This guide will walk you through how to install Nagios Plugins on CentOS 9 Stream. Nagios plugins are standalone extensions that enables Nagios to monitor databases, operating systems, services, applications, network equipment, protocols etc.
To use Nagios Plugins, you need to have installed and Setup Nagios Core server. Follow the link below to install Nagios server on CentOS 9 Stream.
Install Nagios Server on CentOS 9 Stream
Table of Contents
Installing Nagios Plugins on CentOS 9 Stream
Once you have setup the Nagios Core server, proceed to install the Nagios plugins.
Well, there are two ways in which you can install Nagios Plugins.
- Building Nagios Plugins from the source
- Installing Nagios Plugins from EPEL Repos (Probably the easiest)
We will cover the two installation methods.
Install Nagios Plugins from the Source on CentOS 9 Stream
Install Required Build Tools and Dependencies
Nagios plugins are build from the source code. Hence, you need to install required build tools and dependencies.
Some of the packages below might have been installed if you followed the Nagios guide above.
dnf install -y \
gcc \
glibc glibc-common \
make \
gettext \
automake autoconf \
wget \
openssl-devel
Download Nagios Plugins Source Code
You can check for any latest Nagios plugins on Nagios Plugins page.
Get the latest stable release version number and substitute the value of the VER variable below;
VER=2.4.12Next, download Nagios plugins source code.
wget https://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-${VER}.tar.gz
Extract Nagios Plugins Source Code
Once downloaded, extract it by running the command below
tar xzf nagios-plugins-${VER}.tar.gz
Configure Nagios Plugins
Navigate to Nagios plugins source directory and run the configure script to adapt the plugins to the system and check for any missing dependency.
cd nagios-plugins-${VER}
./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios
Compile Nagios Plugins on CentOS 9 Stream
If there is no configuration error, proceed to compile Nagios.
Ensure that user nagios is already created before you can proceed. You might need to install NRPE agent first.
getent passwd nagios
nagios:x:974:974::/var/spool/nagios:/sbin/nologin
The compile Nagios plugins.
make
Install Nagios Plugins on CentOS 9 Stream
You can now run the command below to install Nagios Plugins.
make install
This will install default Nagios plugins under the /usr/local/nagios/libexec/ directory.
ls -1 /usr/local/nagios/libexec/
check_apt check_dhcp check_flexlm check_ifoperstatus check_load check_nagios check_ntp_peer check_ping check_sensors check_ssl_validity check_udp negate
check_breeze check_disk check_ftp check_ifstatus check_log check_nntp check_ntp_time check_pop check_simap check_ssmtp check_ups remove_perfdata
check_by_ssh check_disk_smb check_http check_imap check_mailq check_nntps check_nwstat check_procs check_smtp check_swap check_uptime urlize
check_clamd check_dummy check_icmp check_ircd check_mrtg check_nt check_oracle check_real check_spop check_tcp check_users utils.pm
check_cluster check_file_age check_ide_smart check_jabber check_mrtgtraf check_ntp check_overcr check_rpc check_ssh check_time check_wave utils.sh
Restart Nagios Core service
Now restart Nagios core service.
systemctl restart nagios
After that, login Nagios Server Web interface on the browser to confirm that the localhost services and state are now being monitored.
Verify Host and Service Monitoring on Nagios Server
Navigate to Nagios Web interface and check the local host status by clicking on the Hosts under Current Status on the left panel.
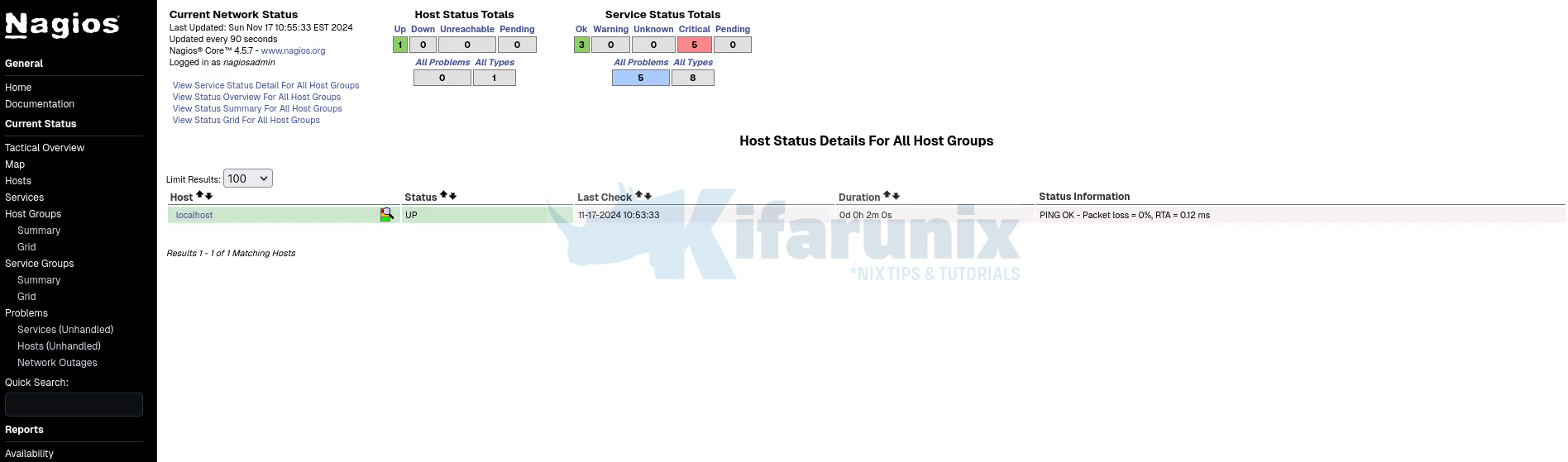
Check the status of the localhost services by clicking Services under Current Status on the left panel.
