Follow through this post to learn how to deploy Ceph storage cluster on AlmaLinux. Ceph is a scalable distributed storage system designed for cloud infrastructure and web-scale object storage. It can also be used to provide Ceph Block Storage as well as Ceph File System storage.
As of this writing, Ceph 18 (code named Reef) is the current stable release.
We are using AlmaLinux 9.3 (Shamrock Pampas Cat) in this guide.
Table of Contents
Deploying Ceph Storage Cluster on AlmaLinux
The Ceph Storage Cluster Daemons
Ceph Storage Cluster is made up of different daemons eas performing specific role.
- Ceph Object Storage Daemon (OSD,
ceph-osd)- It provides ceph object data store.
- It also performs data replication , data recovery, rebalancing and provides storage information to Ceph Monitor.
- At least an OSD is required per storage device.
- Ceph Monitor (
ceph-mon)- It maintains maps of the entire Ceph cluster state including monitor map, manager map, the OSD map, and the CRUSH map.
- manages authentication between daemons and clients.
- A Ceph cluster must contain a minimum of three running monitors in order to be both redundant and highly-available.
- Ceph Manager (
ceph-mgr)- keeps track of runtime metrics and the current state of the Ceph cluster, including storage utilization, current performance metrics, and system load.
- manages and exposes Ceph cluster web dashboard and API.
- At least two managers are required for HA.
- Ceph Metadata Server (MDS):
- Manages metadata for the Ceph File System (CephFS). Coordinates metadata access and ensures consistency across clients.
- One or more, depending on the requirements of the CephFS.
- RADOS Gateway (RGW):
- Also called “Ceph Object Gateway”
- is a component of the Ceph storage system that provides object storage services with a RESTful interface. RGW allows applications and users to interact with Ceph storage using industry-standard APIs, such as the S3 (Simple Storage Service) API (compatible with Amazon S3) and the Swift API (compatible with OpenStack Swift).
Ceph Storage Cluster Deployment Methods
There are different methods you can use to deploy Ceph storage cluster.
cephadmleverages container technology (specifically, Docker containers) to deploy and manage Ceph services on a cluster of machines.Rookdeploys and manages Ceph clusters running in Kubernetes, while also enabling management of storage resources and provisioning via Kubernetes APIs.ceph-ansibledeploys and manages Ceph clusters using Ansible.- ceph-salt installs Ceph using Salt and cephadm.
- jaas.ai/ceph-mon installs Ceph using Juju.
- Install Ceph via Puppet.
- Ceph can also be installed manually.
Use of cephadm and rooks are the recommended methods for deploying Ceph storage cluster.
Ceph Depolyment Requirements
Depending on the deployment method you choose, there are different requirements for deploying Ceph storage cluster
In this tutorial, we will use cephadm to deploy Ceph storage cluster.
Below are the requirements for deploying Ceph storage cluster via cephadm;
- Python 3 (installed by default on AlmaLinux)
- Systemd
- Podman or Docker for running containers (we use docker in this setup)
- Time synchronization (such as chrony or NTP)
- LVM2 for provisioning storage devices. We are using raw devices without any filesystem in this guide.
All the required dependencies are installed automatically by the bootstrap process.
Prepare Ceph Nodes for Ceph Storage Cluster Deployment on AlmaLinux
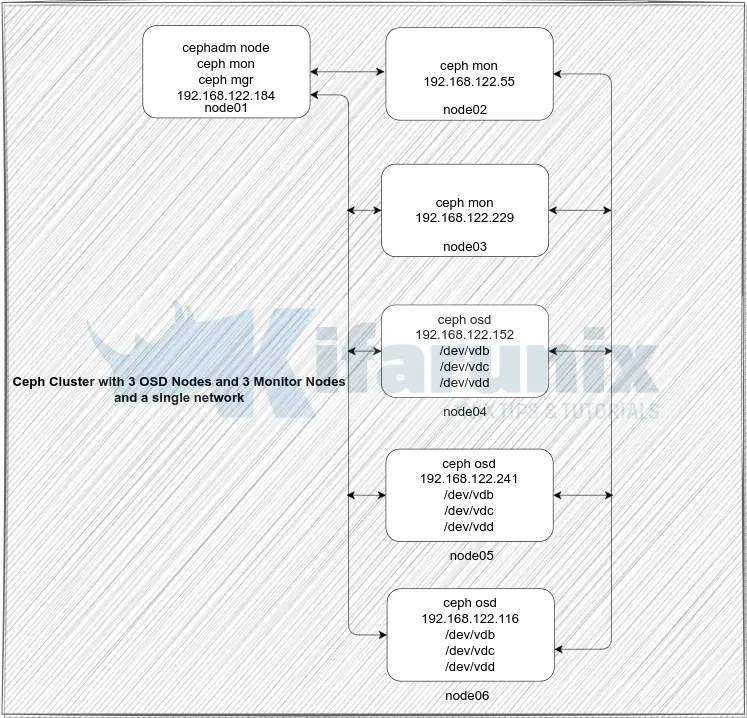
Our Ceph Storage Cluster Deployment Architecture
The diagram below depicts our ceph storage cluster deployment architecture. In a typical production environment, you would have at least 3 monitor nodes as well as at least 3 OSDs.
