In this guide, we will learn how to install BackupPC on Debian 12. BackupPC is a free, high-performance enterprise-grade backup software suite with a web-based frontend that can be used for backing up Linux, Windows and mac OSXs PCs and laptops to a server’s disk.
Table of Contents
Installing BackupPC on Debian 12
What features does BackupPC offer?
BackupPC features:
- Clever pooling scheme minimizes disk storage and disk I/O. Identical files across multiple backups of the same or different PC are stored only once resulting in substantial savings in disk storage and disk writes. Also known as “data deduplication”.
- Optional compression provides additional reductions in storage. CPU impact of compression is low since only new files (those not already in the pool) need to be compressed.
- A powerful http/cgi user interface allows administrators to view log files, configuration, current status and allows users to initiate and cancel backups and browse and restore files from backups very quickly.
- No client-side software is needed. On WinXX the smb protocol is used. On Linux or Unix clients, rsync or tar (over ssh/rsh/nfs) can be used
- Flexible restore options. Single files can be downloaded from any backup directly from the CGI interface. Zip or Tar archives for selected files or directories can also be downloaded from the CGI interface.
- BackupPC supports mobile environments where laptops are only intermittently connected to the network and have dynamic IP addresses (DHCP).
- Flexible configuration parameters allow multiple backups to be performed in parallel.
Install BackupPC Server
Update and upgrade your system packages.
apt update
Once the system update is done, proceed to install BackupPC.
BackupPC is usually available on the default APT repositories (Check releases to compare with the version available on repos.):
apt-cache policy backuppc
backuppc:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 4.4.0-8
Version table:
4.4.0-8 500
500 http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm/main amd64 Packages
As of this writing, BackupPC 4.4.0 is the current release. The above confirms that the default Debian 12 repos provide the latest BackupPC packages.
Hence, BackupPC can be installed using the package, backuppc by running the command below;
apt install -y backuppc
During the installation, you will be prompted to choose the web server to be used by BackupPC. Apache web server is used in this guide.
A default BackupPC administrative user, backuppc, and its password is also created during the installation. This user is used to administer various tasks such as access to BackupPC web dashboard, carry out backups etc.
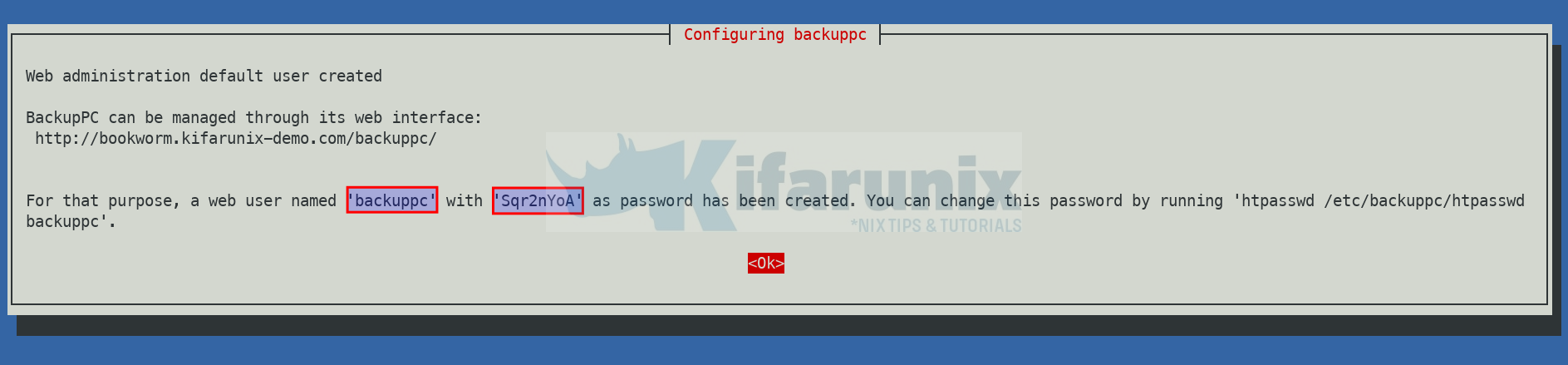
You can choose to copy the password provided or you can proceed and reset the password later by executing the command below;
htpasswd /etc/backuppc/htpasswd backuppc
Configuring BackupPC Server on Debian 12
Define BackupPC Backup Protocol
BackupPC uses different protocols to get backup data from devices being backed up:
- smb – used for backing up windows machines
- tar – used for backing up Linux/Unix/MacOSX systems
- rsync – used for backing up Linux/Unix/MacOSX systems. This can also be used to backup Windows systems.
