In this tutorial, you will learn how to install Fleet osquery manager on Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04. With the official retirement of the Kolide Fleet as on November 4th, 2020, there has been yet another Fleet that offers the same functionality as Kolide Fleet. According to its Github repository, “Fleet is the most widely used open source osquery manager. Deploying osquery with Fleet enables programmable live queries, streaming logs, and effective management of osquery across 50,000+ servers, containers, and laptops. It’s especially useful for talking to multiple devices at the same time.“
If you are using Debian 10, follow the guide below to install Fleet Osquery on Debian 10;
Install Fleet Osquery Manager on Debian 10
Install Osquery Fleet Manager on Ubuntu
Prerequisites
In order to install Fleet osquery manager on Ubuntu, there are a few requirements. In our setup, we will be using Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04 as our base OS.
Install MySQL Database on Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04
Fleet uses MySQL as its main database
In this setup, we will use MariaDB database. Hence, create latest MariaDB (currently v10.8) APT repository
apt install software-properties-common gnupg2 zip -ywget -qO- https://mariadb.org/mariadb_release_signing_key.asc | gpg --dearmor > /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/mariadb.gpgecho "deb [arch=amd64] http://sfo1.mirrors.digitalocean.com/mariadb/repo/10.8/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mariadb-10.8.listIf you need, you can choose other MariaDB mirrors closed to your region.
Update your package cache.
apt updateRun the command install MariaDB server 10.5 on Ubuntu 20.04
apt install mariadb-serverMariaDB is started and enabled to run on system boot upon installation.
systemctl status mariadb.service
● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.8.5 database server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /etc/systemd/system/mariadb.service.d
└─migrated-from-my.cnf-settings.conf
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-09-26 17:16:45 UTC; 2min 4s ago
Docs: man:mariadbd(8)
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
Process: 3526 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/install -m 755 -o mysql -g root -d /var/run/mysqld (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3527 ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c systemctl unset-environment _WSREP_START_POSITION (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3529 ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c [ ! -e /usr/bin/galera_recovery ] && VAR= || VAR=`cd /usr/bin/..; /usr/bin/galera_recovery`; [ $? -eq 0 ] && systemctl set-en>
Process: 3575 ExecStartPost=/bin/sh -c systemctl unset-environment _WSREP_START_POSITION (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3577 ExecStartPost=/etc/mysql/debian-start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3558 (mariadbd)
Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..."
Tasks: 9 (limit: 4574)
Memory: 78.1M
CPU: 359ms
CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service
└─3558 /usr/sbin/mariadbd
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: 2022-09-26 17:16:45 0 [Note] Plugin 'FEEDBACK' is disabled.
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: 2022-09-26 17:16:45 0 [Note] InnoDB: Loading buffer pool(s) from /var/lib/mysql/ib_buffer_pool
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: 2022-09-26 17:16:45 0 [Warning] You need to use --log-bin to make --expire-logs-days or --binlog-expire-logs-seconds work.
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: 2022-09-26 17:16:45 0 [Note] Server socket created on IP: '127.0.0.1'.
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: 2022-09-26 17:16:45 0 [Note] InnoDB: Buffer pool(s) load completed at 220926 17:16:45
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: 2022-09-26 17:16:45 0 [Note] /usr/sbin/mariadbd: ready for connections.
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish mariadbd[3558]: Version: '10.8.5-MariaDB-1:10.8.5+maria~ubu2204' socket: '/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock' port: 3306 mariadb.org binary distribution
Sep 26 17:16:45 jellyfish systemd[1]: Started MariaDB 10.8.5 database server.
Create Fleet Database and Database User
Run the initial MySQL security script, mysql_secure_installation, to remove anonymous database users, test tables, disable remote root login.
mysql_secure_installationBy default, MariaDB 10.5 uses unix_socket for authentication by default and hence, can login by just running, mysql -u root. If have however enabled password authentication, simply run;
mysql -u root -pNext, create the Fleet database.