Ceph Storage Nodes Hardware Requirements
Check the hardware recommendations page for the Ceph storage cluster nodes hardware requirements.
Storage Devices for Creating Ceph OSDs
Each Ceph OSD node in our architecture above has unallocated raw disk of 50 GB each.
lsblkSample output;
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS
vda 252:0 0 50G 0 disk
├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot
└─vda2 252:2 0 49G 0 part
├─rl-root 253:0 0 45G 0 lvm /
└─rl-swap 253:1 0 4G 0 lvm [SWAP]
vdb 252:16 0 50G 0 disk
vdc 252:32 0 50G 0 disk
vdd 252:48 0 50G 0 disk
Set Hostnames and Update Hosts File
To begin with, setup up your nodes hostnames;
hostnamectl set-hostname node01Set the respective hostnames on other nodes.
If you are not using DNS for name resolution, then update the hosts file accordingly.
For example, in our setup, each node hosts file should contain the lines below;
less /etc/hosts127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.122.240 node01
192.168.122.55 node02
192.168.122.229 node03
192.168.122.152 node04
192.168.122.241 node05
192.168.122.116 node06
Set Time Synchronization
Ensure that the time on all the nodes is synchronized. Thus install Chrony on each and set it up such that all nodes uses the same NTP server. It might already be installed!
dnf install chrony -yEdit the Chrony configuration and set your NTP server by replacing the NTP server pools with your NTP server address.
vim /etc/chrony/chrony.confDefine your NTP Server. Replace ntp.kifarunix-demo.com with your respective NTP server address. Otherwise, use the global time servers if you don’t have your own.
...
# pool ntp.ubuntu.com iburst maxsources 4
# pool 0.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst maxsources 1
# pool 1.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst maxsources 1
# pool 2.ubuntu.pool.ntp.org iburst maxsources 2
pool ntp.kifarunix-demo.com iburst
...
Restart Chronyd
systemctl restart chronydInstall SSH Server on Each Node
Ceph deployment through cephadm utility requires that an SSH server is installed on all the nodes.
AlmaLinux comes with SSH server already installed. If not, install and start it as follows;
dnf install openssh-serversystemctl enable --now sshdInstall Python3
Python is required to deploy Ceph on AlmaLinux. Python 3 is installed by default on AlmaLinux;
python -VPython 3.9.18Install LVM2 on AlmaLinux
LVM2 is required for Ceph to manage OSDs (Object Storage Devices) on the host.
You can install using the command below;
dnf install lvm2 -yInstall Docker CE on Each Node
The cephadm utility is used to bootstrap a Ceph cluster and to manage ceph daemons deployed with systemd and Docker containers.
Thus, on each Node, install Docker. You can follow the guide below to install Docker on AlmaLinux;
Install Docker on Rocky Linux 8|9
Enable Root Login on Other Nodes from Ceph Admin Node
In order to add other nodes to the Ceph cluster using Ceph Admin Node, you will have to use the root user account.
Thus, on the Ceph Monitor, Ceph OSD nodes, enable root login from the Ceph Admin node.
Ensure access to SSH via root is restricted. For now, I will just enable root SSH login.
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config#PermitRootLogin prohibit-password
PermitRootLogin yesSave and exit the file.
Reload ssh;
systemctl reload sshdSetup Ceph Storage Cluster on AlmaLinux
Install cephadm Utility on Ceph Admin Node
On the Ceph admin node, you need to install the cephadm utility. In this guide, we are using node01 as ceph admin node.
Cephadm installs and manages a Ceph cluster using containers and systemd, with tight integration with the CLI and dashboard GUI.
- cephadm only supports Octopus and newer releases.
- cephadm is fully integrated with the new orchestration API and fully supports the new CLI and dashboard features to manage cluster deployment.
- cephadm requires container support (podman or docker) and Python 3.
To install cephadm on AlmaLinux 9;
CEPH_RELEASE=18.2.0curl -sLO https://download.ceph.com/rpm-${CEPH_RELEASE}/el9/noarch/cephadmMake the binary executable;
chmod +x ./cephadmNext, execute the commands below to install cephadm for Ceph Reef on AlmaLinux;
./cephadm add-repo --release reef./cephadm installConfirm the installation of cephadm command.
which cephadmYou should see the path to the cephadm binary printed, /usr/sbin/cephadm.
The command will also install podman. So whichever it will find first between it and Docker, it will use it.
Initialize Ceph Cluster Monitor On Ceph Admin Node
Your nodes are now ready to deploy a Ceph storage cluster. As such, it is time to bootstrap the Ceph cluster in order to create the first Ceph monitor daemon on our first node, node01.
Thus, run the command below, substituting the IP address with that of the Ceph admin node, which also doubles up as our ceph monitor node01 in this guide..
cephadm bootstrap --mon-ip 192.168.122.240Creating directory /etc/ceph for ceph.conf
Verifying podman|docker is present...
Verifying lvm2 is present...
Verifying time synchronization is in place...