In this tutorial we are going to configure BackupPC to use the rsync protocol as a backup method.
Thus, change the line;
$Conf{XferMethod} = 'smb';To;
$Conf{XferMethod} = 'rsync';Using the command;
sed -i '/$Conf{XferMethod} =/s/smb/rsync/' /etc/backuppc/config.plThis is customizable per client system being backed up as well.
Define BackupPC Backup User
Also, by default, BackupPC is using root user to run backup tasks. However, in this guide, we are going to use a backuppc user to execute backup tasks.
backuppc user is created automatically during installation of BackupPC.
id backuppcuid=117(backuppc) gid=125(backuppc) groups=125(backuppc)If you happen to change the backup user, edit BackupPC configuration file, /etc/backuppc/config.pl and replace the root user with a user you are using for backup under the Rsync/Rsyncd Configuration.
sed '/RsyncSshArgs/s/-l root/-l backuppc/' /etc/backuppc/config.plThe line should look like;
$Conf{RsyncSshArgs} = ['-e', '$sshPath -l backuppc'];Configure BackupPC Apache Authentication
BackupPC uses htpasswd user files to restrict access to web interface.
As such, you require a valid user in order to authenticate.
The Web authentication user and its hashed credential password is stored under the /etc/backuppc/htpasswd.
The password is generated during the installation. If you want, you can reset the password by running;
htpasswd /etc/backuppc/htpasswd backuppcAllow external access to BackupPC, which is set to only allow connections from localhost by default.
sed -i 's/local/all granted/' /etc/backuppc/apache.confThis is how the BackupPC Apache config file looks like without comment lines;
cat /etc/backuppc/apache.conf
Alias /backuppc /usr/share/backuppc/cgi-bin/
<Directory /usr/share/backuppc/cgi-bin/>
AllowOverride None
# Uncomment the line below to ensure that nobody can sniff important
# info from network traffic during editing of the BackupPC config or
# when browsing/restoring backups.
# Requires that you have your webserver set up for SSL (https) access.
#SSLRequireSSL
Options ExecCGI FollowSymlinks
AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
DirectoryIndex index.cgi
AuthUserFile /etc/backuppc/htpasswd
AuthType basic
AuthName "BackupPC admin"
<RequireAll>
# Comment out this line once you have setup HTTPS and uncommented SSLRequireSSL
Require all granted
# This line ensures that only authenticated users may access your backups
Require valid-user
</RequireAll>
</Directory>
Next, restart both backuppc and Apache service to apply the changes made above.
systemctl restart backuppc apache2
Open Apache HTTP Server on Firewall
If UFW is running, allow external access to Apache.
ufw allow "WWW Full"
Accessing BackupPC Web Interface
You should now be able to access you via your server IP or resolvable domain name.
http://IP-or-domain/backuppcYou will be prompted to authenticate. Use the basic auth credentials created above.
Generate Backup User SSH Keys
For rsync to work, BackupPC requires passwordless SSH login for backuppc user to every client it will be getting backup data from.
This also means that you should create a dedicated backuppc user on the hosts you need to backup, at least using the rsync protocol.
