Follow through this guide to learn how to easily install etcdctl on Kubernetes cluster. Kubernetes cluster relies on etcd, a distributed key-value store, to store configuration data required to maintain the cluster state. And while the Kubernetes API offers a robust set of tools for administering it, sometimes you might need to directly interact with etcd to troubleshoot issues, retrieve data, or perform specific configurations. This is where etcdctl comes in handy.
Table of Contents
Installing etcdctl on Kubernetes Cluster
Why Install etcdctl?
You might be asking yourself why you need to install etcdctl command line tool on your cluster, yet the etcd pods already comes pre-packaged with the etcdctl tool.
While that is true, installing etcdctl on a local Kubernetes control plane, provides flexibility and convenience for managing the cluster’s configuration, monitoring its health, or troubleshooting issues without having to directly access the Kubernetes pods.
Get Installed etcd Version Number
Ideally, the version of etcdctl should match the version of etcd with which it is intended to interact. Therefore, before you can proceed to install etcdctl tool, you need to get the version of the currently installed etcd.
To get the version of etcd, you would usually run the command;
etcd --versionHowever, for the Kubernetes cluster, you need to get the version number from the etcd pod.
List the pods, from control plane;
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l component=etcdNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
etcd-master-01 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 24h
etcd-master-02 1/1 Running 0 24h
etcd-master-03 1/1 Running 0 24h
So, you can get the version of etcd from one of the etcd pod;
kubectl exec etcd-master-01 -n kube-system -- etcd --versionetcd Version: 3.5.12
Git SHA: e7b3bb6cc
Go Version: go1.20.13
Go OS/Arch: linux/amd64
From the command output, you can see that we are running etcd version 3.5.12.
Install etcdctl command line tool
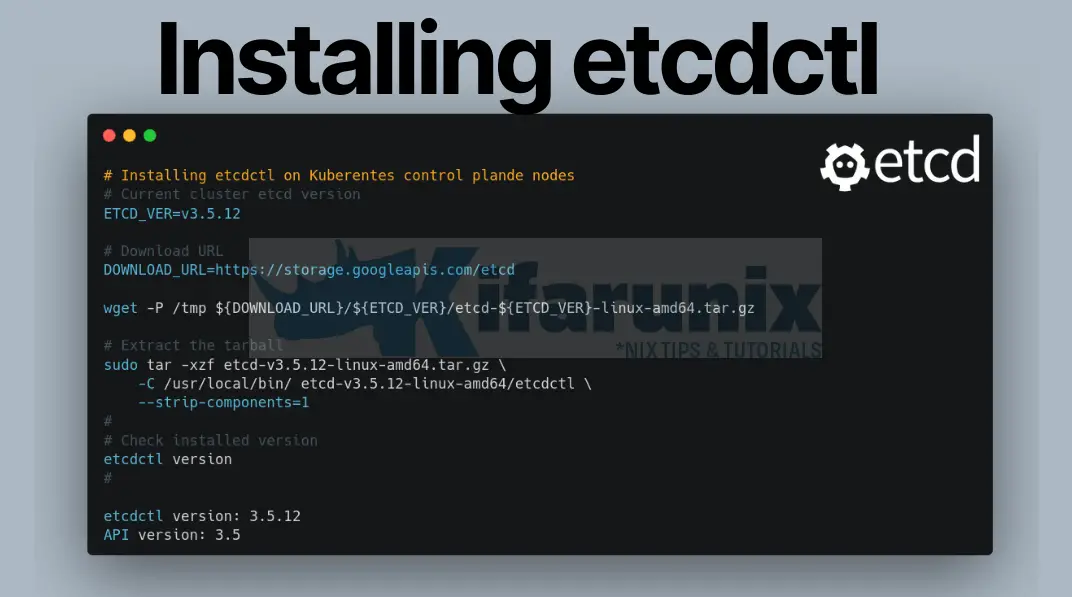
There are different ways of installing etcdctl tool on Linux, right from running it as docker container, as systemd service unit etc. However, we are installing it on a local system just as a binary in this guide as follows.
Download etcd source tarball
Set the version of a running etcd to a variable as shown below. Replace the version number of etcd accordingly.