Unit chronyd.service is enabled and running
Repeating the final host check...
podman (/usr/bin/podman) version 4.6.1 is present
systemctl is present
lvcreate is present
Unit chronyd.service is enabled and running
Host looks OK
Cluster fsid: f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
Verifying IP 192.168.122.240 port 3300 ...
Verifying IP 192.168.122.240 port 6789 ...
Mon IP `192.168.122.240` is in CIDR network `192.168.122.0/24`
Mon IP `192.168.122.240` is in CIDR network `192.168.122.0/24`
Internal network (--cluster-network) has not been provided, OSD replication will default to the public_network
Pulling container image quay.io/ceph/ceph:v18...
Ceph version: ceph version 18.2.0 (5dd24139a1eada541a3bc16b6941c5dde975e26d) reef (stable)
Extracting ceph user uid/gid from container image...
Creating initial keys...
Creating initial monmap...
Creating mon...
Waiting for mon to start...
Waiting for mon...
mon is available
Assimilating anything we can from ceph.conf...
Generating new minimal ceph.conf...
Restarting the monitor...
Setting mon public_network to 192.168.122.0/24
Wrote config to /etc/ceph/ceph.conf
Wrote keyring to /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring
Creating mgr...
Verifying port 9283 ...
Verifying port 8765 ...
Verifying port 8443 ...
Waiting for mgr to start...
Waiting for mgr...
mgr not available, waiting (1/15)...
mgr not available, waiting (2/15)...
mgr not available, waiting (3/15)...
mgr not available, waiting (4/15)...
mgr is available
Enabling cephadm module...
Waiting for the mgr to restart...
Waiting for mgr epoch 5...
mgr epoch 5 is available
Setting orchestrator backend to cephadm...
Generating ssh key...
Wrote public SSH key to /etc/ceph/ceph.pub
Adding key to root@localhost authorized_keys...
Adding host node01...
Deploying mon service with default placement...
Deploying mgr service with default placement...
Deploying crash service with default placement...
Deploying ceph-exporter service with default placement...
Deploying prometheus service with default placement...
Deploying grafana service with default placement...
Deploying node-exporter service with default placement...
Deploying alertmanager service with default placement...
Enabling the dashboard module...
Waiting for the mgr to restart...
Waiting for mgr epoch 9...
mgr epoch 9 is available
Generating a dashboard self-signed certificate...
Creating initial admin user...
Fetching dashboard port number...
Ceph Dashboard is now available at:
URL: https://node01:8443/
User: admin
Password: amw3p3yy2e
Enabling client.admin keyring and conf on hosts with "admin" label
Saving cluster configuration to /var/lib/ceph/f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730/config directory
Enabling autotune for osd_memory_target
You can access the Ceph CLI as following in case of multi-cluster or non-default config:
sudo /usr/sbin/cephadm shell --fsid f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730 -c /etc/ceph/ceph.conf -k /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring
Or, if you are only running a single cluster on this host:
sudo /usr/sbin/cephadm shell
Please consider enabling telemetry to help improve Ceph:
ceph telemetry on
For more information see:
https://docs.ceph.com/en/latest/mgr/telemetry/
According to the documentation, the bootstrap command;
- Create a monitor and manager daemon for the new cluster on the localhost.
- Generate a new SSH key for the Ceph cluster and add it to the root user’s
/root/.ssh/authorized_keysfile. - Write a copy of the public key to
/etc/ceph/ceph.pub. - Write a minimal configuration file to
/etc/ceph/ceph.conf. This file is needed to communicate with the new cluster. - Write a copy of the
client.adminadministrative (privileged!) secret key to/etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring. - Add the
_adminlabel to the bootstrap host. By default, any host with this label will (also) get a copy of/etc/ceph/ceph.confand/etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring.
As you can see, cephadm used podman container management tool, podman (/usr/bin/podman) version 4.6.1 is present, from the bootstrap command output.
You can see created containers;
podman psCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b0001264bf0e quay.io/ceph/ceph:v18 -n mon.node01 -f ... 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-mon-node01
673b69975d89 quay.io/ceph/ceph:v18 -n mgr.node01.gvh... 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-mgr-node01-gvhmuc
4d4739e59495 quay.io/ceph/ceph@sha256:4ce43f6b683448acc5d45ef184be9a44a569cf9c0019d6bb21472523aa52873c -n client.ceph-ex... 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-ceph-exporter-node01
9123d699b6a9 quay.io/ceph/ceph@sha256:4ce43f6b683448acc5d45ef184be9a44a569cf9c0019d6bb21472523aa52873c -n client.crash.n... 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-crash-node01
0be1d3e87064 quay.io/prometheus/node-exporter:v1.5.0 --no-collector.ti... 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-node-exporter-node01
3a6e81492858 quay.io/prometheus/prometheus:v2.43.0 --config.file=/et... 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-prometheus-node01
c7f4e180775c quay.io/prometheus/alertmanager:v0.25.0 --cluster.listen-... 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-alertmanager-node01
177cc82138c4 quay.io/ceph/ceph-grafana:9.4.7 /bin/bash 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730-grafana-node01
If you are using Docker, then list the containers using;
docker psSimilarly, systemd unit files are also created for these containers;
systemctl list-units 'ceph*' UNIT LOAD ACTIVE SUB DESCRIPTION
ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730@alertmanager.node01.service loaded active running Ceph alertmanager.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730@ceph-exporter.node01.service loaded active running Ceph ceph-exporter.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
[email protected] loaded active running Ceph crash.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
[email protected] loaded active running Ceph grafana.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730@mgr.node01.gvhmuc.service loaded active running Ceph mgr.node01.gvhmuc for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
[email protected] loaded active running Ceph mon.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730@node-exporter.node01.service loaded active running Ceph node-exporter.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730@prometheus.node01.service loaded active running Ceph prometheus.node01 for f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
ceph-f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730.target loaded active active Ceph cluster f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
ceph.target loaded active active All Ceph clusters and services
LOAD = Reflects whether the unit definition was properly loaded.