As a result, switch to backuppc user on BackupPC server and generate passwordless ssh keys and copy them to every host you want to backup.
usermod -s /bin/bash backuppcsu - backuppc
This will opens up the sh shell. You can run bash command to launch bash shell.
Generate SSH key pair by running the following command;
ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/var/lib/backuppc/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/var/lib/backuppc/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /var/lib/backuppc/.ssh/id_rsa
Your public key has been saved in /var/lib/backuppc/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:Oe5pz3Yuo7cKcHSV5PfriLmHd7ae3V7bdtBPYgQEwu0 backuppc@bookworm
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 3072]----+
| ..o++. |
| .+o . |
| . ... .. |
| . . .E. .. |
| . . S ... |
| o . . +.o|
| . . . ..+o|
| o.o*o+oooO|
| .=*BXo+==*|
+----[SHA256]-----+
Create Backup User Account On Clients
On Linux client servers you want to backup, login and create an account dedicated for backup purposes.
For example, create a backuppc user account on remote client.
useradd -m backuppc
passwd backuppc
Copy BackupPC Server SSH Keys to Backup Clients
Now login backup to backuppc user on the BackupPC server and copy the SSH public key for backuppc user to backuppc user on the client. Copy the keys while logged as backuppc user.
whoamibackuppcssh-copy-id [email protected]
- Where 192.168.43.214 is my client IP address. Once you copy the key, you should be able to login without being prompted for a password.
Now, test the login to client with the backup user to ensure user can successfully login to client. You can use root user if you didn’t make the changes above.
su - backuppcssh -l backuppc client_IP whoamiSample output;
backuppcor
ssh -l root client_IP whoamiSample output
rootAllow Backup User to Run Rsync with Passwordless Sudo
If you changed your backup user to non-root user on the BackupPC server, for example backuppc user in this case, then login to the client host as an administrative user and allow the non-user to run the rsync command without being prompted for password by adding the user to sudoers list. backuppc user is used in this case.
ssh user@client_IPRun the command below to find the absolute path of rsync.
which rsync
If rsync command is not installed, run the following commands to install it.
apt install rsync -yyum install rsync -yNext, update the sudoers file.
echo "backuppc ALL=NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/rsync" | sudo tee /etc/sudoers.d/backuppcConfirm if there is any error with sudoers file;
visudo -c -f /etc/sudoersSecure BackupPC Login on the Backup Client
You may also want to disable ssh agent-forwarding, port-forwarding or even the pty for backuppc user logging in to the client from BackupPC.
To do this, login to client, edit the ssh authorized key file and add the line below before the ssh-rsa keyword.
from=”backuppc_server_ip”,no-agent-forwarding,no-port-forwarding,no-ptyReplace the backuppc_server_ip with the IP address of the backuppc server.
vim /home/backuppc/.ssh/authorized_keys
from="192.168.43.154",no-agent-forwarding,no-port-forwarding,no-pty ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1SSSc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDYuDSNIPxQL6hNh6FeW4wj3hYJ+p42SD9BGVg5Rn6HuzIAi1zrU2pRceQ5VDRj5nXxSjs+oJJ4lXZ/HTaUQDBFysVyIe9Sc4Z9Z5nmmmGWIJnKWfuvzSYbV2JbSJjcTfUPjH32DOvU+4PMdil/4GjKW7pr8fyywl4XuhZMU6RfVw0LgzYuqzUQX5D6Q4MsgIN4HGqBsnVIBvSz2TcPc0hovtfKQMmUBQvp7L9Ob3AKuG01ZZznQ8Q6+eGL7EJHnS30h/FLM8rKBxsvI6El8xog2E0/ALnNGKWsg2NTEqWqQ3xpUDEnA6exgHEm+2xCuKAy1sAuSJHJHScUMLZIUE36t2+nB0Vn [email protected]Next, you can also configure ssh logins to backuppc user accounts on clients hosts from the BackupPC server only. This can be done by editing sshd_config file on the client and configuring as shown below;
sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Add the line below to SSHd configuration to allow login to the client as backuppc from the BackupPC server only.
