Welcome to our guide on how to install LibModsecurity with Apache on Ubuntu 20.04. Libmodsecurity (Modsecurity v3), is an open source, cross platform web application firewall (WAF) developed by Trustwave’s SpiderLabs. It is a complete rewrite of ModSecurity v2 and it provides a robust event-based programming language which protects web applications against a wide range of attacks such as SQL injection, Cross-site Scripting (XSS), Local File Include, Remote File Include e.tc. It also allows for HTTP traffic monitoring, logging and real-time analysis.
Install Modsecurity3 with Apache on Ubuntu 20.04
Run System Update
Resynchronize your system packages to their latest versions.
apt updateapt upgrade
Install LAMP Stack
Before you can install and configure LibModsecurity with Apache on Ubuntu 20.04, you need to have LAMP Stack installed and running your server. Follow the link below to setup LAMP stack on Ubuntu 20.04.
Install LAMP Stack on Ubuntu 20.04
Install Required Build Tools and Dependencies
To install Libmodsecurity or Modsecurity v3 on Ubuntu 20.04, we are going to build it from source. Hence, you need to install some required build tools and dependencies for a successful build.
apt install g++ flex bison curl apache2-dev doxygen libyajl-dev ssdeep liblua5.2-dev libgeoip-dev libtool dh-autoreconf libcurl4-gnutls-dev libxml2 libpcre++-dev libxml2-dev gitCompile and Install LibModsecurity on Ubuntu 20.04
Once your system is setup, you can proceed to install Modsecurity v3 on Ubuntu 20.04.
Download LibModsecurity Source Code
To install the latest stable version of LibModsecurity, you need to compile it from the source.
Therefore, navigate to ModSecurity releases page and download ModSecurity source code. You can simply use wget to pull it.
wget https://github.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity/releases/download/v3.0.4/modsecurity-v3.0.4.tar.gzExtract the ModSecurity source code.
tar xzf modsecurity-v3.0.4.tar.gzCompile and Install LibModsecurity
Navigate to the LibModsecurity source directory, configure, compile and install it
cd modsecurity-v3.0.4Configure LibModsecurity to adapt it to your system and check if any required dependency is missing.
./build.shYou can safely ignore the fatal: not a git repository (or any of the parent directories): .git error messages.
./configureBe sure to fix any dependency issue, if any, before you can proceed to compile and install LibModsecurity.
If the configure script above completes with no error, proceed to compile and install LibModSecurity on Ubuntu 20.04.
makemake installLibModSecurity aka ModSecurity v3 has now been installed on Ubuntu 20.04
Install ModSecurity-Apache Connector
The ModSecurity-apache connector provides a communication channel between Apache and libModsecurity. Now that libmodsecurity is installed, follow through the following steps to install Modsecurity Apache connector.
Clone the git repository for the ModSecurity Apache connector.
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/SpiderLabs/ModSecurity-apacheNavigate to ModSecurity-apache directory and run the following commands to compile and install it.
cd ModSecurity-apache./autogen.sh./configure --with-libmodsecurity=/usr/local/modsecurity/make
make installConfigure Apache with LibModsecurity
Load the Apache ModSecurity Connector Module
Configure Apache to load Modsecurity Apache connector module by adding the line below to the main Apache configuration file.
echo "LoadModule security3_module /usr/lib/apache2/modules/mod_security3.so" | sudo tee -a /etc/apache2/apache2.confConfigure ModSecurity
Create ModSecurity configuration directory under /etc/apache2
sudo mkdir /etc/apache2/modsecurity.dCopy the sample ModSecurity configuration file from the source code directory to the ModSec configuration directory created above renaming it as follows.
sudo cp ~/modsecurity-v3.0.4/modsecurity.conf-recommended /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsecurity.confAlso copy the unicode.mapping file from ModSecurity source directory to Apache Modsecurity configuration directory.
sudo cp ~/modsecurity-v3.0.4/unicode.mapping /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/Turn on ModSecurity by changing the value of SecRuleEngine to On.
sed -i 's/SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly/SecRuleEngine On/' /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsecurity.confNext, you need to configure ModSecurity rules. Therefore, create a file where you can define the rules to include, say, /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsec_rules.conf.
cat > /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsec_rules.conf << 'EOL'
Include "/etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsecurity.conf"
Include "/etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crs/crs-setup.conf"
Include "/etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crs/rules/*.conf"
EOL
Since we have included the OWASP Rules as part of ModSecurity 3 rules, proceed to install them.
Install OWASP ModSecurity Core Rule Set (CRS) on Ubuntu
The OWASP ModSecurity Core Rule Set (CRS) is a set of generic attack detection rules for use with ModSecurity. It aims at protecting the web applications from a wide range of attacks, including the OWASP Top Ten, minimum of false alerts.
Clone the CRS from GitHub repository to /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/ as shown below;
git clone https://github.com/SpiderLabs/owasp-modsecurity-crs.git /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crsNext, rename crs-setup.conf.example to crs-setup.conf.
sudo cp /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crs/crs-setup.conf{.example,}Activate ModSecurity
After all that, activate the modsecurity on the default site configuration file or on any virtual host configuration file. In this guide, we are using Apache’s default site configuration file.
cp /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf{,.old}See our sample default site virtual host configuration with no comments;
cat > /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf << 'EOL'
<VirtualHost *:80>
modsecurity on
modsecurity_rules_file /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsec_rules.conf
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
EOL
The lines;
modsecurity on
modsecurity_rules_file /etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/modsec_rules.conf Turns on Modsecurity and specifies the location of the Modsecurity rules.