Note: the database database names used here are not standard. Choose any name of your preference.
create database fleetdb;Create Fleet database user with all grants on Fleet DB created above.
grant all on fleetdb.* to fleetadmin@localhost identified by 'StrongP@SS';Reload privileges tables and exit the database;
flush privileges;
exitInstall Redis on Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04
Fleet uses Redis to ingest and queue the results of distributed queries, cache data, etc.
To install the latest stable version of Redis, run the command below;
curl -fsSL https://packages.redis.io/gpg | gpg --dearmor > /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/redis.gpg echo "deb https://packages.redis.io/deb $(lsb_release -cs) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/redis.listNext, update the package cache;
apt updateInstall Redis on Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04;
apt install redisRedis server is similarly started upon installation;
systemctl status redis-server.service
● redis-server.service - Advanced key-value store
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/redis-server.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-09-26 17:24:43 UTC; 25s ago
Docs: http://redis.io/documentation,
man:redis-server(1)
Main PID: 4457 (redis-server)
Status: "Ready to accept connections"
Tasks: 5 (limit: 4574)
Memory: 2.8M
CPU: 100ms
CGroup: /system.slice/redis-server.service
└─4457 "/usr/bin/redis-server 127.0.0.1:6379" "" "" "" "" "" "" ""
Sep 26 17:24:43 jellyfish systemd[1]: Starting Advanced key-value store...
Sep 26 17:24:43 jellyfish systemd[1]: Started Advanced key-value store.
Enable it to run on system boot;
systemctl enable redis-serverInstalling Osquery Fleet Manager on Ubuntu
Install the Fleet binary on Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04
The Fleet application is distributed as a single static binary. This binary serves:
- The Fleet web interface
- The Fleet application API endpoints
- The osquery TLS server API endpoints
To download the latest Fleet and Fleetctl binaries (v4.20.1 currently), navigate to the releases page and grab the archive. You can get the url and simply execute the command below;
curl -LO https://github.com/fleetdm/fleet/releases/download/fleet-v4.20.1/fleet_v4.20.1_linux.tar.gzcurl -LO https://github.com/fleetdm/fleet/releases/download/fleet-v4.20.1/fleetctl_v4.20.1_linux.tar.gzExtract the binaries for Linux platform:
tar xzf fleet_v4.20.1_linux.tar.gztar xzf fleetctl_v4.20.1_linux.tar.gzCopy Fleet binaries to binaries directories;
cp fleet_v4.20.1_linux/fleet /usr/local/bin/cp fleetctl_v4.20.1_linux/fleetctl /usr/local/bin/To verify the binaries are in place;
which fleet fleetctl/usr/local/bin/fleet
/usr/local/bin/fleetctlRunning Fleet Server on Ubuntu 20.04/Ubuntu 22.04
Initialize Fleet Database
To initialize Fleet infrastructure after installing and setting up all the requirements above, use the fleet prepare db as follows;
fleet prepare db --mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 --mysql_database=fleetdb --mysql_username=fleetadmin --mysql_password=StrongP@SSIf the initialization completes successfully, you should get the output,
INFO: 17:46:26 Adding software_id column to software_cve table...
INFO: 17:46:26 Done adding software_id column to software_cve table...
INFO: 17:46:26 Updating software_id column in software_cve table...
INFO: 17:46:26 Nothing to update ...
INFO: 17:46:26 Done updating 'software_id'...
INFO: 17:46:26 Adding index to 'software_id'...
INFO: 17:46:26 Done adding index to 'software_id'...
INFO: 17:46:26 Trying to acquire lock...
INFO: 17:46:26 Lock acquired...
INFO: 17:46:26 Removing duplicates in the software_cve table
INFO: 17:46:26 Adding unique constraint on (cve, software_id) to software_cve table...
INFO: 17:46:26 Done adding unique constraint on (cve, software_id) to software_cve table...