ACTIVE = The high-level unit activation state, i.e. generalization of SUB.
SUB = The low-level unit activation state, values depend on unit type.
10 loaded units listed. Pass --all to see loaded but inactive units, too.
To show all installed unit files use 'systemctl list-unit-files'.
Enable Ceph CLI
When bootstrap command completes, a command for accessing Ceph CLI is provided. Execute that command to access Ceph CLI;
/usr/sbin/cephadm shell \
--fsid f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730 \
-c /etc/ceph/ceph.conf \
-k /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring
This drops you onto Ceph container CLI;
You can run the ceph commands eg to check the Ceph status;
ceph -s cluster:
id: f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
health: HEALTH_WARN
OSD count 0 < osd_pool_default_size 3
services:
mon: 1 daemons, quorum node01 (age 6m)
mgr: node01.gvhmuc(active, since 4m)
osd: 0 osds: 0 up, 0 in
data:
pools: 0 pools, 0 pgs
objects: 0 objects, 0 B
usage: 0 B used, 0 B / 0 B avail
pgs:
You can exit the ceph CLI by pressing Ctrl+D or type exit and press ENTER.
There are other ways in which you can access the Ceph CLI. For example, you can run Ceph CLI commands using cephadm command.
cephadm shell -- ceph -sOr You could install Ceph CLI tools on the host;
cephadm add-repo --release reefcephadm install ceph-commonWith this method, then you can just ran the Ceph commands easily;
ceph -sCopy SSH Keys to Other Ceph Nodes
Copy the SSH key generated by the bootstrap command to all the monitor and OSD nodes root user account. Ensure Root Login is allowed on the Ceph monitor node.
for i in {02..06}; do sudo ssh-copy-id -f -i /etc/ceph/ceph.pub root@node$i; doneDrop into Ceph CLI
You can drop into the Ceph CLI to execute the next commands.
sudo /usr/sbin/cephadm shell \
--fsid f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730 \
-c /etc/ceph/ceph.conf \
-k /etc/ceph/ceph.client.admin.keyring
Or if you installed the ceph-common package, no need to drop into the cli as you can directly execute the ceph commands from the terminal.
Add Other Ceph Monitor Nodes to Ceph Cluster
At this point, we have just provisioned Ceph Admin node only. You can list all the hosts known to the Ceph ochestrator (ceph-mgr) using the command below;
ceph orch host lsSample output;
HOST ADDR LABELS STATUS
ceph-admin 192.168.122.240 _admin
1 hosts in cluster
By default, cephadm will deploy 5 monitor daemons on arbitrary hosts. It is recommended to deploy five monitors if there are five or more nodes in your cluster.
To allow deployment of monitor daemons on arbitrary hosts, execute the command below to add the nodes to the cluster;
for i in {02..03}; do ceph orch host add node$i; doneSample command output;
Added host 'node02' with addr '192.168.122.55'
Added host 'node03' with addr '192.168.122.229'You should now have three nodes in the cluster.
Next, label the nodes with its role.
ceph orch host label add node01 mon01ceph orch host label add node02 mon02ceph orch host label add node03 mon03Confirm the labelling;
ceph orch host lsHOST ADDR LABELS STATUS
node01 192.168.122.240 _admin,mon01
node02 192.168.122.55 mon02
node03 192.168.122.229 mon03
3 hosts in cluster
If you want to manually add monitors, then you need to disable automated monitor deployment, by running this command:
ceph orch apply mon --unmanagedTo deploy each additional monitor:
ceph orch daemon add mon *<host1:ip>Add Ceph OSD Nodes to Ceph Cluster
Similarly, add the OSD Nodes to the cluster;
ceph orch host add node04ceph orch host add node05ceph orch host add node06Define their respective labels;
for i in {04..06}; do ceph orch host label add node$i osd$i; doneList Ceph Cluster Nodes;
You can list the Ceph cluster nodes;
ceph orch host lsSample output;
HOST ADDR LABELS STATUS
node01 192.168.122.240 _admin,mon01
node02 192.168.122.55 mon02
node03 192.168.122.229 mon03
node04 192.168.122.152 osd04
node05 192.168.122.241 osd05
node06 192.168.122.116 osd06
6 hosts in cluster
Create Ceph OSDs from Attached Storage Devices
In our setup, we have 3 unallocated raw disks of 50G on each OSD node to be used as bluestore for OSD daemons.