Match Host 192.168.43.154
AllowUsers backuppcReload SSH configurations
systemctl reload ssh
Accessing BackupPC Web User Interface
You can login as shown above.
Backup Hosts using BackupPC
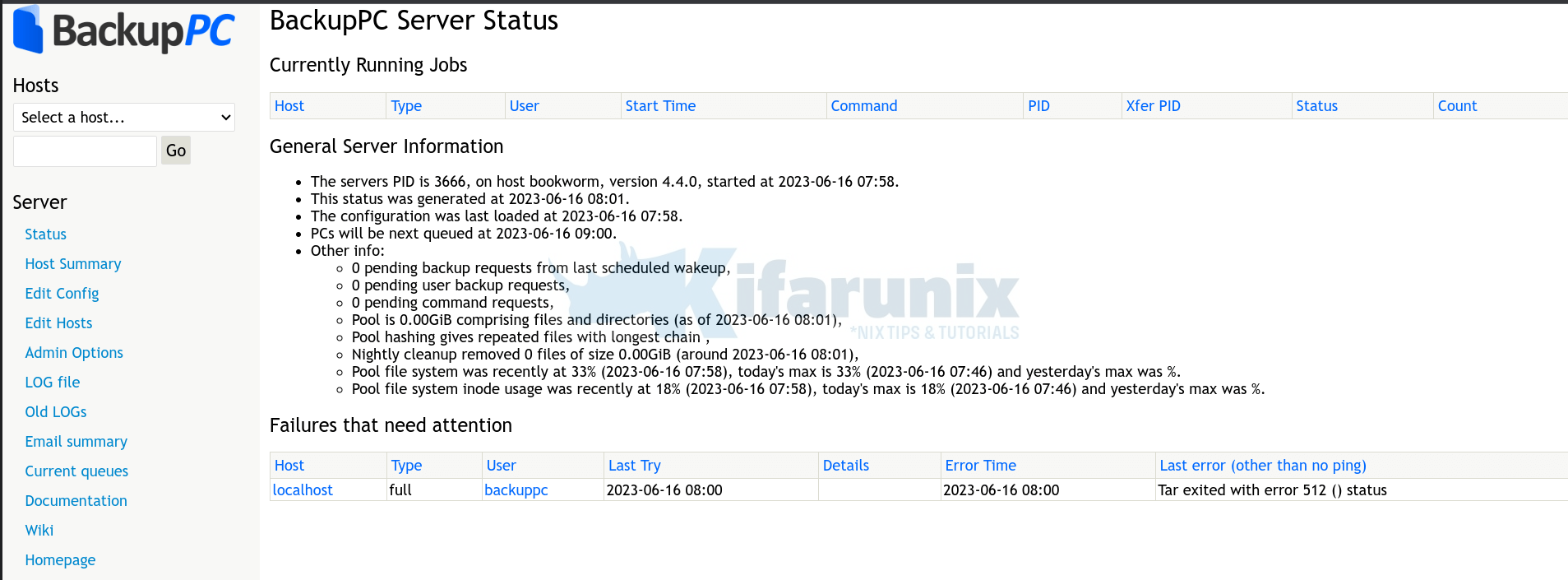
If you noticed, the localhost, which is the server running backuppc is already added as one of the backup hosts.
The backup tried to run but failed, due to some default backup protocol (tar) errors.
Since we are using rsync as a backup protocol in this guide, you need to update this for the localhost backup to run.
Hence, click on hostname (localhost for example) > edit config > Xfer > XferMethod > Rsync.