INFO: 17:46:26 Creating table mobile_device_management_solutions...
INFO: 17:46:26 Done creating table mobile_device_management_solutions...
INFO: 17:46:26 Adding column mdm_id to table host_mdm...
INFO: 17:46:26 Done adding column mdm_id to table host_mdm...
INFO: 17:46:26 Adding index on mdm_id of table host_mdm...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done adding index on mdm_id of table host_mdm...
INFO: 17:46:27 Adding index on enrolled, installed_from_dep of table host_mdm...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done adding index on enrolled, installed_from_dep of table host_mdm...
INFO: 17:46:27 Increasing width of software.vendor...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done increasing width of software.vendor...
INFO: 17:46:27 Creating table munki_issues...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done creating table munki_issues...
INFO: 17:46:27 Creating table host_munki_issues...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done creating table host_munki_issues...
INFO: 17:46:27 Deleting dummy software_cpe entries...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done deleting dummy cpe_id entries...
INFO: 17:46:27 Removing cpe_id from software_cve...
INFO: 17:46:27 Done removing cpe_id from software_cve...
Migrations completed.
Generate SSL/TLS Certificates
Fleet server is used to run the main HTTPS server. Hence, run the command below to generate self-signed certificates.
NOTE: If you are using Self Signed Certificates as in this demo, DO NOT use wildcards lest enrollment of hosts won’t work.
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 3650 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/fleet.key -out /etc/ssl/certs/fleet.cert -subj "/CN=*.kifarunix-demo.com/"If you can, use the commercial TLS certificates from your preferred trusted CA.
Launching Fleet Osquery Manager
Once you have initialized the database, obtained the TLS certs, you can then launch it to verify that it can run successfully using the fleet serve command as shown below.
The syntax for running fleet serve is given below;
fleet serve [flags]There are different ways in which you can specify Fleet flags;
Specifying Fleet Manager Flags on Command line
You can specify the flags on command line as shown below;
fleet serve --mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 \
--mysql_database=fleetdb --mysql_username=fleetadmin --mysql_password=StrongP@SS \
--server_cert=/etc/ssl/certs/fleet.cert --server_key=/etc/ssl/private/fleet.key \
--logging_json If all is well, you should see that Fleet server is now running on 0.0.0.0:8080 and hence can be accessed on https://<server-IP>:8080.
{"component":"redis","level":"info","mode":"standalone","ts":"2022-09-26T17:52:54.28424084Z"}
{"component":"crons","cron":"vulnerabilities","level":"info","periodicity":"1h0m0s","ts":"2022-09-26T17:52:54.295821803Z"}
{"level":"info","msg":"metrics endpoint disabled (http basic auth credentials not set)","ts":"2022-09-26T17:52:54.312885518Z"}
{"address":"0.0.0.0:8080","msg":"listening","transport":"https","ts":"2022-09-26T17:52:54.313178069Z"}
{"component":"crons","cron":"vulnerabilities","level":"info","msg":"software inventory not configured","ts":"2022-09-26T17:53:04.300608097Z"}Press Ctrl+c to stop Fleet server.
Specifying Fleet Manager Flags Using Environment Variables
Similarly, you can specify the Fleet flags using environment variables as shown below (update the values for the environment variables and paste the command on the terminal);
FLEET_MYSQL_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:3306 \
FLEET_MYSQL_DATABASE=fleetdb \
FLEET_MYSQL_USERNAME=fleetadmin \
FLEET_MYSQL_PASSWORD=StrongP@SS \
FLEET_REDIS_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1:6379 \
FLEET_SERVER_CERT=/etc/ssl/certs/fleet.cert \
FLEET_SERVER_KEY=/etc/ssl/private/fleet.key \
FLEET_LOGGING_JSON=true \
$(which fleet) serveSimilarly, press Ctrl+c to stop Fleet server.
