In this guide, we are going to learn how to install and setup NoMachine on CentOS 8. NoMachine is a cross platform, fastest and highest quality remote desktop tool that enables you to access desktop of any other machine with NoMachine installed.
Installing NoMachine on CentOS 8
Download NoMachine Linux Installation Package
NoMachine is not available on default CentOS 8 repositories. However, an RPM binary installer can be downloaded from the NoMachine Linux downloads page.
Choose the installer for you respective system architecture and download it. You can simply grab the link and pull it using the wget command.
wget https://download.nomachine.com/download/6.9/Linux/nomachine_6.9.2_1_x86_64.rpmInstall NoMachine on CentOS 8
Once you have downloaded the RPM binary installer, you can simply install it as follows;
dnf install nomachine_6.9.2_1_x86_64.rpmWell, if your system has direct internet access, you would simply run the installation of NoMachine on CentOS 8 by executing the command;
dnf install https://download.nomachine.com/download/6.9/Linux/nomachine_6.9.2_1_x86_64.rpmnomachine_6.9.2_1_x86_64.rpm 1.4 MB/s | 45 MB 00:31
Dependencies resolved.
=======================================================================================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
=======================================================================================================================================================
Installing:
nomachine x86_64 6.9.2-1 @commandline 45 M
Transaction Summary
=======================================================================================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total size: 45 M
Installed size: 47 M
Is this ok [y/N]: y...
NX> 700 Starting install at: Sat Mar 21 08:54:47 2020.
NX> 700 Installing: nxclient version: 6.9.2.
NX> 700 Using installation profile: Red Hat.
NX> 700 Install log is: /usr/NX/var/log/nxinstall.log.
NX> 700 Compiling the USB module.
NX> 700 Installing: nxplayer version: 6.9.2.
NX> 700 Using installation profile: Red Hat.
NX> 700 Install log is: /usr/NX/var/log/nxinstall.log.
NX> 700 To connect the remote printer to the local desktop,
NX> 700 the user account must be a member of the CUPS System Group: sys.
NX> 700 Installing: nxnode version: 6.9.2.
NX> 700 Using installation profile: Red Hat.
NX> 700 Install log is: /usr/NX/var/log/nxinstall.log.
NX> 700 Creating configuration in: /usr/NX/etc/node.cfg.
NX> 700 Installing: nxserver version: 6.9.2.
NX> 700 Using installation profile: Red Hat.
NX> 700 Install log is: /usr/NX/var/log/nxinstall.log.
NX> 700 Creating configuration in: /usr/NX/etc/server.cfg.
NX> 700 Install completed at: Sat Mar 21 08:55:42 2020.
NX> 700 NoMachine was configured to run the following services:
NX> 700 NX service on port: 4000
Verifying : nomachine-6.9.2-1.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
nomachine-6.9.2-1.x86_64
Complete!Setup NoMachine for Remote Connections
Once NoMachine is installed, you can be able to launch it from the activities tab at the top left corner. You should see NoMachine and NoMachine service manager.

NoMachine service manager is a small application which gives you access to server NoMachine management tools and User Interface and advises you when someone is requesting to connect.
It enables you to check server status, connected users, active transfers, NoMachine Server preferences, restart, stop or shutdown NoMachine server.
Open NoMachine Ports on Firewall
In order to be able to connect to your desktop via NoMachine from a remote machine, you need to open some ports on firewall preferably; port 4000/TCP, 4011-4999/UDP (mostly for transmitting video and audio streams). There are other ports like 4080 and 4443 for web connections.
Read more on Default ports used by NoMachine 4 or later.
Consult your respective system documentation on how to open ports on firewall. For example, on RHEL based systems, you would simply open the NoMachine TCP and UDP ports by running the command below;
firewall-cmd --add-port=4000/tcp --add-port=4011-4999/udp --permanentfirewall-cmd --reloadCreate NoMachine Connections on CentOS 8
Launch NoMachine from the activities tap. From the interface that opens up, you will see some guidelines on using NoMachine.
Click Continue from the screen above to view NoMachine recent connections, open recent connections or create new connections.
Since this is a new installation, you will such a screen.