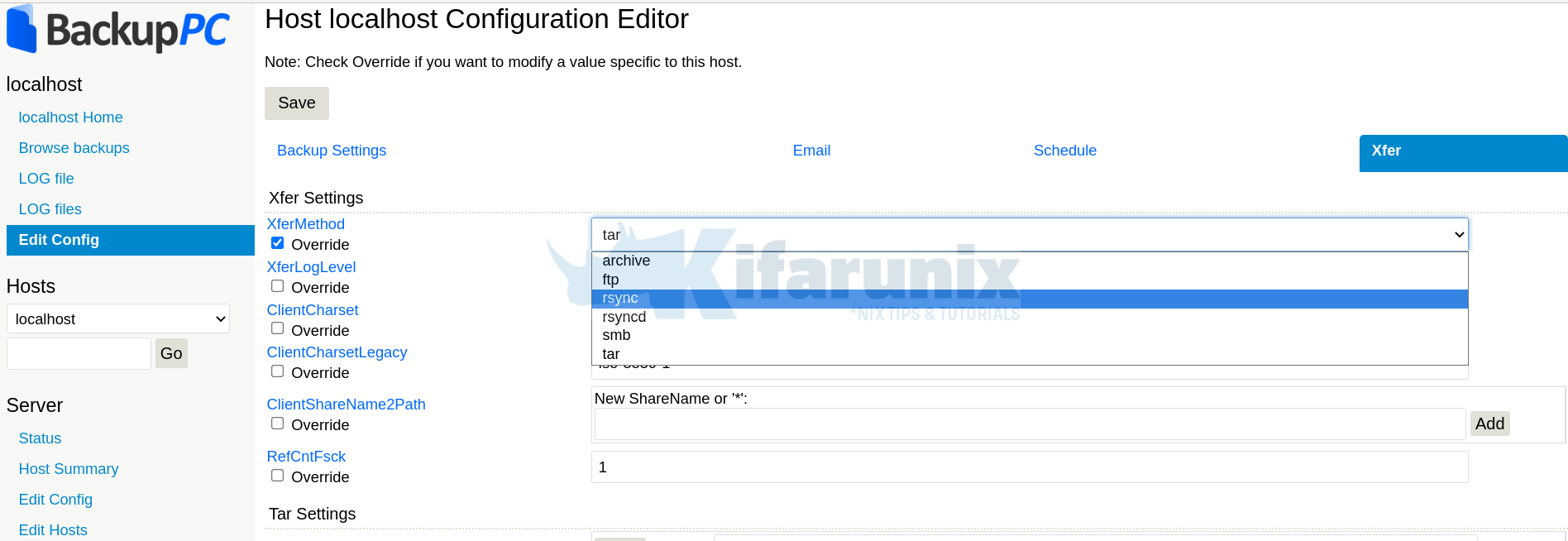
Update RsyncShareName
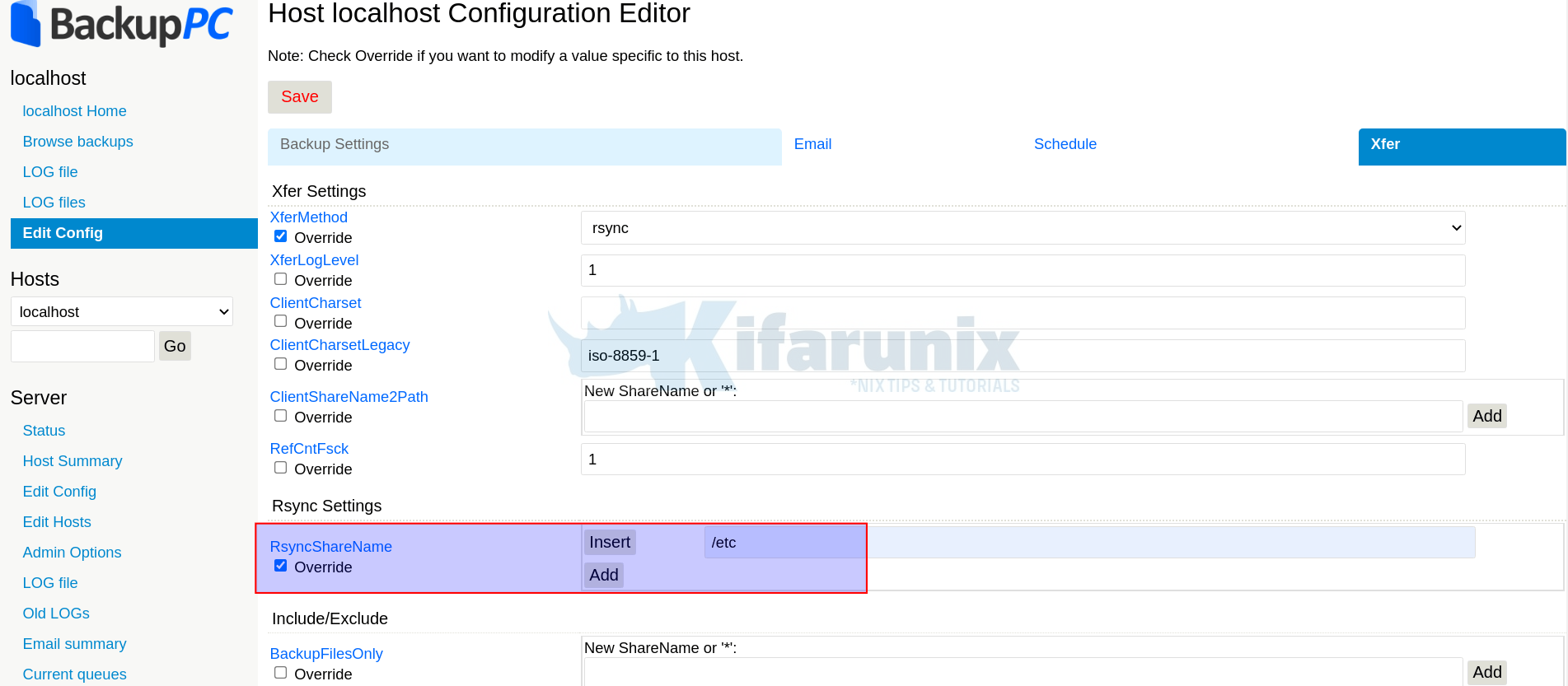
Click Save.
Reset the local account password for backuppc user.
passwd backuppcKeep the password save.
Install rsync and allow BackupPC user to execute rsync with sudo without password.