Setting the Fleet Manager Flags in a Configuration file
You can create a YAML configuration file where you can define the flags and their options. For example, let us create a configuration file, e.g /etc/fleet/fleet.yml.
mkdir /etc/fleetThe, create a YAML configuration file under the directory above.
You can simply execute the command below and be sure to replace your settings appropriately.
cat > /etc/fleet/fleet.yml << 'EOL'
mysql:
address: 127.0.0.1:3306
database: fleetdb
username: fleetadmin
password: StrongP@SS
redis:
address: 127.0.0.1:6379
server:
cert: /etc/ssl/certs/fleet.cert
key: /etc/ssl/private/fleet.key
logging:
json: true
# auth:
# jwt_key: cw1h9ww06XwWDOwDDBpi9pxwNqEVf6Ig
EOL
Next, launch the Fleet manager by running the command below;
fleet serve -c /etc/fleet/fleet.ymlSimilarly, press Ctrl+c to stop Fleet server.
Create Fleet Systemd Service Unit on Ubuntu 20.04
Once you have verified that Fleet is running fine, create a systemd service file, /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service. You can use any method shown above to specify the flags for ExecStart option while creating the systemd service unit file.
Example of Fleet systemd service unit file with Flags specified in ‘cli’ like format.
cat > /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Fleet Osquery Fleet Manager
After=network.target
[Service]
LimitNOFILE=8192
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/fleet serve \
--mysql_address=127.0.0.1:3306 \
--mysql_database=fleetdb \
--mysql_username=fleetadmin \
--mysql_password=StrongP@SS \
--redis_address=127.0.0.1:6379 \
--server_cert=/etc/ssl/certs/fleet.cert \
--server_key=/etc/ssl/private/fleet.key \
--logging_json
ExecStop=/bin/kill -15 $(ps aux | grep "fleet serve" | grep -v grep | awk '{print$2}')
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
The method I preferred myself is to use the configuration file instead. The below service file uses the configuration file with Fleet flags defined as shown above.
cat > /etc/systemd/system/fleet.service << 'EOL'
[Unit]
Description=Fleet Osquery Fleet Manager
After=network.target
[Service]
LimitNOFILE=8192
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/fleet serve -c /etc/fleet/fleet.yml
ExecStop=/bin/kill -15 $(ps aux | grep "fleet serve" | grep -v grep | awk '{print$2}')
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOL
Reload systemd configurations.
systemctl daemon-reloadStart and enable Fleet service.
systemctl enable --now fleetCheck the status;
systemctl status fleet
● fleet.service - Fleet Osquery Fleet Manager
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/fleet.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2022-09-26 18:01:12 UTC; 6s ago
Main PID: 5422 (fleet)
Tasks: 9 (limit: 4574)
Memory: 16.0M
CPU: 120ms
CGroup: /system.slice/fleet.service
└─5422 /usr/local/bin/fleet serve -c /etc/fleet/fleet.yml
Sep 26 18:01:12 jellyfish systemd[1]: Started Fleet Osquery Fleet Manager.
Sep 26 18:01:12 jellyfish fleet[5422]: Using config file: /etc/fleet/fleet.yml
Sep 26 18:01:12 jellyfish fleet[5422]: {"component":"redis","level":"info","mode":"standalone","ts":"2022-09-26T18:01:12.109487031Z"}
Sep 26 18:01:12 jellyfish fleet[5422]: {"component":"crons","cron":"vulnerabilities","level":"info","periodicity":"1h0m0s","ts":"2022-09-26T18:01:12.121929269Z"}
Sep 26 18:01:12 jellyfish fleet[5422]: {"level":"info","msg":"metrics endpoint disabled (http basic auth credentials not set)","ts":"2022-09-26T18:01:12.13573016Z"}
Sep 26 18:01:12 jellyfish fleet[5422]: {"address":"0.0.0.0:8080","msg":"listening","transport":"https","ts":"2022-09-26T18:01:12.13588821Z"}
Access Fleet Web Interface
Fleet can be accessed on the browser using the URL https://<server-IP_OR_hostname>:8080.
