 *:9090 *:* users:(("systemd",pid=1,fd=261))Accessing Cockpit Web Interface
You can now access your Debian/Ubuntu system via the Cockpit web interface via the address http://<server-IP-or-resolvable-domain>:9090.
Of course you need to open the port on firewall if any firewall is running.
For example, if you are using UFW, then open the port using the command below;
To allow access to the service from anywhere;
ufw allow 9090/tcpTo allow from specific IP. Replace <IP> and <YOUR COMMENT> accordingly;
ufw allow from <IP> to any port 9090 proto tcp comment "<YOUR COMMENT>"if you using iptables;
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 9090 -j ACCEPTTo allow from specific IP address;
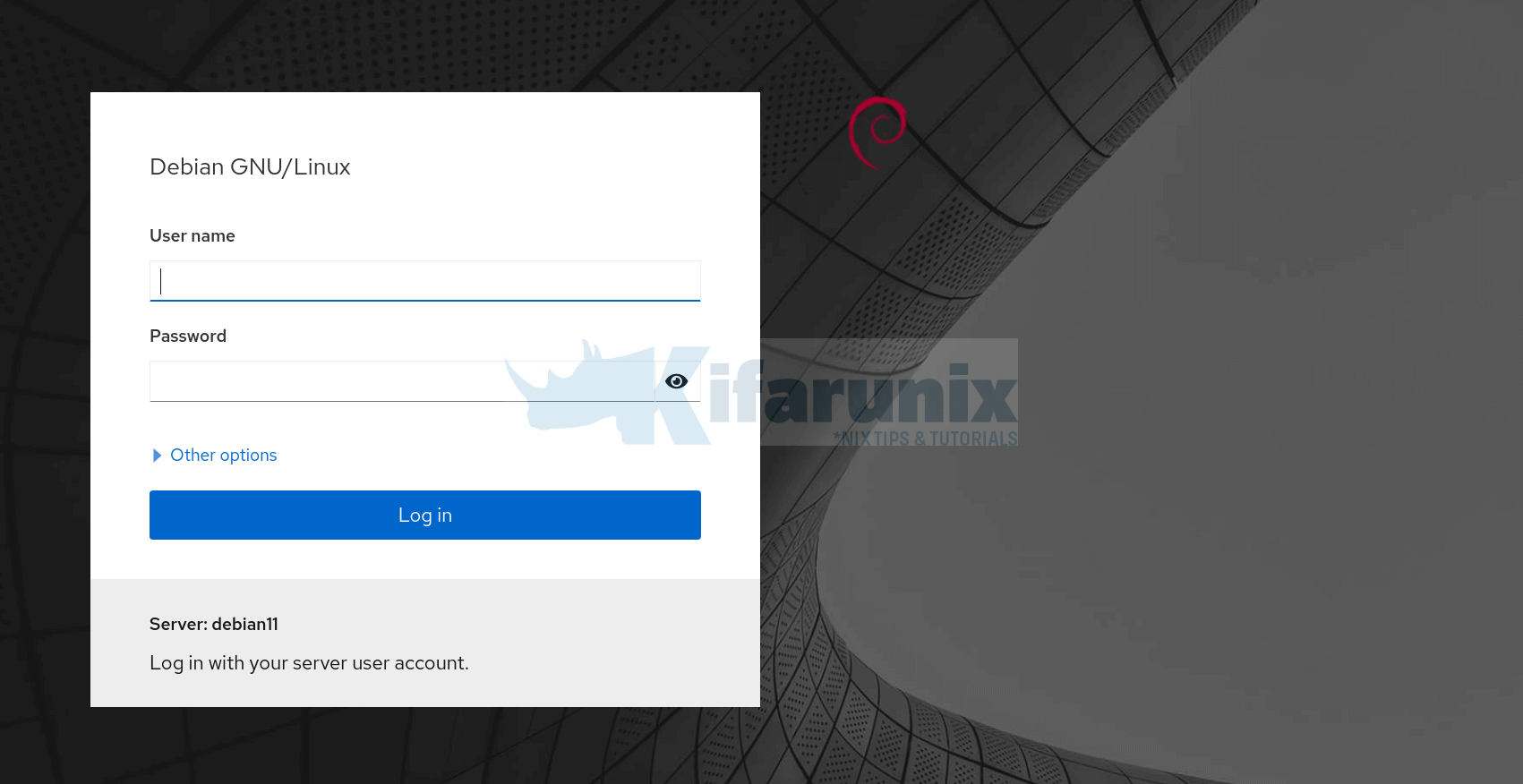
iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.59.1/32 -p tcp --dport 9090 -j ACCEPTCockpit login Interface.