apt install rsyncecho "backuppc ALL=NOPASSWD: $(which rsync)" | sudo tee /etc/sudoers.d/backuppcsu - backuppcCopy the password generated above to server itself.
ssh-copy-id backuppc@localhostInitiate localhost backup.
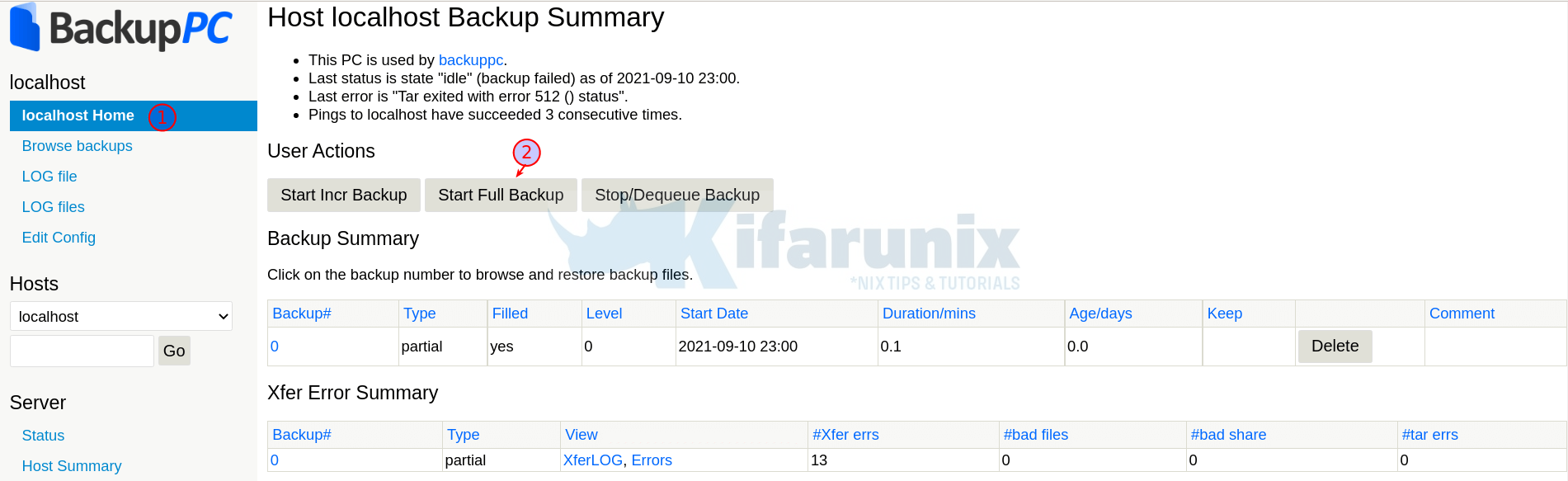