You can list the devices that are available on the OSD nodes for creating OSDs using the command below;
ceph orch device lsA storage device is considered available if all of the following conditions are met:
- The device must have no partitions.
- The device must not have any LVM state.
- The device must not be mounted.
- The device must not contain a file system.
- The device must not contain a Ceph BlueStore OSD.
- The device must be larger than 5 GB.
Sample output;
HOST PATH TYPE DEVICE ID SIZE AVAILABLE REFRESHED REJECT REASONS
node04 /dev/vdb hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node04 /dev/vdc hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node04 /dev/vdd hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node05 /dev/vdb hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node05 /dev/vdc hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node05 /dev/vdd hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node06 /dev/vdb hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node06 /dev/vdc hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
node06 /dev/vdd hdd 50.0G Yes 5s ago
You can add all the available devices to ceph OSDs at once or just add them one by one.
To attach them all at once;
ceph orch apply osd --all-available-devices --method {raw|lvm}Use raw method if you are using raw disks. otherwise, if you are using LVM disks, use lvm method.
Command output;
Scheduled osd.all-available-devices update...Note that when you add devices using this approach, then;
- If you add new disks to the cluster, they will be automatically used to create new OSDs.
- In the event that an OSD is removed, and the LVM physical volume is cleaned, a new OSD will be generated automatically.
If you wish to prevent this behavior (i.e., disable the automatic creation of OSDs on available devices), use the 'unmanaged' parameter:
ceph orch apply osd --all-available-devices --unmanaged=trueTo manually create an OSD from a specific device on a specific host:
ceph orch daemon add osd <host>:<device-path>NOTE: The deployment of OSDs with --all-available-devices is generally used for smaller clusters. For larger clusters, use the OSD specification file.
Check Ceph Cluster Health
To verify the health status of the ceph cluster, simply execute the command ceph s on the admin node or even on each OSD node (if you have installed cephadm/ceph commands there).
To check Ceph cluster health status from the admin node;
ceph -sAfter sometime, you should see such an output;
cluster:
id: f14cb896-889a-11ee-abf4-525400ac8730
health: HEALTH_OK
services:
mon: 5 daemons, quorum node01,node02,node03,node04,node06 (age 8m)
mgr: node01.gvhmuc(active, since 83m), standbys: node02.gpynef
osd: 9 osds: 9 up (since 38s), 9 in (since 74s)
data:
pools: 1 pools, 1 pgs
objects: 2 objects, 449 KiB
usage: 639 MiB used, 449 GiB / 450 GiB avail
pgs: 1 active+clean
Check OSDs;
ceph osd treeID CLASS WEIGHT TYPE NAME STATUS REWEIGHT PRI-AFF
-1 0.43918 root default
-5 0.14639 host node04
0 hdd 0.04880 osd.0 up 1.00000 1.00000
4 hdd 0.04880 osd.4 up 1.00000 1.00000
7 hdd 0.04880 osd.7 up 1.00000 1.00000
-3 0.14639 host node05
1 hdd 0.04880 osd.1 up 1.00000 1.00000
3 hdd 0.04880 osd.3 up 1.00000 1.00000
6 hdd 0.04880 osd.6 up 1.00000 1.00000
