In this tutorial, you will learn how to setup Portainer with SSL Certificates. By default, Portainer web interface and API is exposed over HTTPS with a self-signed certificate. To ensure a secured access to your Portainer, especially if your are going to be accessing it via the public networks, then it is a good idea to use a commercially signed SSL/TLS certificates.
Setup Portainer with SSL Certificates
In this guide, we will be working with Portainer deployed as a standalone Docker container. Note that there are other deployments such as Docker swarm/Kubernetes environments.
There are two ways in which you can configure Portainer to use SSL certificates;
Install SSL Certificates on Portainer via Portainer UI
If you want to configure Portainer with SSL certificates after the installation, login to your Portainer web interface.
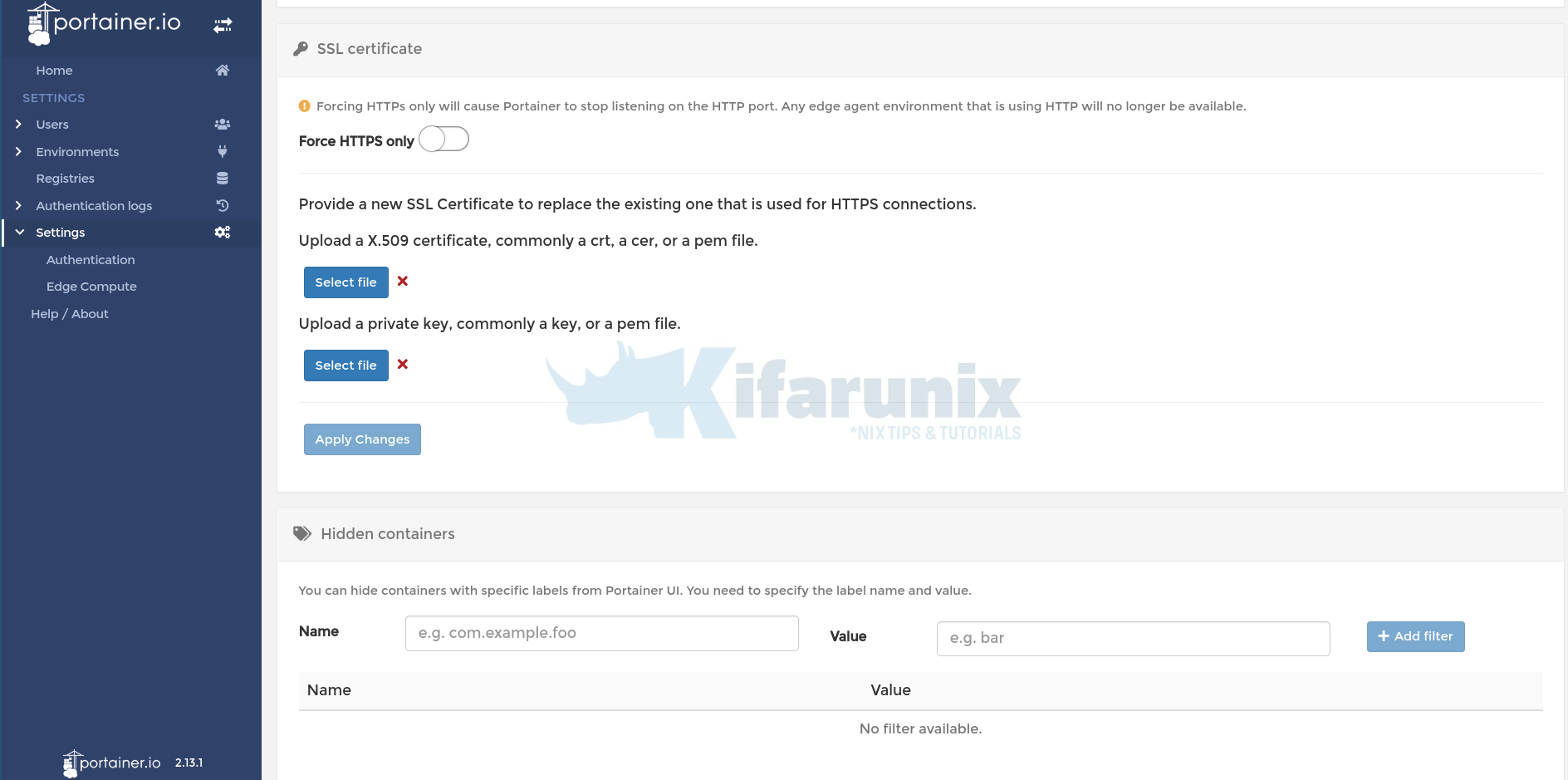
- Navigate to Settings > SSL Ceritificate.