Check Apache for configuration errors and restart it.
apachectl -tIf there is no error, you should get the output, Syntax OK.
systemctl restart apache2Testing Modsecurity
Next, test the effectiveness of Modsecurity, for example, command injection. Run the command below;
curl localhost?doc=/bin/ls
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//IETF//DTD HTML 2.0//EN">
<html><head>
<title>403 Forbidden</title>
</head><body>
<h1>Forbidden</h1>
<p>You don't have permission to access this resource.</p>
<hr>
<address>Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) Server at localhost Port 80</address>
</body></html>
Check Modsecurity logs;
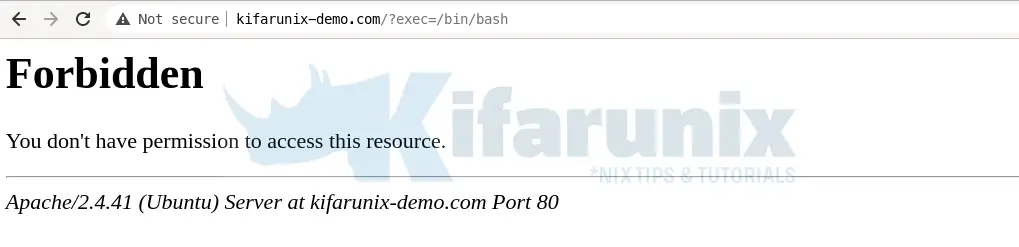
tail /var/log/modsec_audit.logModSecurity: Warning. Matched "Operator `PmFromFile' with parameter `unix-shell.data' against variable `ARGS:doc' (Value: `/bin/ls' ) [file "/etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crs/rules/REQUEST-932-APPLICATION-ATTACK-RCE.conf"] [line "496"] [id "932160"] [rev ""] [msg "Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Code Found"] [data "Matched Data: bin/ls found within ARGS:doc: /bin/ls"] [severity "2"] [ver "OWASP_CRS/3.2.0"] [maturity "0"] [accuracy "0"] [tag "application-multi"] [tag "language-shell"] [tag "platform-unix"] [tag "attack-rce"] [tag "paranoia-level/1"] [tag "OWASP_CRS"] [tag "OWASP_CRS/WEB_ATTACK/COMMAND_INJECTION"] [tag "WASCTC/WASC-31"] [tag "OWASP_TOP_10/A1"] [tag "PCI/6.5.2"] [hostname "127.0.1.1"] [uri "/"] [unique_id "161428003146.366446"] [ref "o1,6v10,7t:urlDecodeUni,t:cmdLine,t:normalizePath,t:lowercase"]ModSecurity: Access denied with code 403 (phase 2). Matched "Operator `Ge' with parameter `5' against variable `TX:ANOMALY_SCORE' (Value: `5' ) [file "/etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crs/rules/REQUEST-949-BLOCKING-EVALUATION.conf"] [line "80"] [id "949110"] [rev ""] [msg "Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 5)"] [data ""] [severity "2"] [ver "OWASP_CRS/3.2.0"] [maturity "0"] [accuracy "0"] [tag "application-multi"] [tag "language-multi"] [tag "platform-multi"] [tag "attack-generic"] [hostname "127.0.1.1"] [uri "/"] [unique_id "161428003146.366446"] [ref ""]Access the site from browser and test command injection attack, http://domain.name/?exec=/bin/bash.
Tailing the Apache error logs;
tail -f /var/log/apache2/error.log[Thu Feb 25 19:29:06.385428 2021] [:error] [pid 38210] [client 192.168.57.1:45916] ModSecurity: Warning. Matched "Operator `PmFromFile' with parameter `unix-shell.data' against variable `ARGS:exec' (Value: `/bin/bash' ) [file "/etc/apache2/modsecurity.d/owasp-crs/rules/REQUEST-932-APPLICATION-ATTACK-RCE.conf"] [line "496"] [id "932160"] [rev ""] [msg "Remote Command Execution: Unix Shell Code Found"] [data "Matched Data: bin/bash found within ARGS:exec: /bin/bash"] [severity "2"] [ver "OWASP_CRS/3.2.0"] [maturity "0"] [accuracy "0"] [tag "application-multi"] [tag "language-shell"] [tag "platform-unix"] [tag "attack-rce"] [tag "paranoia-level/1"] [tag "OWASP_CRS"] [tag "OWASP_CRS/WEB_ATTACK/COMMAND_INJECTION"] [tag "WASCTC/WASC-31"] [tag "OWASP_TOP_10/A1"] [tag "PCI/6.5.2"] [hostname "127.0.1.1"] [uri "/"] [unique_id "161428134623.117562"] [ref "o1,8v11,9t:urlDecodeUni,t:cmdLine,t:normalizePath,t:lowercase"]As a result, this confirms that the Modsecurity is functioning as expected.
Reference:
Related Guides
Restrict Access to WordPress Login Page to Specific IPs with libModSecurity
Create Kibana Visualization Dashboards for ModSecurity Logs
Process and Visualize ModSecurity Logs on ELK Stack