-7 0.14639 host node06
2 hdd 0.04880 osd.2 up 1.00000 1.00000
5 hdd 0.04880 osd.5 up 1.00000 1.00000
8 hdd 0.04880 osd.8 up 1.00000 1.00000
Get a list of Ceph services;
ceph orch psNAME HOST PORTS STATUS REFRESHED AGE MEM USE MEM LIM VERSION IMAGE ID CONTAINER ID
alertmanager.node01 node01 *:9093,9094 running (18m) 2m ago 88m 16.0M - 0.25.0 c8568f914cd2 db6532ab83d6
ceph-exporter.node01 node01 running (89m) 2m ago 89m 7054k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 4d4739e59495
ceph-exporter.node02 node02 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 15.9M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 86f8b6c06fad
ceph-exporter.node03 node03 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 25.4M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 3cebac8c8354
ceph-exporter.node04 node04 running (14m) 3m ago 14m 25.2M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 c6e64e48a377
ceph-exporter.node05 node05 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 26.9M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 54aceb24e802
ceph-exporter.node06 node06 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 27.0M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 895f2924d8bc
crash.node01 node01 running (89m) 2m ago 89m 6665k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 9123d699b6a9
crash.node02 node02 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 7379k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 323988bc0599
crash.node03 node03 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 7348k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 de5041df3615
crash.node04 node04 running (14m) 3m ago 14m 7375k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 869911b5699e
crash.node05 node05 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 7516k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 216d5290bf12
crash.node06 node06 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 7363k - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 53f443a15f0c
grafana.node01 node01 *:3000 running (88m) 2m ago 88m 82.8M - 9.4.7 2c41d148cca3 177cc82138c4
mgr.node01.gvhmuc node01 *:9283,8765,8443 running (89m) 2m ago 89m 517M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 673b69975d89
mgr.node02.gpynef node02 *:8443,9283,8765 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 437M - 18.2.0 10237bca3285 d62a305af919
mon.node01 node01 running (89m) 2m ago 89m 72.1M 2048M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 b0001264bf0e
mon.node02 node02 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 49.7M 2048M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 ac9bd2a4215b
mon.node03 node03 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 44.0M 2048M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 a0593be7e384
mon.node04 node04 running (14m) 3m ago 14m 48.5M 2048M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 2cc1fd067cc4
mon.node06 node06 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 45.8M 2048M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 0be533449aa9
node-exporter.node01 node01 *:9100 running (88m) 2m ago 88m 15.3M - 1.5.0 0da6a335fe13 0be1d3e87064