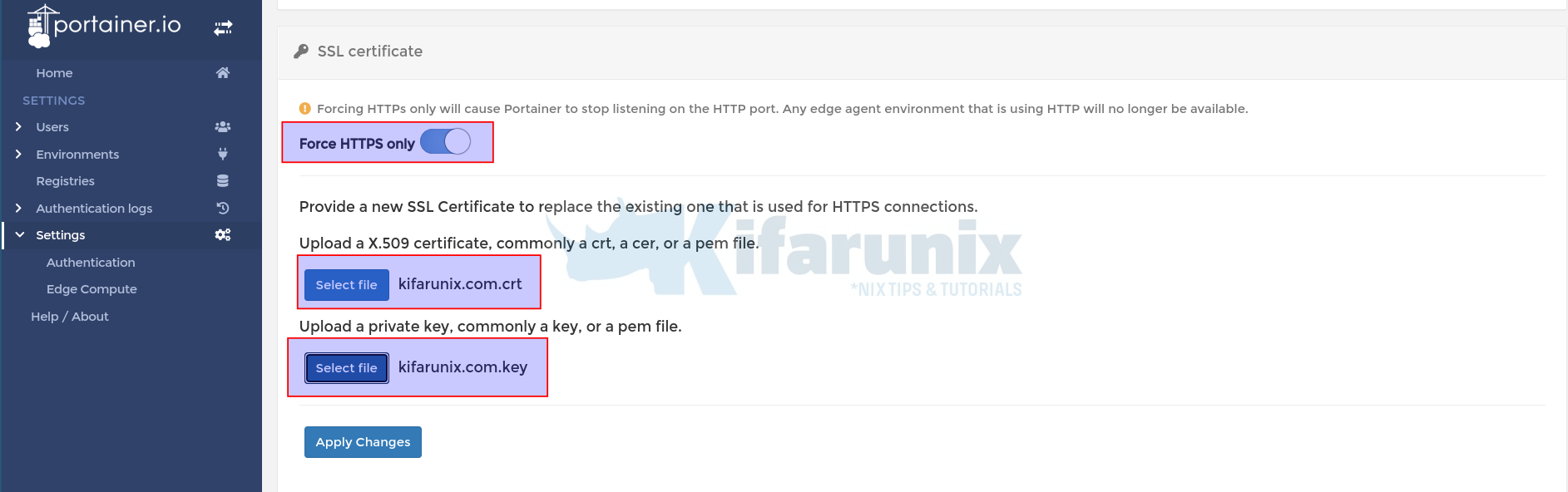
- Next, configure Portainer to listen on HTTPS ONLY by toggling the Force HTTPS only button ON. As already warned, Any edge agent environment that is using HTTP will no longer be available. Also ensure you can access Portainer with HTTPS (self-signed) with no issues before.
- Upload the X.509 SSL certificate by clicking Select File button. The certificates should be in PEM format.
- Similarly, upload the private key.
- Save the changes by clicking Apply Changes button.
- Immediately you apply the changes, you may be disconnected for a second.
- You can now re-access your Portainer using the domain name, https://portainer-domain-name:9443.
Configure Portainer with SSL Certificates during Portainer Installation
You can also while install Portainer, configure it to use your custom SSL certificates instead of the automatically generated self-signed ones.
- Generate and store the SSL certificates and keys on specific path on the Portainer host server.
- For example, our certificates/keys are stored under the Portainer host server path,
/etc/ssl/certs/portainer/.
- For example, our certificates/keys are stored under the Portainer host server path,
ls -1 /etc/ssl/certs/portainer/kifarunix.com.crt
kifarunix.com.key- Once you have the certificates in place, then you can now proceed to install Portainer docker container with SSL certificates by adding a few command line options to the installation command we used in our guides before.
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 -p 9443:9443 --name portainer --restart=always \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \
-v /etc/ssl/certs/portainer:/certs \
-v pt_data:/data \
portainer/portainer-ce:latest \
--ssl --sslcert /certs/kifarunix.com.crt \
--sslkey /certs/kifarunix.com.keyNote the --ssl/--sslcert/--sslkey options comes after specify the Portainer image.
Demistifying the docker command line options used above;
-d/--detach: Causes the container to run in the background and print container ID-p/--publish: Exposes/Publishes a container’s port(s) to the host.- For example,
9443:9443means Portainer server container port 9443 can be accessed on the main Docker host on port 9443.
- For example,
--name: Assign a name to the container.--restart: Restart policy to apply when a container exits (default “no”)alwaysmeans Always restart the container regardless of the exit status- it also causes the container to start on daemon startup, regardless of the current state of the container
-v/--volume: Bind mount a Docker container volume.-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock: This causes the Portainer Server container process to communicate with the main host Docker process.-v pt_data:/data: Mounts the Portainer Server container data,/data, to the host path/var/lib/docker/volumes/pt_data.-v /etc/ssl/certs/portainer:/certs: Mounts the Portainer Hosts SSL certificate path to the Portainer Docker container /certs directory so that the container can access the certificates internally.
- And then of course the Portainer image we are using, the Portainer CE latest container image,
portainer/portainer-ce:latest. --ssl/--sslcert/--sslkey: defines how the Portainer container will access the certificates internally.
And there you go. You should now be able to access your Portainer Web interface with secure HTTPS.
And that is how you can configure Portainerto use SSL Certificates on a standalone Docker deployment option.
Referece;
Other Tutorials
Create Locally Trusted SSL Certificates with mkcert on Ubuntu 20.04
Monitor SSL/TLS Certificate Expiry with Prometheus and Grafana