You can login using root user account credentials or user with sudo rights.
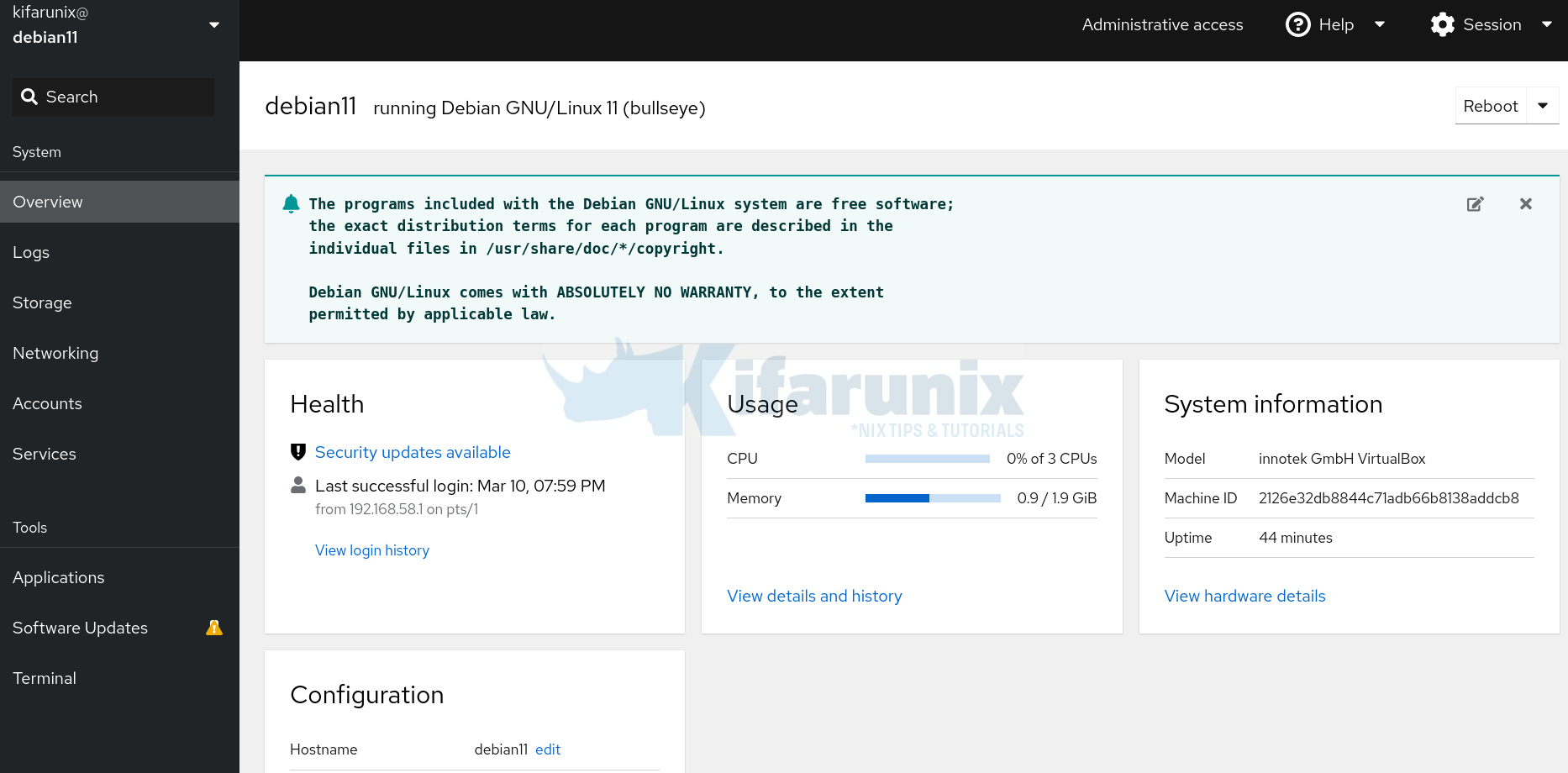
Cockpit web dashboard
If you see a warning Warning alert:Web console is running in limited access mode., ensure the username is assigned sudo rights and that sudo package is installed. Then click Turn on administrative access and enter your password.
You can now administer your system using cockpit.
That concludes our guide on how to install Cockpit on Debian/Ubuntu Linux.