Once the backup is running, you can see status under status menu.
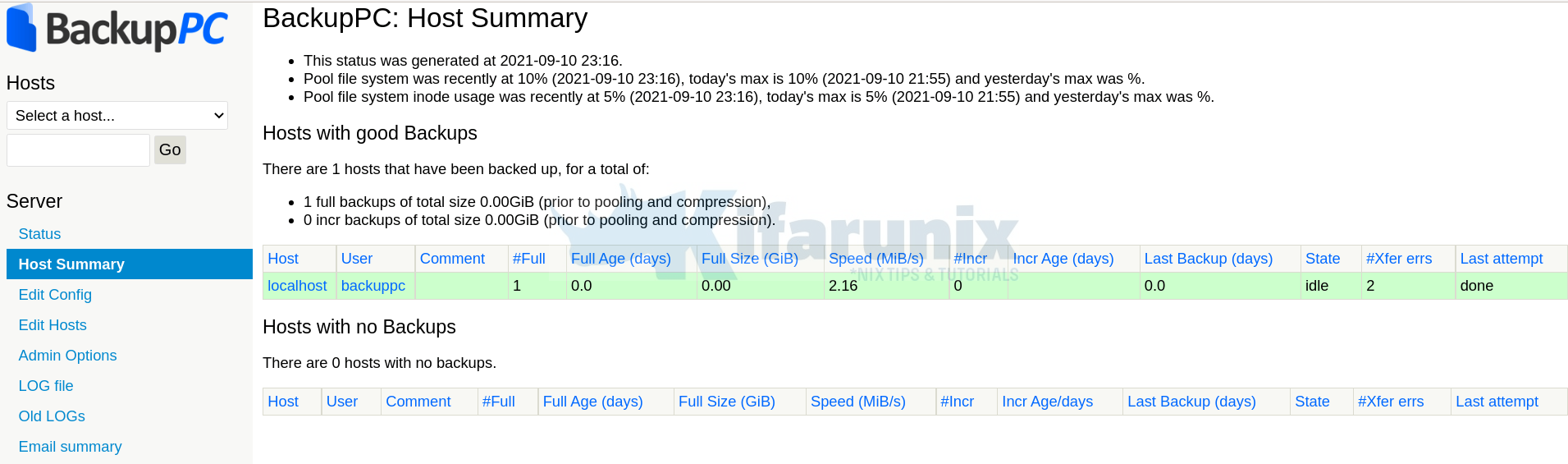
You can now add more hosts to backup.
Update Global BackupPC Server Configurations
You can update the general/global configs of BackupPC by heading over to Edit Config under Server section on the left pane.