node-exporter.node02 node02 *:9100 running (19m) 7m ago 19m 16.0M - 1.5.0 0da6a335fe13 e9df4de91167
node-exporter.node03 node03 *:9100 running (18m) 7m ago 19m 15.5M - 1.5.0 0da6a335fe13 23d2747cb798
node-exporter.node04 node04 *:9100 running (14m) 3m ago 14m 14.3M - 1.5.0 0da6a335fe13 b60b52f3340a
node-exporter.node05 node05 *:9100 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 16.3M - 1.5.0 0da6a335fe13 e0754f0b7925
node-exporter.node06 node06 *:9100 running (13m) 3m ago 13m 15.7M - 1.5.0 0da6a335fe13 b250510fcff0
osd.0 node04 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 52.3M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 cf835e2802b3
osd.1 node05 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 52.5M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 35f0f29eef81
osd.2 node06 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 53.5M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 624ebe681e44
osd.3 node06 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 55.1M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 66b8b4938900
osd.4 node05 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 58.6M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 6b1d6052e588
osd.5 node04 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 59.0M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 e40e66c1c327
osd.6 node06 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 58.9M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 57b06148664c
osd.7 node05 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 54.4M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 5a624c61464a
osd.8 node04 running (6m) 3m ago 6m 53.3M 4096M 18.2.0 10237bca3285 03a0cdaeb9e4
prometheus.node01 node01 *:9095 running (13m) 2m ago 88m 68.0M - 2.43.0 a07b618ecd1d 7d6ae3a65490
Similarly, you can check Ceph service containers created on other nodes;
docker psOr list their systemd unit files;
systemctl list-units 'ceph*'Accessing Ceph Admin Web User Interface
The bootstrap commands give a url and credentials to use to access the Ceph admin web user interface;
...
Ceph Dashboard is now available at:
URL: https://node01:8443/
User: admin
Password: amw3p3yy2e
Since we are running multiple nodes, Ceph manager is deployed on two nodes for HA. From the Ceph status command, ceph -s, you can see under services, that one manager node is active while the other one is on standby.
services:
mon: 5 daemons, quorum node01,node02,node03,node04,node06 (age 15m)
mgr: node01.gvhmuc(active, since 90m), standbys: node02.gpynef
osd: 9 osds: 9 up (since 7m), 9 in (since 8m)Thus, open the browser and navigate to the URL above. Or you can even use the cephadm node IP address if you want..
Open the port on firewall if firewall is running.
Enter the provided credential and reset your admin password and proceed to login to Ceph Admin dashboard.

If you want, you can activate the telemetry module by clicking Activate button or just from the CLI;
ceph telemetry on --license sharing-1-0Telemetry can be disabled at any time with:
ceph telemetry offGo through other Ceph menu to see more about Ceph.
Ceph Dashboard;
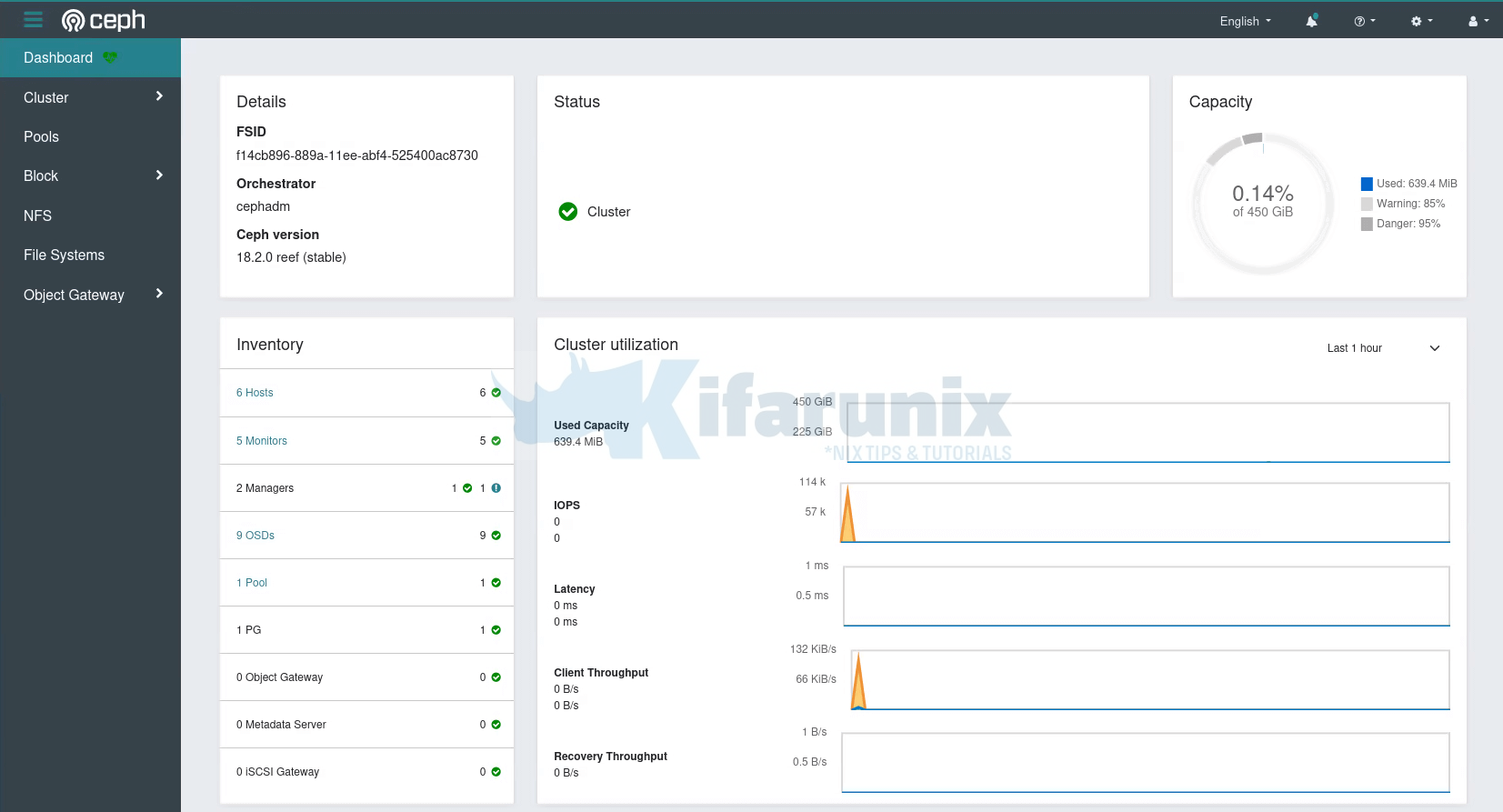
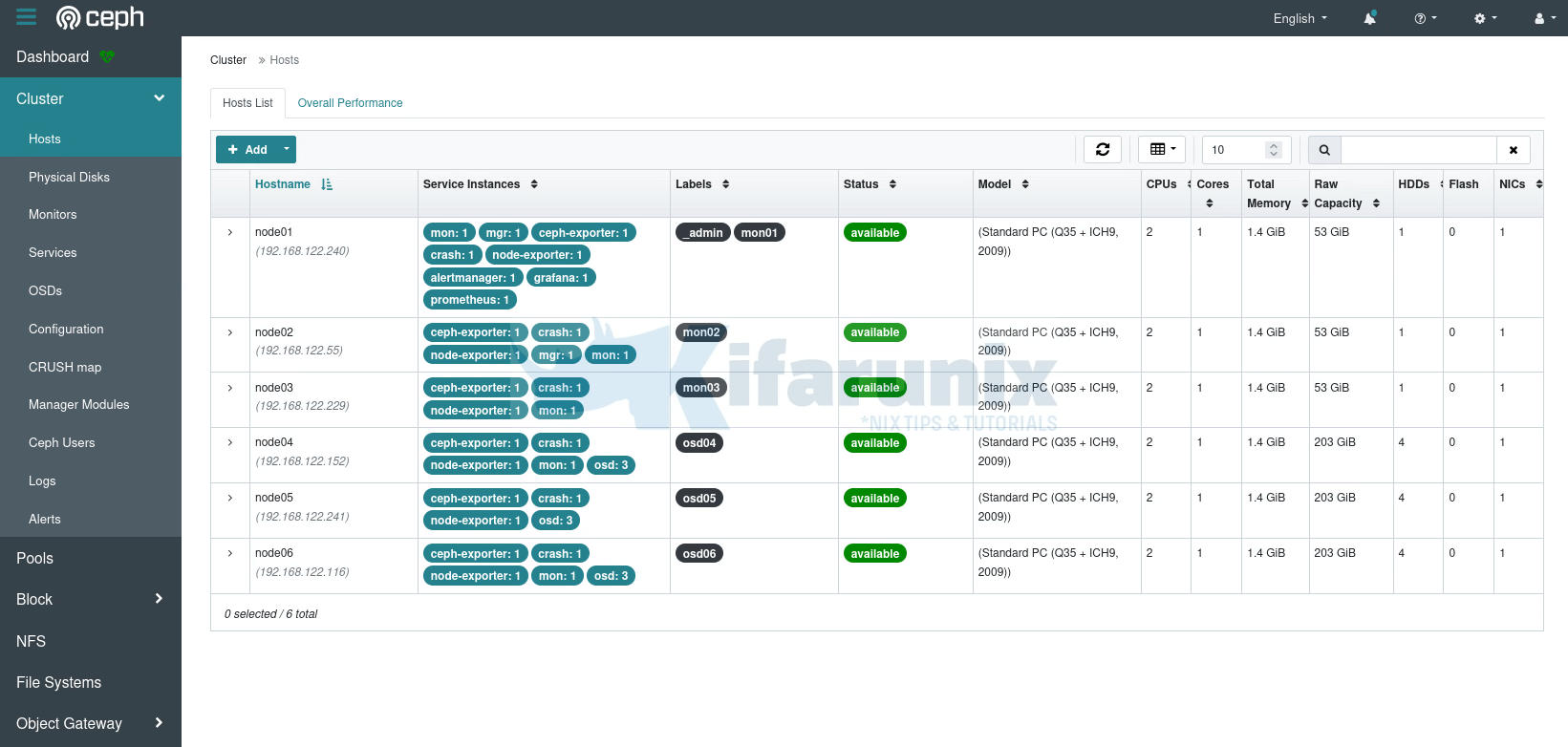
Under the Cluster Menu, you can see quite more details; hosts, disks, OSDs etc.
