This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide on how to install Kubernetes Metrics server on a Kubernetes cluster. Kubernetes Metrics Server plays a vital role in monitoring your Kubernetes cluster by collecting resource utilization data, such as CPU and memory usage, from various components. It provides valuable insights into the health and performance of your applications, nodes, and pods, enabling you to scale resources efficiently, identify bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues promptly.
Table of Contents
Step-by-Step Guide: Installing Metrics Server on Kubernetes Cluster
What is the use of Kubernetes Metrics Server?
Kubernetes Metrics server can be used in Kubernetes cluster for;
Horizontal Scaling: This is also known asscaling outand it involves increasing or decreasing the number of replicas (instances) of an application or service based on CPU or memory usage. With horizontal scaling, additional pods (containers) are added or removed dynamically to distribute the workload across multiple instances. This approach allows for better utilization of resources and improved application performance as the load is distributed evenly. Mostly used for stateless applications that can scaled without impacting data consistency.Vertical Scaling: This is also known asscaling up or downand it involves adjusting the resources (CPU, memory) allocated to individual instances of an application or service. With vertical scaling, you increase or decrease the capacity of each instance by modifying its resource limits. Mostly used for stateful applications that can maintain their own state or data. Vertical scaling has limits dictated by the capacity of the underlying infrastructure.
Installing Kubernetes Metrics Server on a Kubernetes Cluster
Install and Setup Kubernetes Cluster
Before you can proceed, we assume that you already have a K8s cluster up and running.
You can check our previous guide on how to install and setup a Kubernetes cluster;
Check other requirements.
There are two ways in which you can install Metrics server;
- via the Metric server
components manifest fileavailable on the Github repository - Via the official
Helm Chart repository.
In this tutorial, we will use the components manifests file to install Metrics server.
Download Metrics Server Manifests
If you want to update the manifest configurations like resource limits,or other parameters based on your requirements, it is best to download it to your control plane for editing.
Thus, you can download the latest Metrics server components manifest file using the command below;
wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yamlThis is how default Metrics server components manifest file looks like;
cat components.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
name: system:aggregated-metrics-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:
- metrics.k8s.io
resources:
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/metrics
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server-auth-reader
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: extension-apiserver-authentication-reader
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server:system:auth-delegator
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:auth-delegator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:metrics-server
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
selector:
k8s-app: metrics-server
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
image: registry.k8s.io/metrics-server/metrics-server:v0.6.3
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /livez
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
periodSeconds: 10
name: metrics-server
ports:
- containerPort: 4443
name: https
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /readyz
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
initialDelaySeconds: 20
periodSeconds: 10
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-dir
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
serviceAccountName: metrics-server
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: tmp-dir
---
apiVersion: apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: APIService
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io
spec:
group: metrics.k8s.io
groupPriorityMinimum: 100
insecureSkipTLSVerify: true
service:
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
version: v1beta1
versionPriority: 100
Install Kubernetes Metrics Server
One thing to note before you can proceed, is that Metrics server will be communicating with the following components in the cluster;
Control Plane API server: This is the primary way to interact with a Kubernetes cluster and the metrics that are gathered from the cluster components by Metrics server are exposed through this API for consumption by tools like Kubernetes Dashboard.Kubelet: Kubelet is an agent that runs on each worker node in the cluster. It exposes an API endpoint through which Metrics server will scrape the Pods/containers resource usage metrics.
Metrics server is configured to communicate with these endpoints using TLS certificate that should be signed by cluster CA. Thus, for demo purposes you can disable the SSL/TLS verification between the Metrics server and the above endpoints using the option, --kubelet-insecure-tls.
Also, the default components manifest file defines the container port as 10250/tcp. This port is already used by kubelet on the cluster;
sudo ss -atlnp | grep 10250LISTEN 0 4096 *:10250 *:* users:(("kubelet",pid=1185141,fd=20))Hence, let’s change this to a free port, for example, 4443.
vim components.yaml
...
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
...
name: metrics-server
ports:
- containerPort: 4443
name: https
protocol: TCP
Also, to avoid a situation whereby the availability status of Metric-server becomes False with “FailedDiscoveryCheck“, you need to configure the Pods created by the Metric server Deployment to use the host’s network namespace (hostNetwork: true). The Metrics server API service doesn’t run directly within the virtual cluster network (the overlay network used by Pods for communication), hence the use of this host network.
...
spec:
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
...
name: metrics-server
ports:
- containerPort: 4443
name: https
protocol: TCP
Similarly, to solve this “panic: unable to load configmap based request-header-client-ca-file: Get “…”: dial tcp … i/o timeout“, you need to update the roles to allow access to configmaps resources.
...
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
name: system:aggregated-metrics-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:
- metrics.k8s.io
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/metrics
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
In general, this is how our updated configuration is like.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
name: system:aggregated-metrics-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:
- metrics.k8s.io
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes/metrics
verbs:
- get
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server-auth-reader
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: extension-apiserver-authentication-reader
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server:system:auth-delegator
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:auth-delegator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:metrics-server
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
selector:
k8s-app: metrics-server
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
spec:
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP,ExternalIP,Hostname
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --metric-resolution=15s
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
image: registry.k8s.io/metrics-server/metrics-server:v0.7.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /livez
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
periodSeconds: 10
name: metrics-server
ports:
- containerPort: 4443
name: https
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /readyz
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
initialDelaySeconds: 20
periodSeconds: 10
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
seccompProfile:
type: RuntimeDefault
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-dir
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
serviceAccountName: metrics-server
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: tmp-dir
---
apiVersion: apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: APIService
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io
spec:
group: metrics.k8s.io
groupPriorityMinimum: 100
insecureSkipTLSVerify: true
service:
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
version: v1beta1
versionPriority: 100
Open the metrics server port on firewall on all cluster nodes.