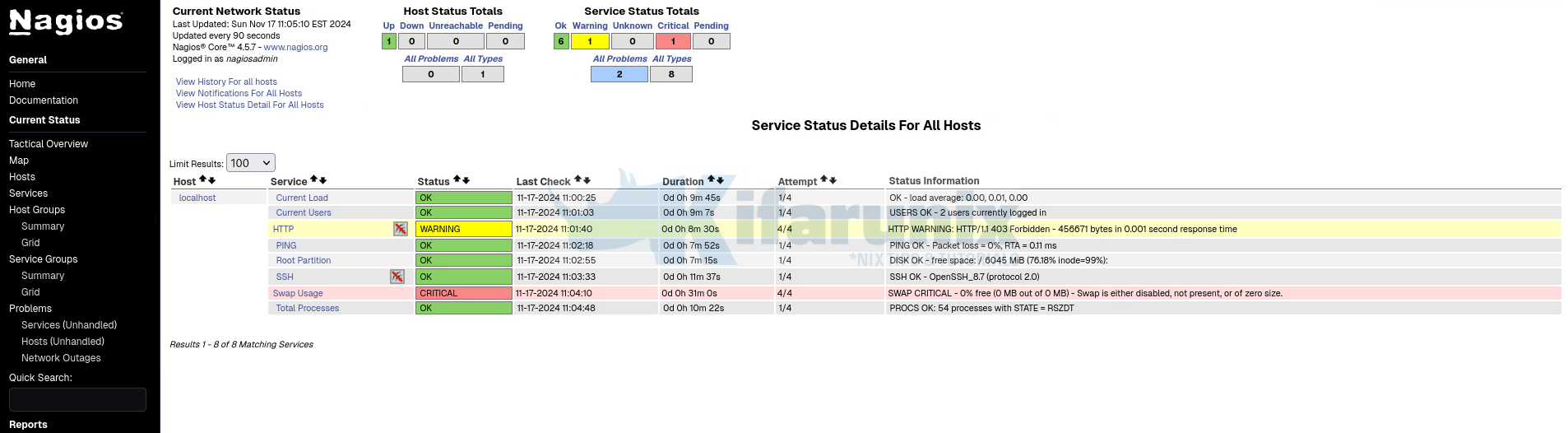
If the services have not updated their status, you can force check by selecting a host from the services host lists > Schedule a check of all services on this host.