You can also monitor Ceph performance via Grafana, https://manager-IP:3000.
Sample Ceph cluster dashboards;
Cluster;
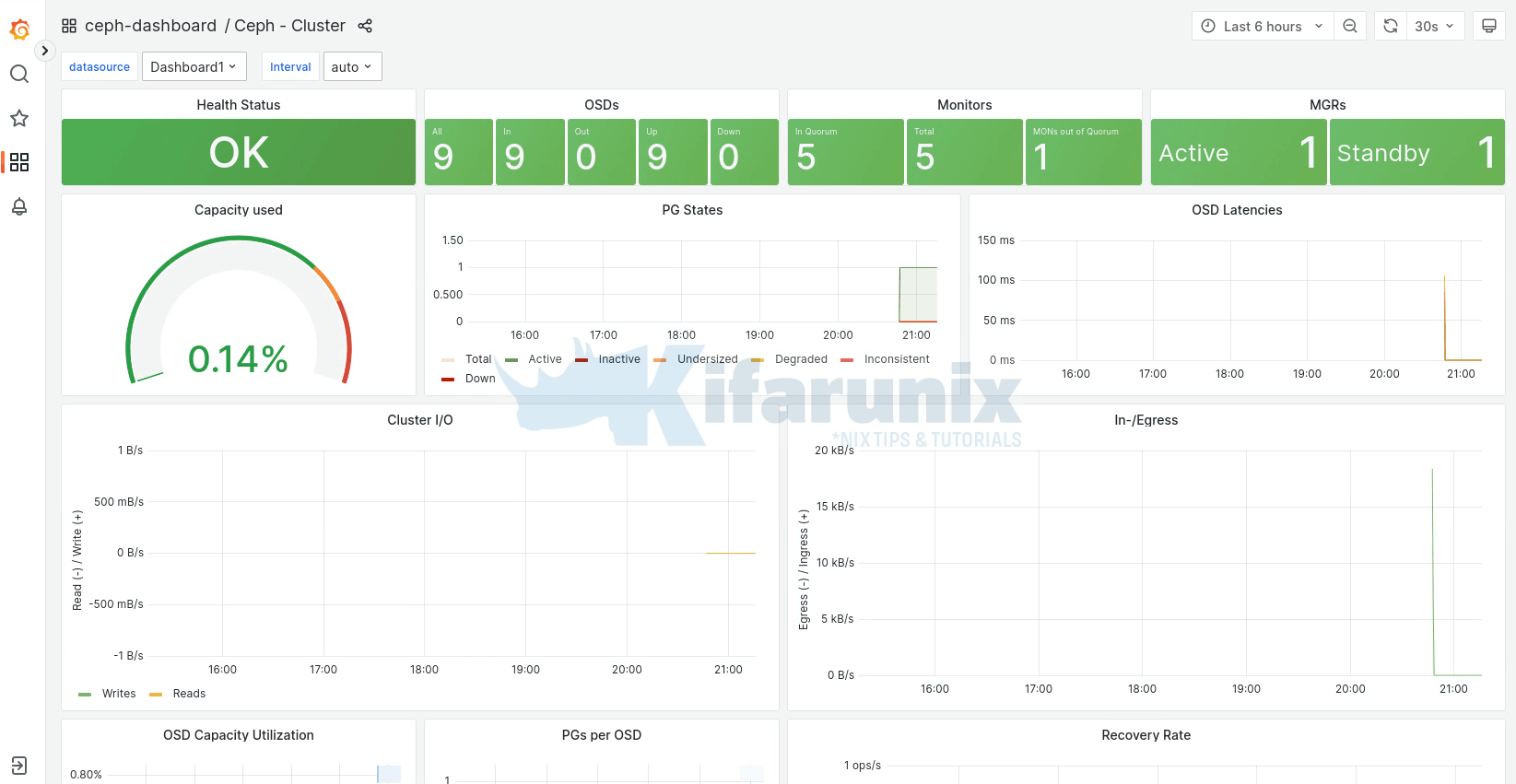
There you go. That marks the end of our tutorial on how to deploy Ceph storage cluster using cephadm on AlmaLinux.
Reference
Other Tutorials