ETCD_VER=v3.5.12Next, download the etcd source code;
wget https://storage.googleapis.com/etcd/${ETCD_VER}/etcd-${ETCD_VER}-linux-amd64.tar.gz -P /tmp/Extract etcdctl binary
The etcd tarball will contain the etcdctl binary we need. See the command output below
tar tf /tmp/etcd-${ETCD_VER}-linux-amd64.tar.gzetcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/README.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/READMEv2-etcdctl.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcdutl
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcdctl
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/README.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/v3election.swagger.json
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/rpc.swagger.json
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/v3lock.swagger.json
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/README-etcdutl.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/README-etcdctl.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcd
We are only interested in etcdctl binary. Hence, just extract it to the local binary files directory;
sudo tar -xzf /tmp/etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin/ etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcdctl --strip-components=1You should now have the etcdctl binary on your path.
which etcdctl/usr/local/bin/etcdctlVerify etcdctl Version Installed
To confirm the version of etcdctl installed, run the command below;
etcdctl versionetcdctl version: 3.5.12
API version: 3.5Interacting with Kubernetes cluster with etcdctl
Once you have the tool installed, you can then use it to interact with the cluster etcd.
For example, am currently logged into one of the cluster control plane where etcd is running.
ss -altnp | grep 2379LISTEN 0 4096 192.168.122.58:2379 0.0.0.0:*
LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:2379 0.0.0.0:*
So, it is listening on both an IP and a loopback interface.
Check etcd Cluster Status
There are different ways in which you can use etcdctl to interact with the cluster. In the very basic way, let’s the status and health of the cluster.
To check etcd status, use the command;
etcdctl endpoint status (--endpoints=$ENDPOINTS|--cluster)For example;
sudo etcdctl endpoint status \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
Without specifying the endpoint, it will try to use loopback address.
Sample output;
127.0.0.1:2379, 7f56434149e2cc7f, 3.5.12, 9.9 MB, true, false, 4, 4745, 4745,You can also specify the IP address.
sudo etcdctl endpoint status \
--endpoints=https://192.168.122.58:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
Output;
https://192.168.122.58:2379, 7f56434149e2cc7f, 3.5.12, 8.0 MB, false, false, 3, 377635, 377635,To check the status of the whole cluster, use –cluster option.
sudo etcdctl endpoint status \
--endpoints=https://192.168.122.58:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key \
--cluster
Output;
https://192.168.122.58:2379, 7f56434149e2cc7f, 3.5.12, 8.0 MB, false, false, 3, 377722, 377722,
https://192.168.122.60:2379, 88c0888f95e69bf2, 3.5.12, 7.9 MB, true, false, 3, 377722, 377722,
https://192.168.122.59:2379, d98ec9634e856042, 3.5.12, 7.4 MB, false, false, 3, 377722, 377722,
You can also display the output in different formats (fields, json, protobuf, simple, table) by passing the option -w|–write-out option.
For example, to show in table format;
sudo etcdctl endpoint status \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt\
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key \
-w table
+----------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
| ENDPOINT | ID | VERSION | DB SIZE | IS LEADER | IS LEARNER | RAFT TERM | RAFT INDEX | RAFT APPLIED INDEX | ERRORS |
+----------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
| 127.0.0.1:2379 | 7f56434149e2cc7f | 3.5.12 | 9.9 MB | true | false | 4 | 4760 | 4760 | |
+----------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
For cluster-wide;
sudo etcdctl endpoint status \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt\
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key \
-w table \
--cluster
+-----------------------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
| ENDPOINT | ID | VERSION | DB SIZE | IS LEADER | IS LEARNER | RAFT TERM | RAFT INDEX | RAFT APPLIED INDEX | ERRORS |
+-----------------------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
| https://192.168.122.58:2379 | 7f56434149e2cc7f | 3.5.12 | 9.9 MB | true | false | 4 | 5255 | 5255 | |
| https://192.168.122.59:2379 | bb52cdc64ee8e59b | 3.5.12 | 9.9 MB | false | false | 4 | 5255 | 5255 | |
| https://192.168.122.60:2379 | f566c3fe95233961 | 3.5.12 | 9.9 MB | false | false | 4 | 5255 | 5255 | |
+-----------------------------+------------------+---------+---------+-----------+------------+-----------+------------+--------------------+--------+
Demystifying the Status Output
What does each field, separated by comma, mean in the status output?