If using UFW;
sudo ufw allow 4443/tcpIf using something else other than ufw, open the port accordingly.
You can now install Metrics server by applying the Metrics server components manifest configuration file using the command below.
kubectl apply -f components.yamlSimilarly, if you want to directly install the Metrics server without modifying the default configs, then you can execute the command below;
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yamlVerify Kubernetes Metrics Server Installation
You can now verify the installation of Metric server on Kubernetes.
Based on the components manifest configuration above, a deployment called metrics-server will be created under the kube-system namespace.
To get the details of the Metrics server deployment, run the command below;
kubectl get deployment metrics-server -n kube-systemSample output;
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
metrics-server 1/1 1 1 8m16s
A Pod is also created;
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
...
metrics-server-7b4c4d4bfd-rdz8t 1/1 Running 0 9m21s
Check API Services;
kubectl get apiservices...
v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io kube-system/metrics-server True 11m
Check Kubernetes Pods/Nodes CPU and Memory Usage
After the installation, the Metrics server will now start collecting resource usage information from the cluster.
Let’s run top command to check CPU and Memory usage of the Pods in the default namespace;
kubectl top pods
NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
nagios-core-deployment-694b75b55b-845mh 2m 32Mi
nagios-core-deployment-694b75b55b-8lflz 2m 32Mi
nagios-core-deployment-694b75b55b-hrw4n 3m 31Mi
Show metrics for all pods in the given namespace;
kubectl top pod --namespace=NAMESPACEShow metrics for a given pod and its containers;
kubectl top pod POD_NAME --containersCheck nodes;
kubectl top nodesNAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
master.kifarunix.com 449m 22% 1516Mi 39%
wk01.kifarunix.com 120m 6% 1022Mi 26%
wk02.kifarunix.com 46m 2% 1035Mi 27%
wk03.kifarunix.com 76m 3% 812Mi 21%
View Metrics on Kubernetes Dashboard
You can install Kubernetes dashboard and used it to view Pods/containers metrics;
Easy Way to Install Kubernetes Dashboard on Ubuntu 22.04/20.04
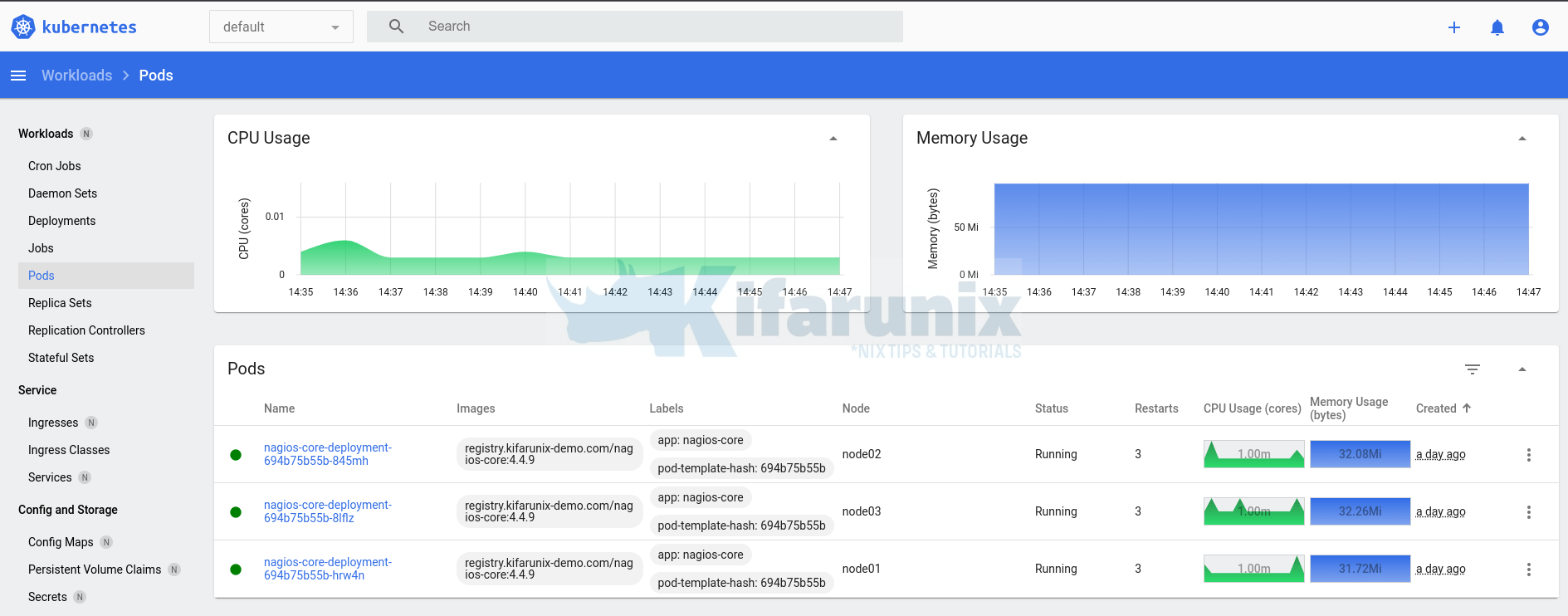
Kubernetes Dashboard automatically integrates with the Metrics Server. The Metrics Server provides the necessary resource utilization metrics, such as CPU and memory usage, which the Dashboard utilizes to display information and statistics about your cluster.
Other Tutorials
What are the core concepts in Kubernetes?
Kubernetes Architecture: A High-level Overview of Kubernetes Cluster Components


Hi,
I am still getting error:
error: Metrics API not available
Hi, yes, there are quite a number of updates you need to make on the default components YAML file. See the guide again for the updates.