If firewall is running, open this port to allow external access;
ufw allow 8080/tcpThen access Fleet Web interface from browser. and proceed to finalize the setup of Fleet Osquery manager on Ubuntu 20.04;
Create the admin user;
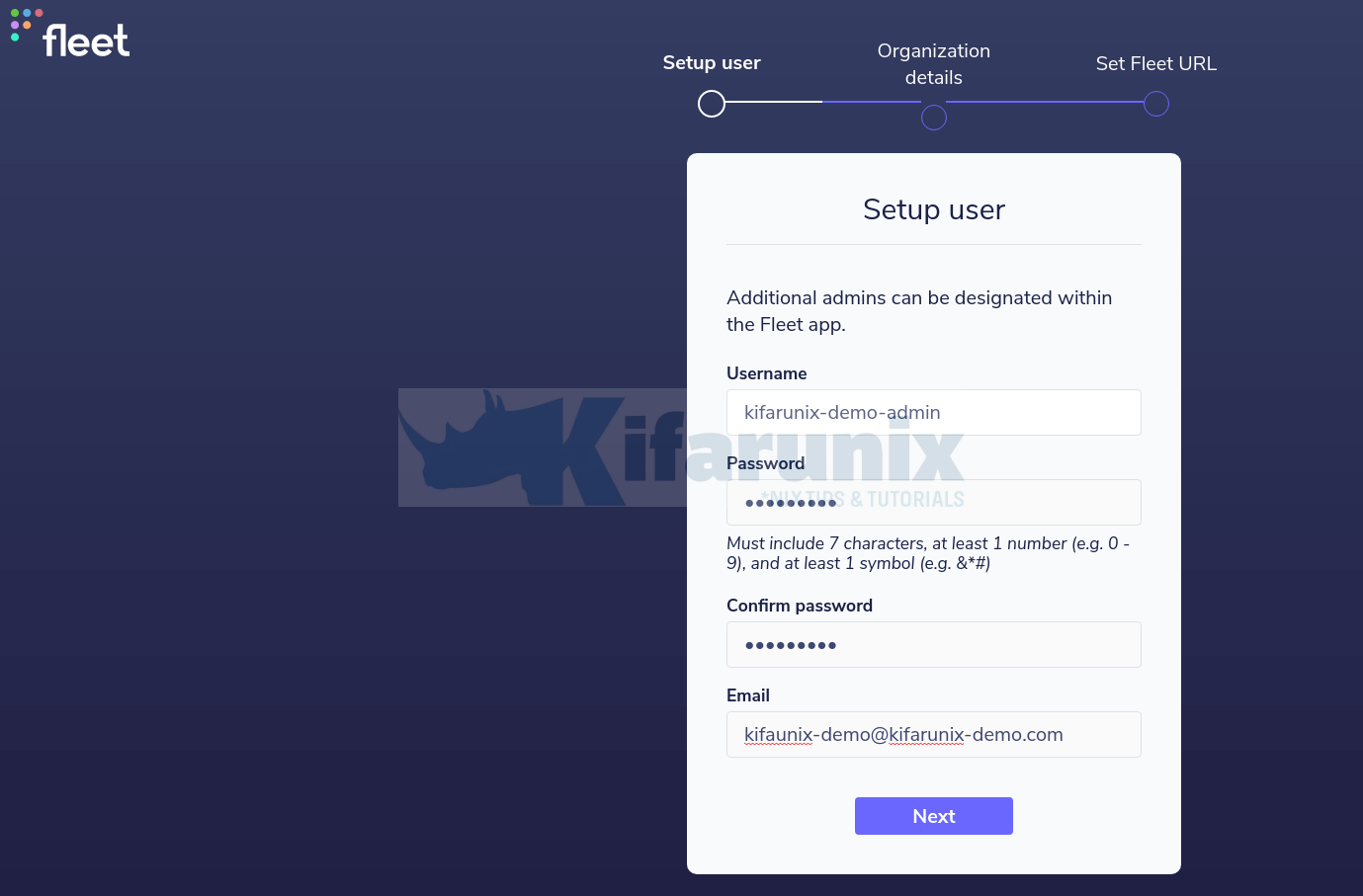
Enter your organization details, Name and url to logo.