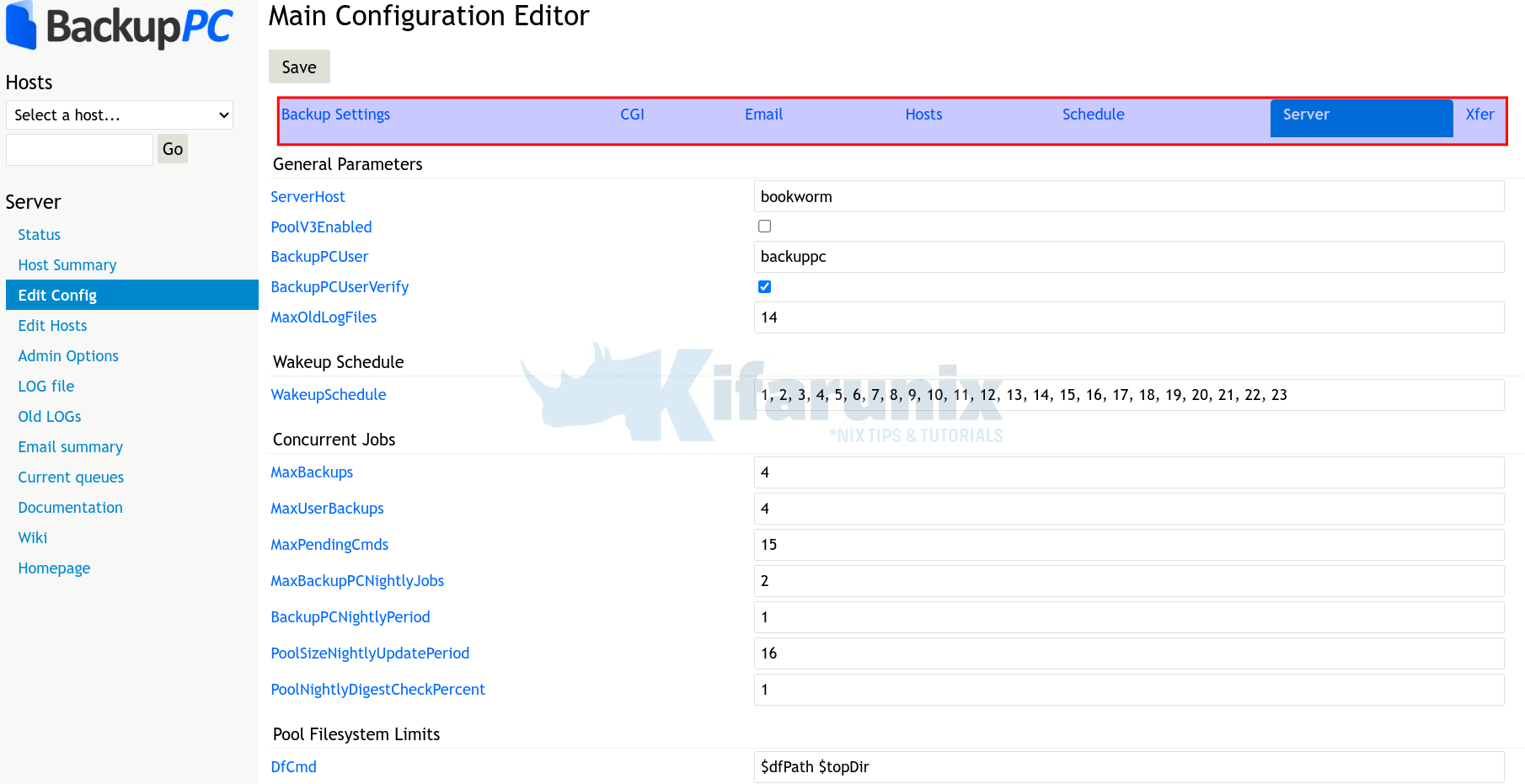
That is basically it on our guide on how to installing BackupPC server on Debian 12.