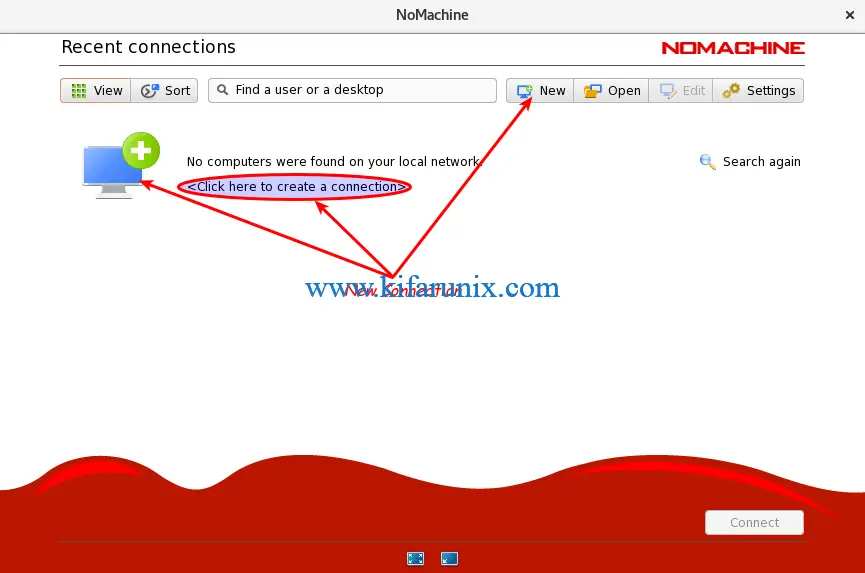
Create NoMachine Connection
To create a new connection, you can click any of the areas highlighted in the screenshot below.
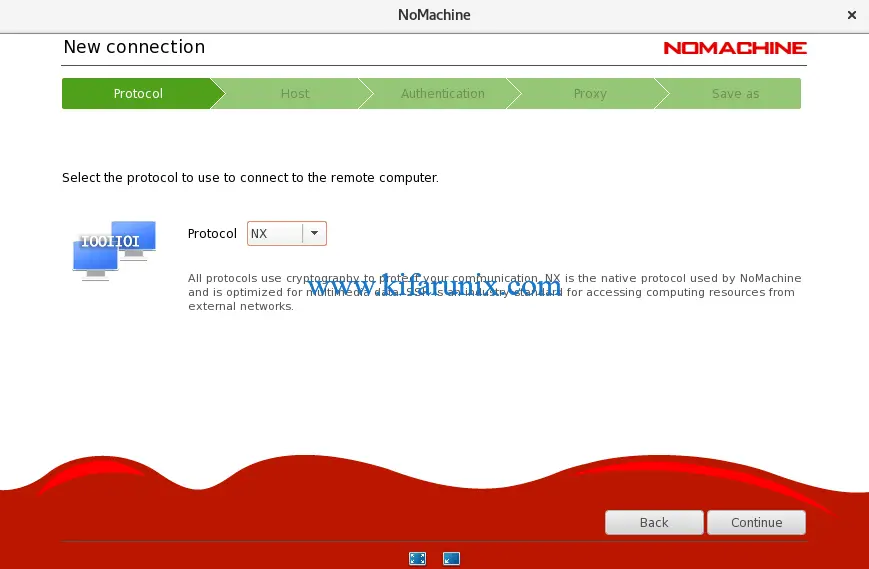
Choose a Connecetion Protocol
Select the protocol you want to use to connect to your remote machines. NoMachine enables you to choose between NX, the native NoMachine protocol and SSH. In this demo, we go with NX.
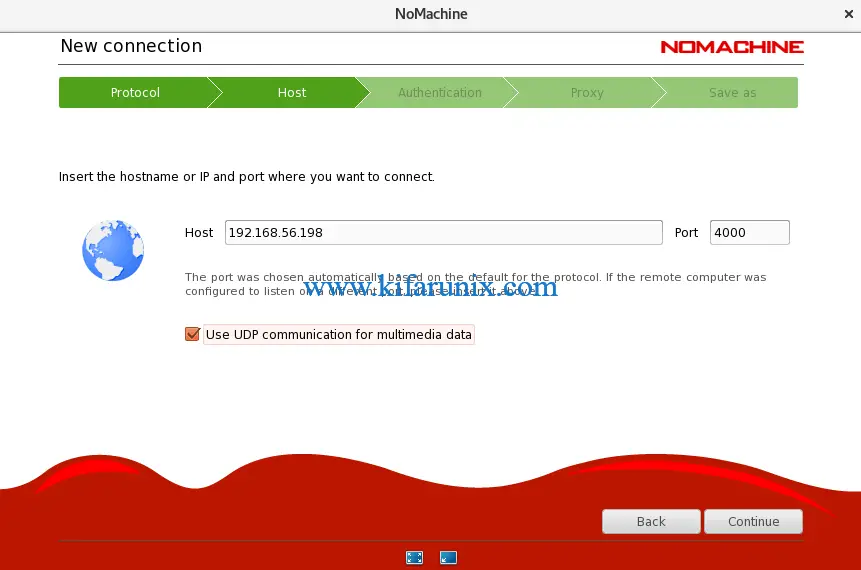
Set the Remote NoMachine Host Address
On the next page, set the address and the connection port as defined on the remote host. In this guide, we are connection to remote system with an IP address, 192.168.56.198 listening on port 4000.
NoMachine Authentication Method
On the Authentication settings page. In our case, we are using Password based authentication.
Define Proxy Connection Settings
If your connection is going through a proxy, be sure to set the proxy connection settings. Otherwise, choose Don’t use Proxy.
Save the NoMachine Connection
Once you are done configuring the NoMachine connections, you can save it with your preferred name and click Done.
You connection is now displayed on the NoMachine desktop.