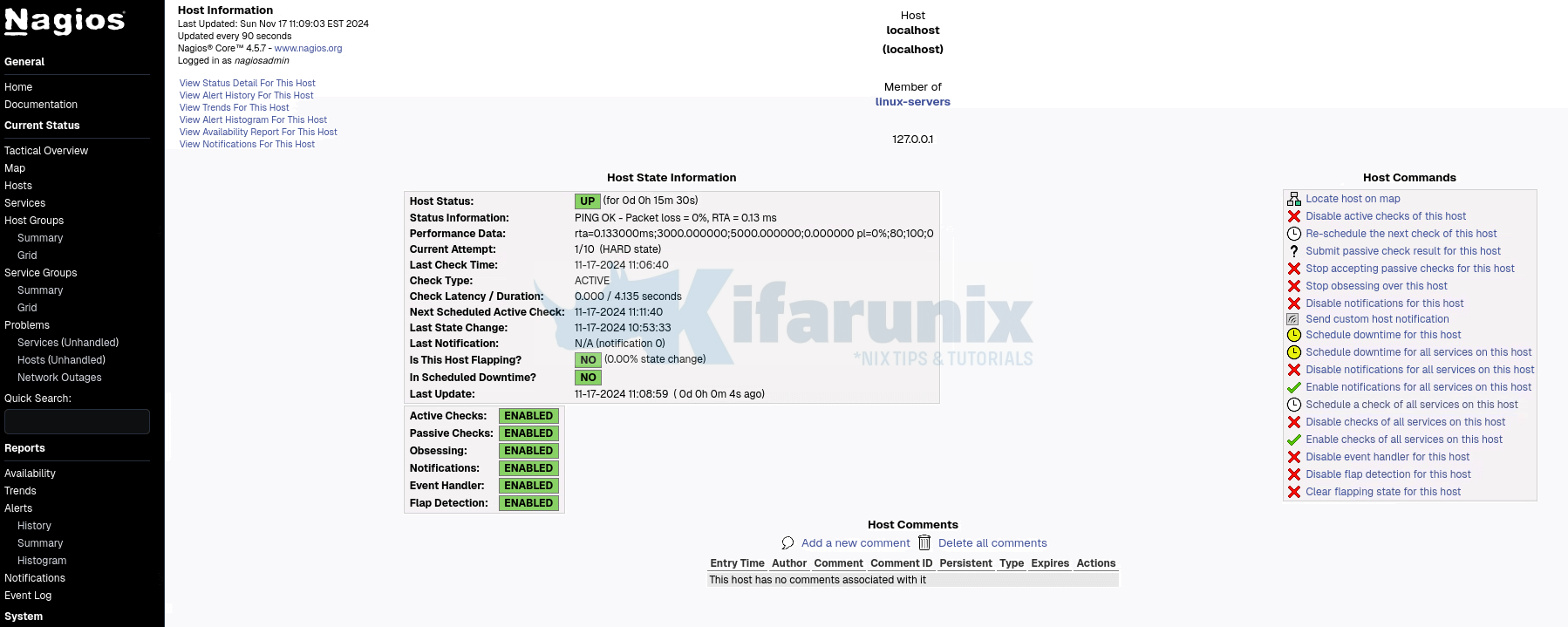
The force check!
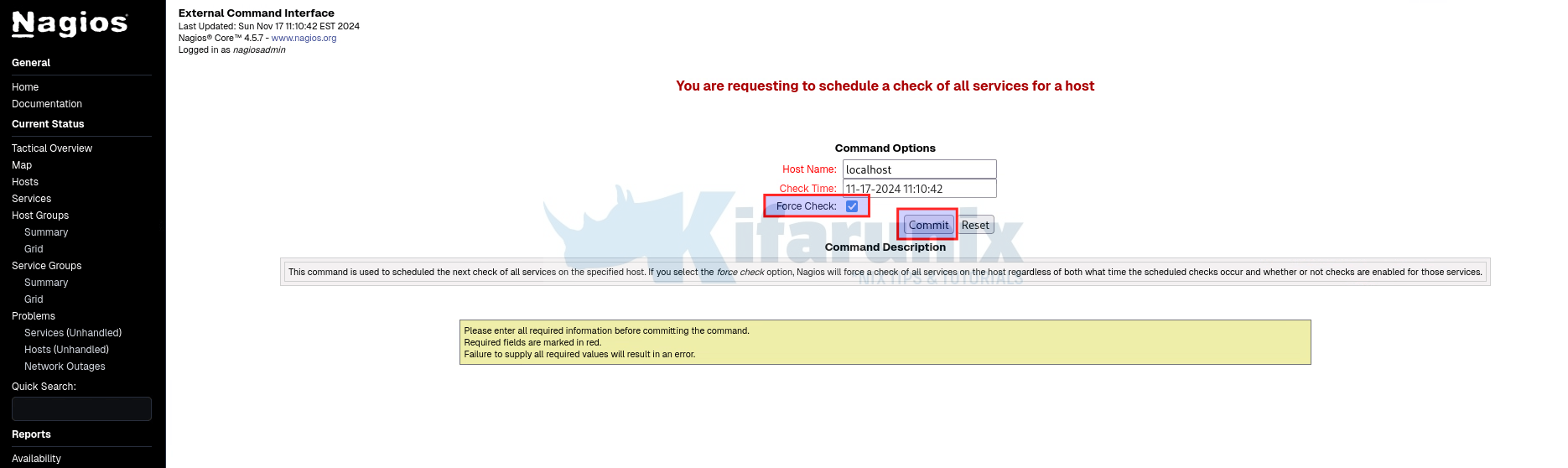
Fix Error: Could not stat() command file ‘/usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.cmd’!
If upon hitting commit button to force check services on a host, you are welcomed by the error:
You are most likely to be dealing with SELinux access controls here!
So, login to the system and check the logs for any issue;
journalctl -n 100 -fI found this, which is really helpful on how to fix the issue;
Nov 17 11:11:50 localhost.localdomain setroubleshoot[45737]: failed to retrieve rpm info for path '/usr/local/nagios/sbin/cmd.cgi':
Nov 17 11:11:50 localhost.localdomain setroubleshoot[45737]: failed to retrieve rpm info for path '/usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.cmd':
Nov 17 11:11:50 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: Started dbus-:[email protected].