- Endpoint URL:
https://192.168.122.58:2379- …
- These are the addresses of the etcd cluster members.
- ID:
7f56434149e2cc7f- …
- These are the unique identifiers of the etcd members.
- Version:
3.5.12: This is the version of the etcd server that each member is running.
- Database Size:
8.0 MB...- This indicates the size of the etcd database on each member.
- Is Leader:
false(for 192.168.122.58 and 192.168.122.59)true(for 192.168.122.60)- This indicates whether the member is currently the leader of the etcd cluster. In this case,
192.168.122.60is the leader.
- Is Learner:
falsefor all members. This field indicates if the member is a learner in the cluster (a non-voting member). All members are not learners here.
- Raft Term:
3: This is the current term of the Raft consensus algorithm. All members are on the same term, indicating they are in sync in terms of Raft consensus.
- Index:
377722: This is the latest index of the committed entries in the etcd log.
- Applied Index:
377722This is the index of the latest entry applied to the state machine.
Check etcd Cluster Health
You can also check the health of the cluster;
etcdctl endpoint health (--endpoints=$ENDPOINTS|--cluster)For example;
sudo etcdctl endpoint health \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
Similarly, without specifying the endpoint, it will try to use loopback address.
Sample output;
127.0.0.1:2379 is healthy: successfully committed proposal: took = 9.873047msYou can also specify the IP address.
sudo etcdctl endpoint health \
--endpoints=https://192.168.122.58:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key
Output;
https://192.168.122.58:2379 is healthy: successfully committed proposal: took = 9.405038msTo check the status of the whole cluster, use –cluster option.
sudo etcdctl endpoint health \
--endpoints=https://192.168.122.58:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key \
--cluster
Output;
https://192.168.122.60:2379 is healthy: successfully committed proposal: took = 12.828208ms
https://192.168.122.58:2379 is healthy: successfully committed proposal: took = 12.474987ms
https://192.168.122.59:2379 is healthy: successfully committed proposal: took = 17.145012ms
In tabular format;
sudo etcdctl endpoint health \
--endpoints=https://192.168.122.58:2379 \
--cacert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt \
--cert=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.crt \
--key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/server.key \
--cluster \
-w table
+-----------------------------+--------+-------------+-------+
| ENDPOINT | HEALTH | TOOK | ERROR |
+-----------------------------+--------+-------------+-------+
| https://192.168.122.58:2379 | true | 10.108583ms | |
| https://192.168.122.59:2379 | true | 10.437731ms | |
| https://192.168.122.60:2379 | true | 10.477674ms | |
+-----------------------------+--------+-------------+-------+
Install etcdutl command line tool
While you can use etcdctl command to restore Kubernetes etcd data, the functionality has been deprecated since etcd v3.5.x and is slated for removal from etcd v3.6. It is recommended to utilize etcdutl instead.
The etcdutl is packaged together with etcdctl in the same source code.
tar tf /tmp/etcd-${ETCD_VER}-linux-amd64.tar.gzetcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/README.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/READMEv2-etcdctl.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcdutl
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcdctl
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/README.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/v3election.swagger.json
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/rpc.swagger.json
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/Documentation/dev-guide/apispec/swagger/v3lock.swagger.json
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/README-etcdutl.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/README-etcdctl.md
etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcd
Therefore, the installation of etcdutl is as simple as extracting the binary using the command below;
sudo tar -xzf /tmp/etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin/ etcd-v3.5.12-linux-amd64/etcdutl --strip-components=1You should now have the etcdctl binary on your path.
which etcdutl/usr/local/bin/etcdutlverify the installed version,
/usr/local/bin/etcdutl versionetcdutl version: 3.5.12
API version: 3.5etcdutl help page;
etcdutl helpUsage:
etcdutl [command]
Available Commands:
backup [legacy] offline backup of etcd directory
defrag Defragments the storage of the etcd
help Help about any command
snapshot Manages etcd node snapshots
version Prints the version of etcdutl
Flags:
-h, --help help for etcdutl
-w, --write-out string set the output format (fields, json, protobuf, simple, table) (default "simple")
Use "etcdutl [command] --help" for more information about a command.
And that is it!
That closes our guide on installing etcdctl and etcdutl on a Kubernetes Cluster.