Connection to a Remote Desktop via NoMachine
Once you have setup a connection, select it from the NoMachine desktop interface and click connection. You can as well right click on a connection and click Start connection.
While establishing a connect, you are asked to verify host authenticity. Accept and proceed.
Enter the login credentials of the user account in the remote desktop system you are connecting to.
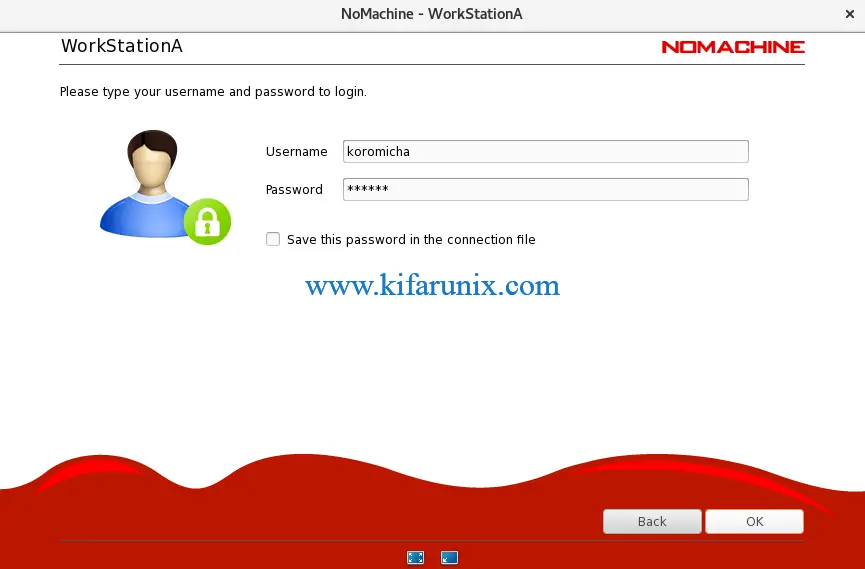
Click Ok to initiate a remote connection.
On the remote desktop, you should see a notification about the connection.
If the NoMachine login user is the same as the user who is currently logged into the system, the connection will just happen without being prompted.
However, if the NoMachine user logging in is different from the user who is currently logged into the system, you will be prompted on whether to allow connection.

Once you allow the connection, you will see a notification like;

Read more about authorizing remote connections on NoMachine authorizing remote connections.
Read more on NoMachine Documentations.
Related Tutorials
How to Install and Use NoMachine Remote Desktop Tool on Ubuntu 18.04
Install AnyDesk on Ubuntu 20.04