Nov 17 11:11:50 localhost.localdomain setroubleshoot[45737]: SELinux is preventing /usr/local/nagios/sbin/cmd.cgi from getattr access on the fifo_file /usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.cmd. For complete SELinux messages run: sealert -l f3d4a4f5-2da0-45d9-a372-4460a40d1a2d
Nov 17 11:11:50 localhost.localdomain setroubleshoot[45737]: SELinux is preventing /usr/local/nagios/sbin/cmd.cgi from getattr access on the fifo_file /usr/local/nagios/var/rw/nagios.cmd.
***** Plugin catchall (100. confidence) suggests **************************
If you believe that cmd.cgi should be allowed getattr access on the nagios.cmd fifo_file by default.
Then you should report this as a bug.
You can generate a local policy module to allow this access.
Do
allow this access for now by executing:
# ausearch -c 'cmd.cgi' --raw | audit2allow -M my-cmdcgi
# semodule -X 300 -i my-cmdcgi.pp
Nov 17 11:12:00 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: dbus-:[email protected]: Deactivated successfully.
Nov 17 11:12:00 localhost.localdomain systemd[1]: setroubleshootd.service: Deactivated successfully.
Nov 17 11:13:33 localhost.localdomain sshd[45754]: Connection closed by 127.0.0.1 port 40564 [preauth]
Nov 17 11:18:33 localhost.localdomain sshd[45769]: Connection closed by 127.0.0.1 port 50120 [preauth]
How to fix this is actually provided. So let’s execute the command provided!
ausearch -c 'cmd.cgi' --raw | audit2allow -M my-cmdcgisemodule -X 300 -i my-cmdcgi.ppSimilarly, you can check for any denied entries in the auditd logs;
tail -f /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep deniedtype=AVC msg=audit(1731861535.230:725): avc: denied { write } for pid=45980 comm="cmd.cgi" name="nagios.cmd" dev="vda1" ino=44536 scontext=system_u:system_r:httpd_sys_script_t:s0 tcontext=system_u:object_r:usr_t:s0 tclass=fifo_file permissive=0You can solve as follows;
tail /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep denied | grep nagios.cmdThe generate SELinux policy module;
tail /var/log/audit/audit.log | grep denied | grep nagios.cmd | audit2allow -M apachenagioscmdActivate the policy;
semodule -i apachenagioscmd.ppRestart Nagios and Apache;
systemctl restart httpd nagiosYou should be able to force check the services now!
There you go. You have successfully installed Nagios Plugins on CentOS 9 Stream for localhost state and and service status monitoring.
Install Nagios Plugins from EPEL Repository
It is also possible to install Nagios plugins from EPEL repository.
Install EPEL repository on CentOS 9 Stream
dnf install epel-release
Once the installation is done, you can search for the available Nagios plugins by running the command below;
dnf search nagios-plugins-*
nagios-plugins-nt.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_nt
nagios-plugins-dns.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_dns
nagios-plugins-all.x86_64 : Nagios Plugins - All plugins
nagios-plugins-apt.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_apt
nagios-plugins-dbi.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_dbi
nagios-plugins-dig.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_dig
nagios-plugins-dns.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_dns
nagios-plugins-fts.noarch : Nagios probes to be run remotely against FTS3 machines
nagios-plugins-log.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_log
nagios-plugins-ntp.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_ntp
nagios-plugins-rpc.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_rpc
nagios-plugins-ssh.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_ssh
nagios-plugins-tcp.x86_64 : Nagios Plugin - check_tcp
...
You can also run the command below to list all plugins.
dnf list nagios-plugins-*
You can now install the specific plugins that you require. For example, to install Nagios plugins that checks the load, http, users, processes, disk space, swap space, uptime,dns, run the command below;
dnf install nagios-plugins-{load,http,users,procs,disk,swap,nrpe,uptime,dns}
Plugins that are installed using the package manager as stored under /usr/lib64/nagios/plugins/.
ls -1 /usr/lib64/nagios/plugins/
check_disk
check_dns
check_http
check_load
check_nrpe
check_procs
check_swap
check_uptime
check_users
eventhandlers
negate
urlize
utils.sh
There you go.
In our next guide, we will discuss how to install Nagios Remote Execution Plugins for remote host monitoring.
See Other similar guides by following the link below;
Nagios SNMP Monitoring of Linux Hosts on AlienVault USM/OSSIM
How to Install Nagios Plugins and NRPE agents on CentOS 7/RHEL 7/Fedora 29
Configure Nagios Availability Monitoring on AlienVault USM/OSSIM
How to Install Nagios Plugins From Source RHEL/CentOS/Oracle Linux