Set the Fleet server URL.
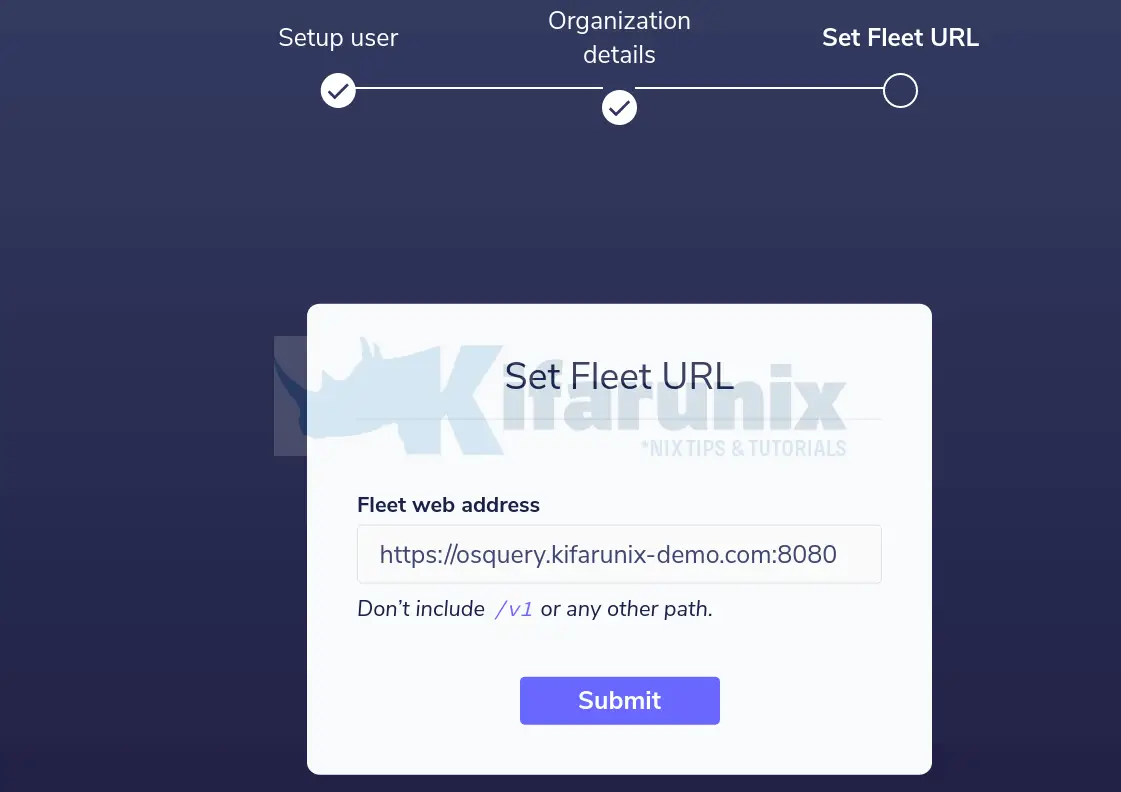
Submit the details and proceed to Fleet web interface.

And that marks the end of our tutorial on how to install Fleet Osquery Manager on Ubuntu 20.04. In our next tutorial, you will learn how to enroll Osquery agents to Fleet manager.
How to Enroll Osquery Hosts on Fleet Manager
Reference
Other Related Tutorials
Install Osquery on Ubuntu 20.04

